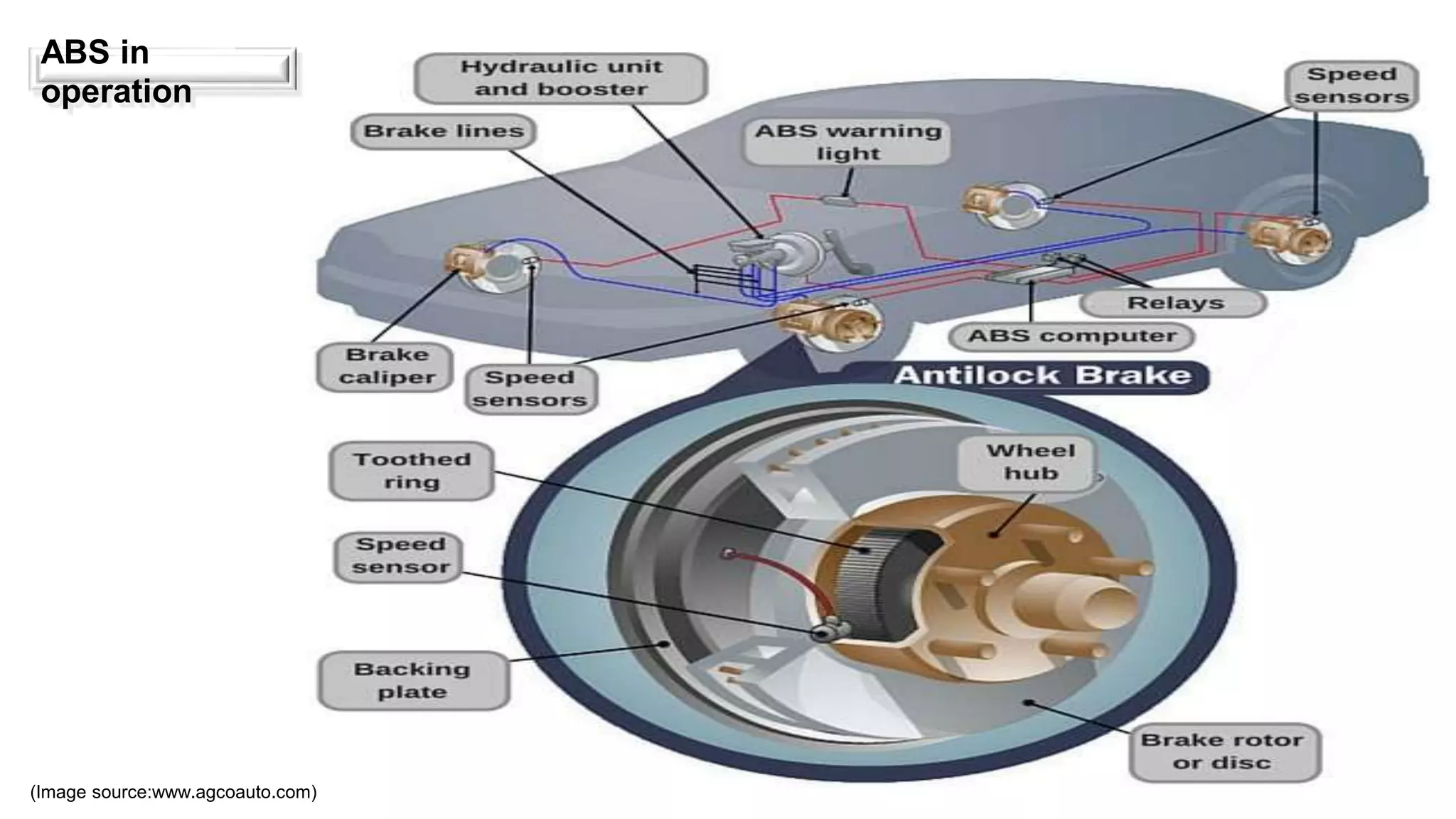
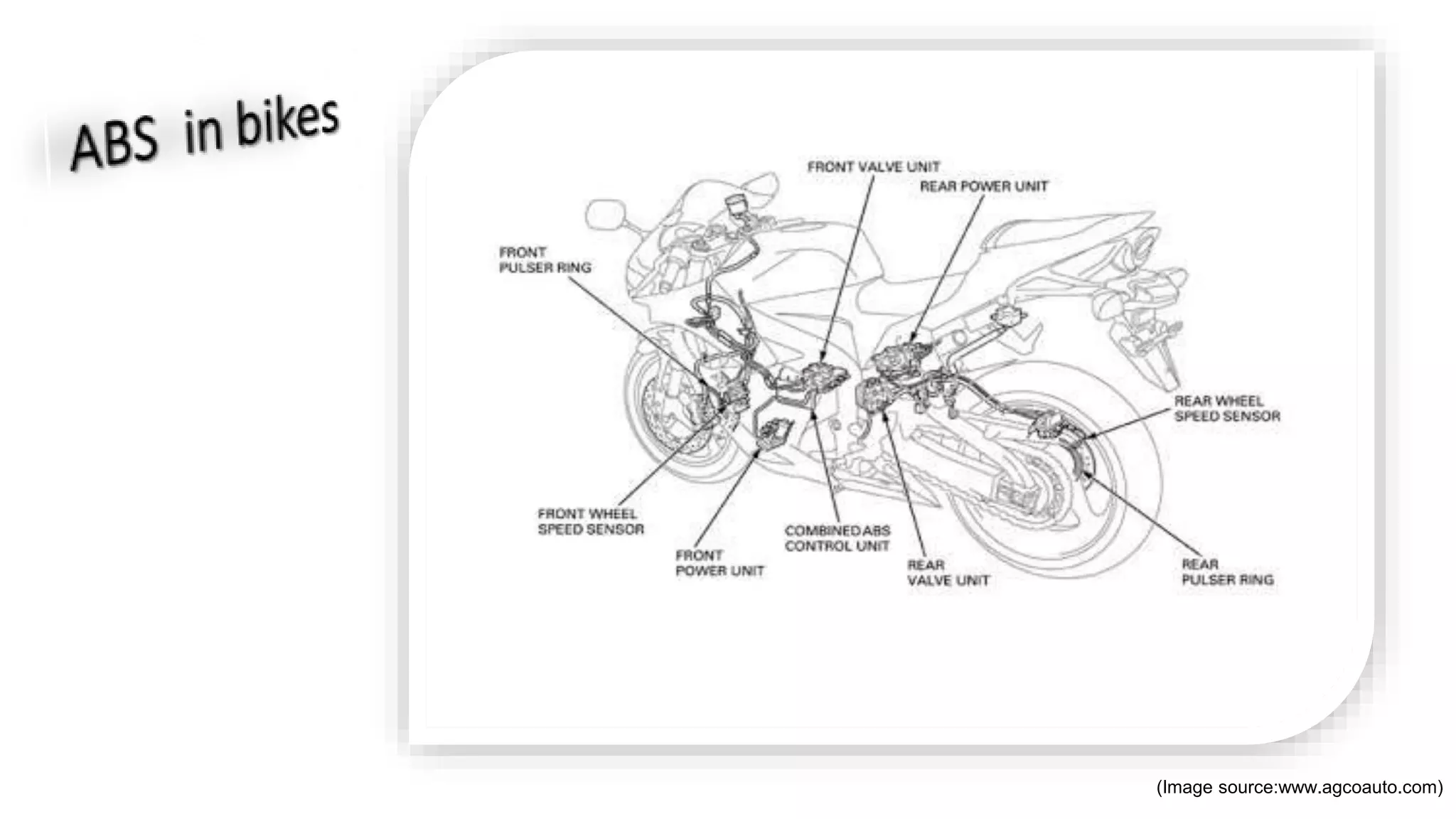
ABS operates by using wheel speed sensors and hydraulic valves to prevent wheel lockup under braking. It monitors each wheel and will reduce hydraulic brake pressure as needed to maintain traction. ABS includes a central electronic control unit, wheel speed sensors, and at least two hydraulic valves. It improves vehicle control and stopping distances compared to non-ABS braking. Motorcycle ABS functions similarly but is tailored for motorcycles, helping riders maintain stability during braking. Combined braking systems work with ABS to coordinate front and rear braking, improving safety.











![CBS and ABS
CBS helps to reduce the danger of wheel locks and fall downs but in certain situations it is possible that CBS
causes a fall down. If brake pressure is distributed from the rear wheel to the front wheel and the friction of
the surfaces changes suddenly (puddle, ice on the street) the front wheel might lock even if only the rear
brake has been applied.
This would lead to a loss of stability and a fall down.
CBS is therefore combined with ABS to avoid this on a motorcycle.
Different approaches are possible to realize this combination: Without active pressure Build up Single
Version: A third additional channel links the rear wheel circuit through a delay valve to the front brake.
Strong brake pressure at the rear wheel (or both wheels) pressurises both brake circuits however this
pressure is adjusted according to wheel speed and brake slip.
The dual version combines Hondas Dual CBS with a secondary master cylinder and a proportional control
valve [with Piston ABS] A modulator regulates the pressure for each With Active Pressure Build up In 2009,
Honda introduced the electronic controlled combined ABS for its high performance sports bikes which
utilizes brake by wire technology. The brake input of the rider is measured by pressure sensors and the
information is provided to an ECU.
Together with the information of the wheel speed sensors the ECU calculates the optimal distribution of
pressure to prevent lockups and to provide best possible deceleration.
Based on this output a motor for each wheel operates a pump which builds up and regulates the brake
pressure on the wheel. This system offers a fast reaction time because of the brake by wire functionality.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ranviramarkant-190611162239/75/ABS-system-14-2048.jpg)

