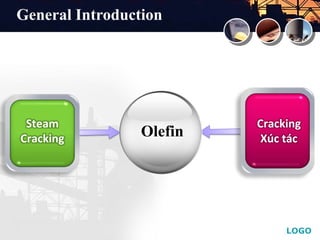
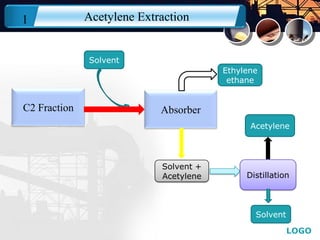
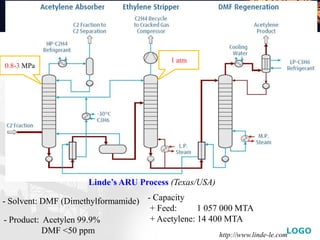
This document provides an overview of acetylene selective hydrogenation processes. It discusses how acetylene is extracted from hydrocarbon streams using solvent absorption or selective hydrogenation. The two main types of selective hydrogenation are front-end, which treats lighter feedstocks before fractionation, and tail-end, which treats C2 fractions after removal of lighter components. Tail-end hydrogenation is more common and uses palladium-based catalysts with high selectivity for acetylene. The document also reviews catalyst regeneration methods used to remove coke and restore activity.


![LOGO
Feedstock %Conv Acetylen
(%wt)
Ethane 65% 0.4 - 0.50
LPG 90% 0.65 - 1.35
Naphta - 0.10 - 1.0
[2]
General Introduction](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acetylenehydrogenation-130902223655-phpapp02/85/Acetylene-hydrogenation-5-320.jpg)

![LOGO
Specs Etylen Raw Propylen Clean Propylen
Axetylen, max
(ppm)
2 * 10 5
* <1ppm [3]
General Introduction](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acetylenehydrogenation-130902223655-phpapp02/85/Acetylene-hydrogenation-7-320.jpg)
![LOGO
General Introduction
[4]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acetylenehydrogenation-130902223655-phpapp02/85/Acetylene-hydrogenation-8-320.jpg)
![LOGO
Acetylene Extraction1
Acetylene Selective Hydrogenation2
[2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acetylenehydrogenation-130902223655-phpapp02/85/Acetylene-hydrogenation-9-320.jpg)



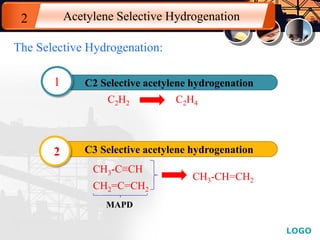
![LOGO
Acetylene Selective Hydrogenation2
[4]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acetylenehydrogenation-130902223655-phpapp02/85/Acetylene-hydrogenation-16-320.jpg)


![LOGO
Add YourText in here
Raw-gas Acetylene Hydrogenation
Drawing of Sud-Chemie [3]
C2,C3+
H2,CO, H2S
- HC feed: C3+ <<
- Catalysts: Ni-
based (Ni-Co-Cr)
[4]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acetylenehydrogenation-130902223655-phpapp02/85/Acetylene-hydrogenation-19-320.jpg)
![LOGO
Add YourText in here
Front-end Acetylene Hydrogenation
C2H2, C2H4, C2H6
H2, CO
Remove
CO2,H2S Drawing of Sud-Chemie [3]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acetylenehydrogenation-130902223655-phpapp02/85/Acetylene-hydrogenation-20-320.jpg)
![LOGO
Add YourText in here
Tail-end Acetylene Hydrogenation
C2H2, C2H4,
C2H6
Removal
CO2,H2S
Drawing of Sud-Chemie [3]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acetylenehydrogenation-130902223655-phpapp02/85/Acetylene-hydrogenation-21-320.jpg)
![LOGO
Hydro hóa chọn lọc AcetylenAcetylene Selective Hydrogenation2
Front-end Tail-end
Feed C2 cut and lighter material.
-Excess hydrogenbecause all
the hydrogen produced in the
cracking furnaces is in the
reactor feed.
C2 cut only
-Hydrogen in the Craked gas
(CG) have been removed
- H2 (99.9%) and CO are
injected in stoichiometric
amountsinto feed
Position Before light end removal After light end removal
H2/C2H2 ratio Uncontrollable
Process Control
Parameters[5]
Temperature Temperature
Hydrogen & CO injection
The selectivity of
hydrogenation reaction
Lower Higher](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acetylenehydrogenation-130902223655-phpapp02/85/Acetylene-hydrogenation-22-320.jpg)
![LOGO
Frond-ent Tail-end
Ethylene
loss
Higher Minimize
Catalysts
- Chervon Phillips: E-Series (Pd-
Ag/Al2O3).
-Sud-Chemie:G-83C (Pd-Ag/Al2O3)
- BASF: HO-21 (Pd-Ag/ SiO2)
-Sud- Chemie:G-58C, G-58D,
G-58H (Pd-Ag)
- AXENS: LT-279
Cycle
length
Long
Typically no regeneration [5]
Exsitu regeneration
Short
Requires frequent regeneration
(1-4 times/years)
Insitu regeneration [3]
Catalyst
deactivation
Coke, COS Coke, Green Oil, COS
Acetylene Selective Hydrogenation2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acetylenehydrogenation-130902223655-phpapp02/85/Acetylene-hydrogenation-23-320.jpg)
![LOGO
s Acetylene Selective Hydrogenation2
Frond-ent Tail-end
Design
parameters
[3]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acetylenehydrogenation-130902223655-phpapp02/85/Acetylene-hydrogenation-24-320.jpg)
![LOGO
Method Number of plants % of Plant
Tail-end 174 64
Front-end (Pd) 69 26
Front-end (Ni) 9 3
Extraction 19 7
Total 269 100%
Acetylene Selective Hydrogenation2
[4]
Tail-end
Front-end (Pd)
Front-end (Ni)
Extraction](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acetylenehydrogenation-130902223655-phpapp02/85/Acetylene-hydrogenation-25-320.jpg)
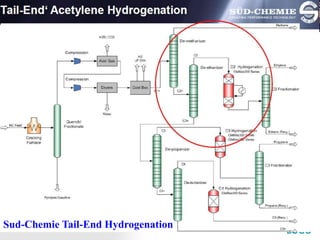
![LOGO
Tail –end Hydrogentation Catalyst
[5]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acetylenehydrogenation-130902223655-phpapp02/85/Acetylene-hydrogenation-27-320.jpg)
![LOGO
Advantages of OleMax 207 new catalyst
Increased:
Ethylene (>10% OleMax 201)
Catalyts Stability
Cycle lengths (>24 months)
Operation without CO injection
Low Polymer Formation
[5]
OleMax 207 catalyst:
+ Pd-Ag promoter/Al2O3
+ 2-4mm spheres](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acetylenehydrogenation-130902223655-phpapp02/85/Acetylene-hydrogenation-28-320.jpg)
![LOGO
[5]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acetylenehydrogenation-130902223655-phpapp02/85/Acetylene-hydrogenation-29-320.jpg)
![LOGO[5]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acetylenehydrogenation-130902223655-phpapp02/85/Acetylene-hydrogenation-30-320.jpg)
![LOGO
[3]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acetylenehydrogenation-130902223655-phpapp02/85/Acetylene-hydrogenation-31-320.jpg)
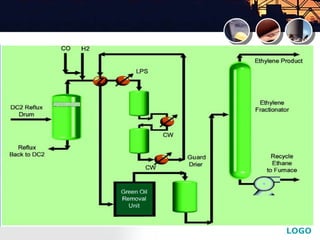
![LOGO
Catalyst regeneration
[4]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acetylenehydrogenation-130902223655-phpapp02/85/Acetylene-hydrogenation-33-320.jpg)

![LOGO
Catalyst regeneration
[4]
Start with warm up by nitrogen injection
to purge residual gases in reactor and
vaporize volatile compounds
Nitrogen and HP](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acetylenehydrogenation-130902223655-phpapp02/85/Acetylene-hydrogenation-35-320.jpg)
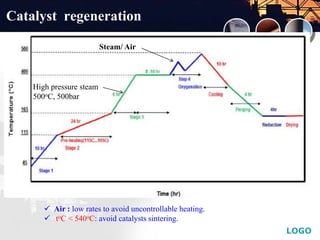
![LOGO
Add YourText in here
Catalyst regeneration
Cooling stage begins when [CO2] in oulets < 1%V
Cooling to 250oC
by air/steam
N2
H2
N2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acetylenehydrogenation-130902223655-phpapp02/85/Acetylene-hydrogenation-37-320.jpg)
![LOGO[6]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acetylenehydrogenation-130902223655-phpapp02/85/Acetylene-hydrogenation-38-320.jpg)


