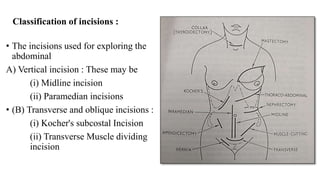
This document discusses different types of abdominal incisions used in surgery. It notes that the ideal incision achieves accessibility, extensibility, and security. Common reasons for abdominal surgery include removing diseased tissue, repairing injuries, creating artificial openings, and inspection. General anesthesia, local anesthesia, spinal anesthesia, and regional anesthesia are types of anesthesia used. Vertical, transverse, and oblique incisions are classifications of abdominal incisions. Specific incisions described include the midline, paramedian, Kocher's subcostal, McBurney grid iron, Pfannenstiel, and Maylard transverse muscle cutting incisions.