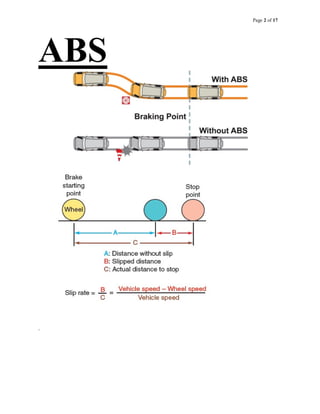
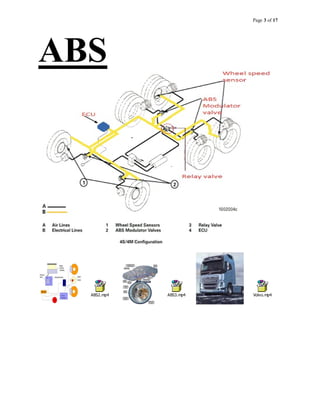
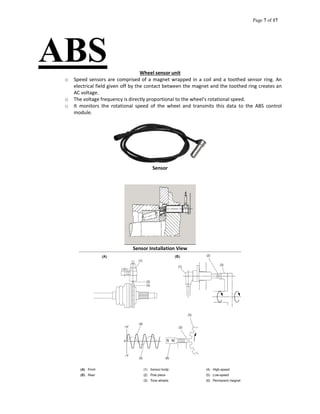
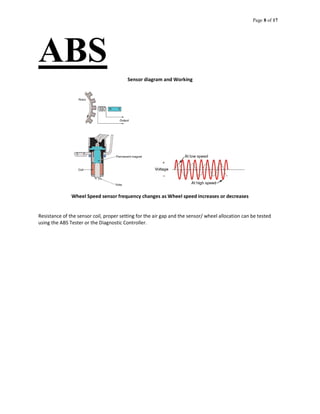
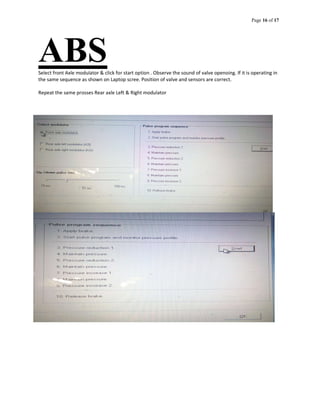
The document provides information about an antilock braking system (ABS), including its objectives, components, and operation. It discusses how ABS works to prevent wheel lockup and maximize traction during braking by regulating brake pressure. It describes the key components of ABS, including electronic control units, hydraulic modulators, wheel speed sensors. It also outlines how ABS is tested and faults diagnosed using a laptop interface kit connected to the vehicle's ABS controller.