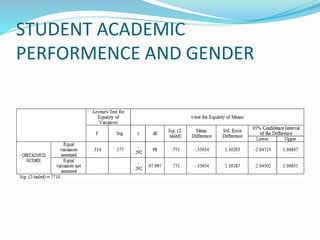
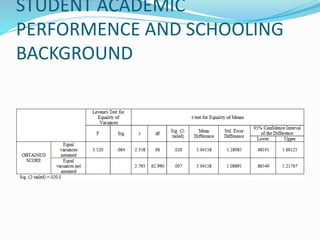
1) The document discusses factors that influence the academic performance of graduate students, including gender, age, schooling background, socioeconomic status, residential area, medium of instruction, tuition trends, and accommodation.
2) It reviews several previous studies on this topic and their findings that academic performance is positively associated with higher socioeconomic status, private schooling, urban residence, and English medium instruction.
3) The methodology section describes a study of 100 graduate students that uses questionnaires to collect data on independent variables and academic performance, which is then analyzed using statistical tests in SPSS and Excel.