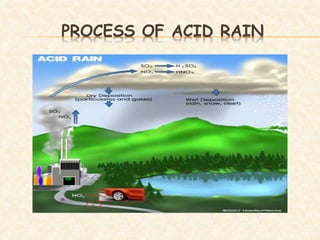
Acid deposition occurs when rainwater has a pH less than 5.6, primarily due to sulfur dioxide (SO2) and nitrogen oxides (NO2) from industrial activities and fossil fuel combustion. Acid rain has harmful effects on aquatic life, soil, and human health, including increased rates of respiratory illnesses. Efforts to control acid rain include reducing emissions of SO2 and NO2 and implementing mitigation strategies for affected ecosystems.