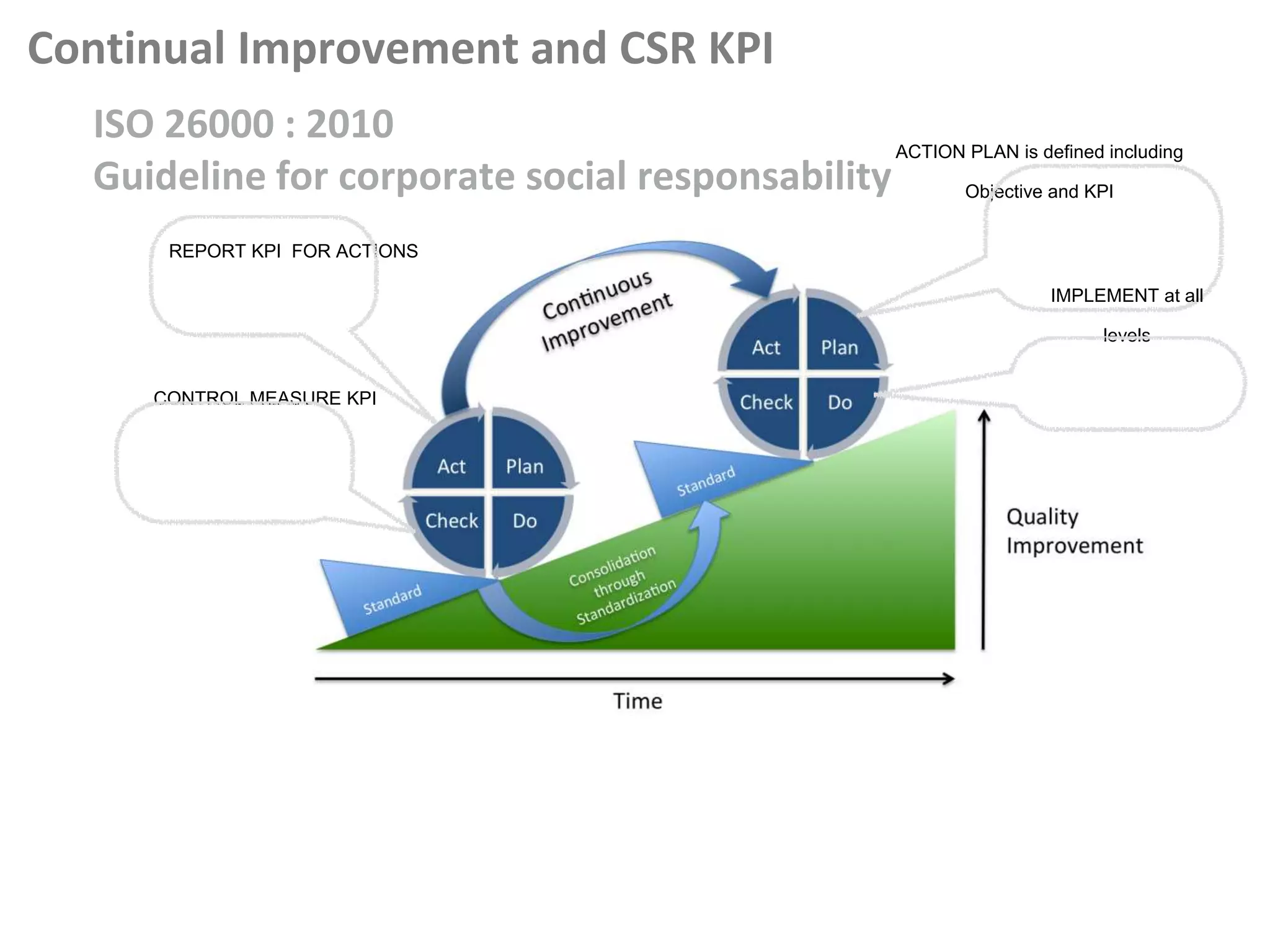
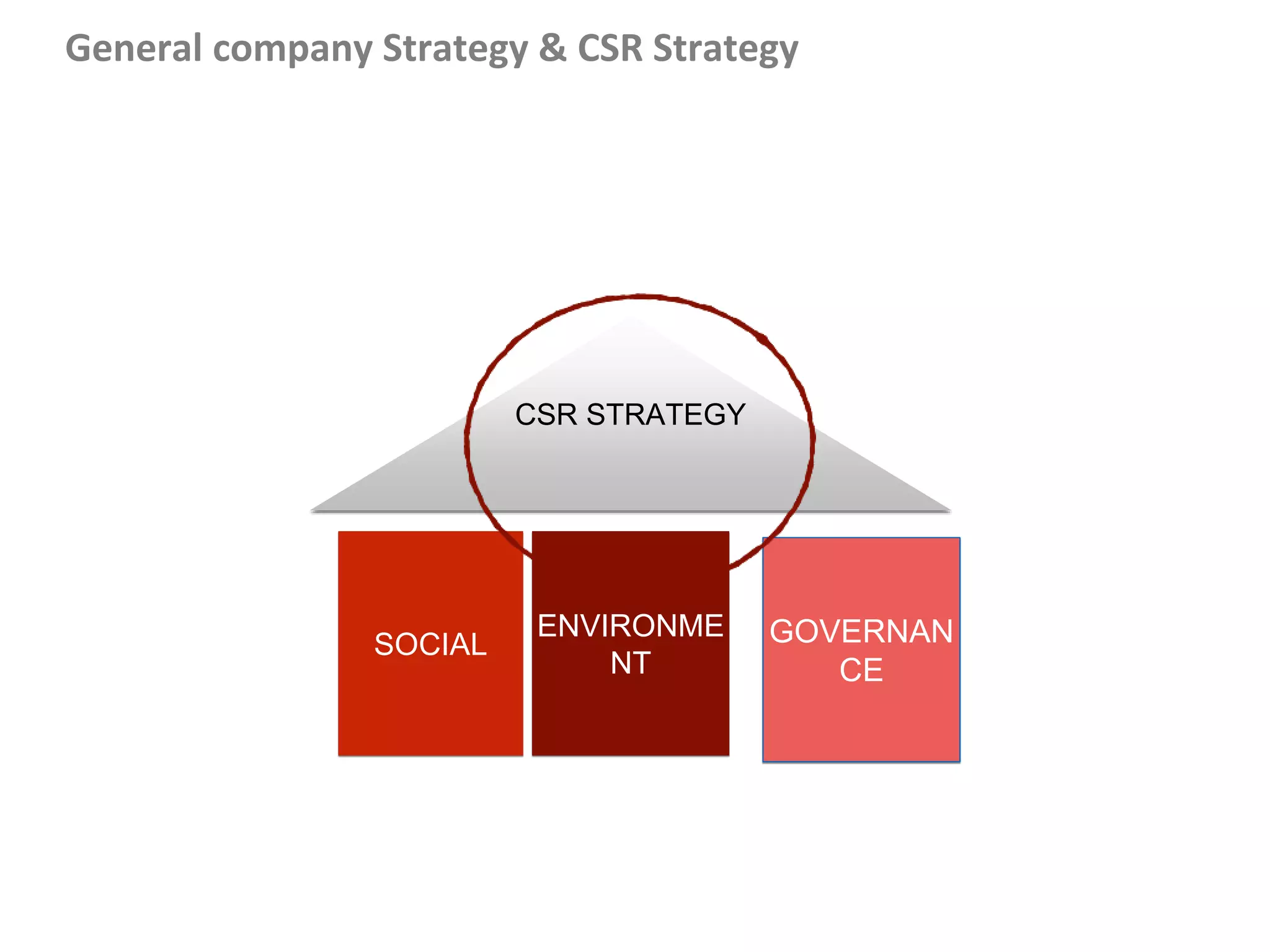
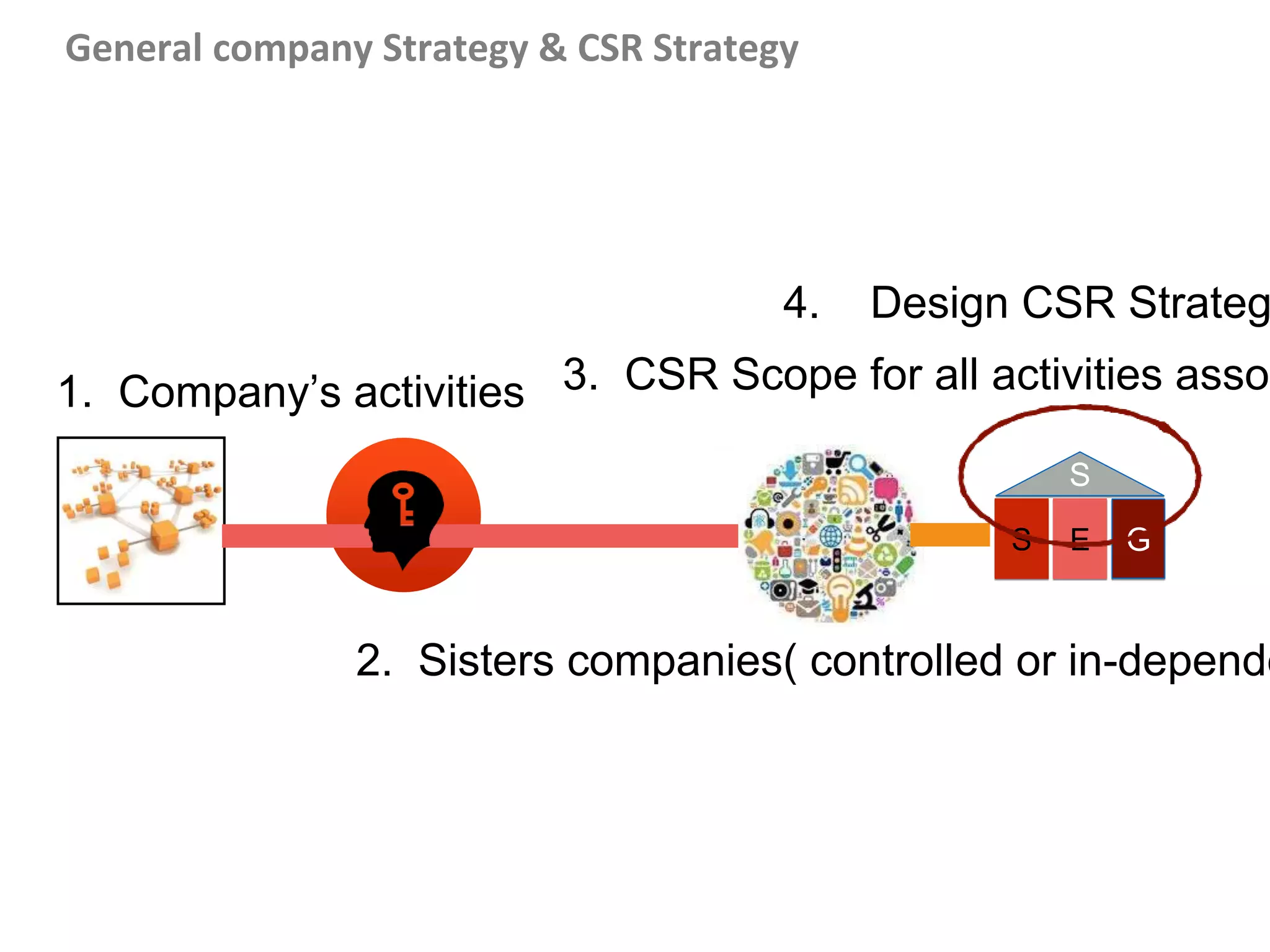
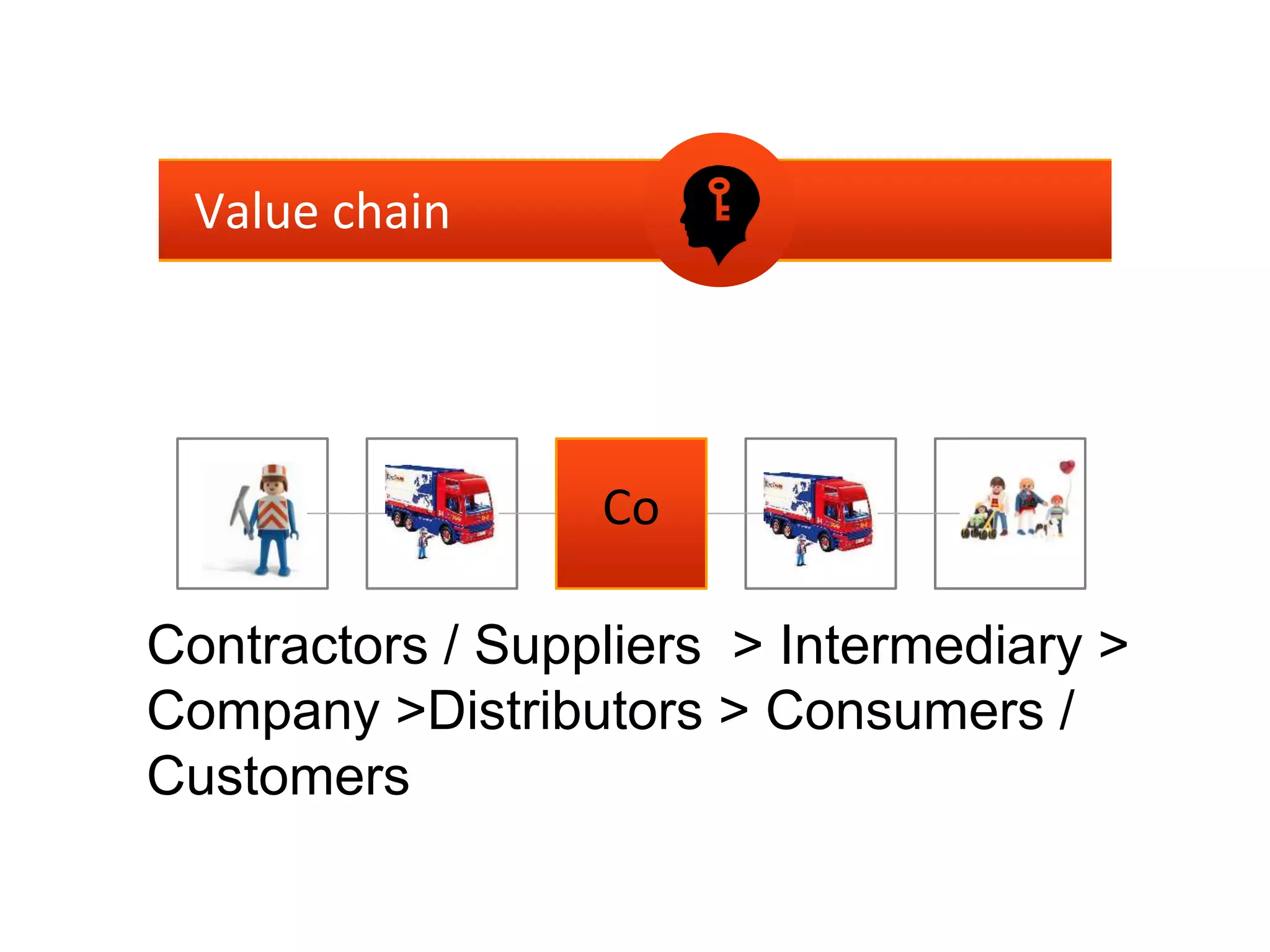
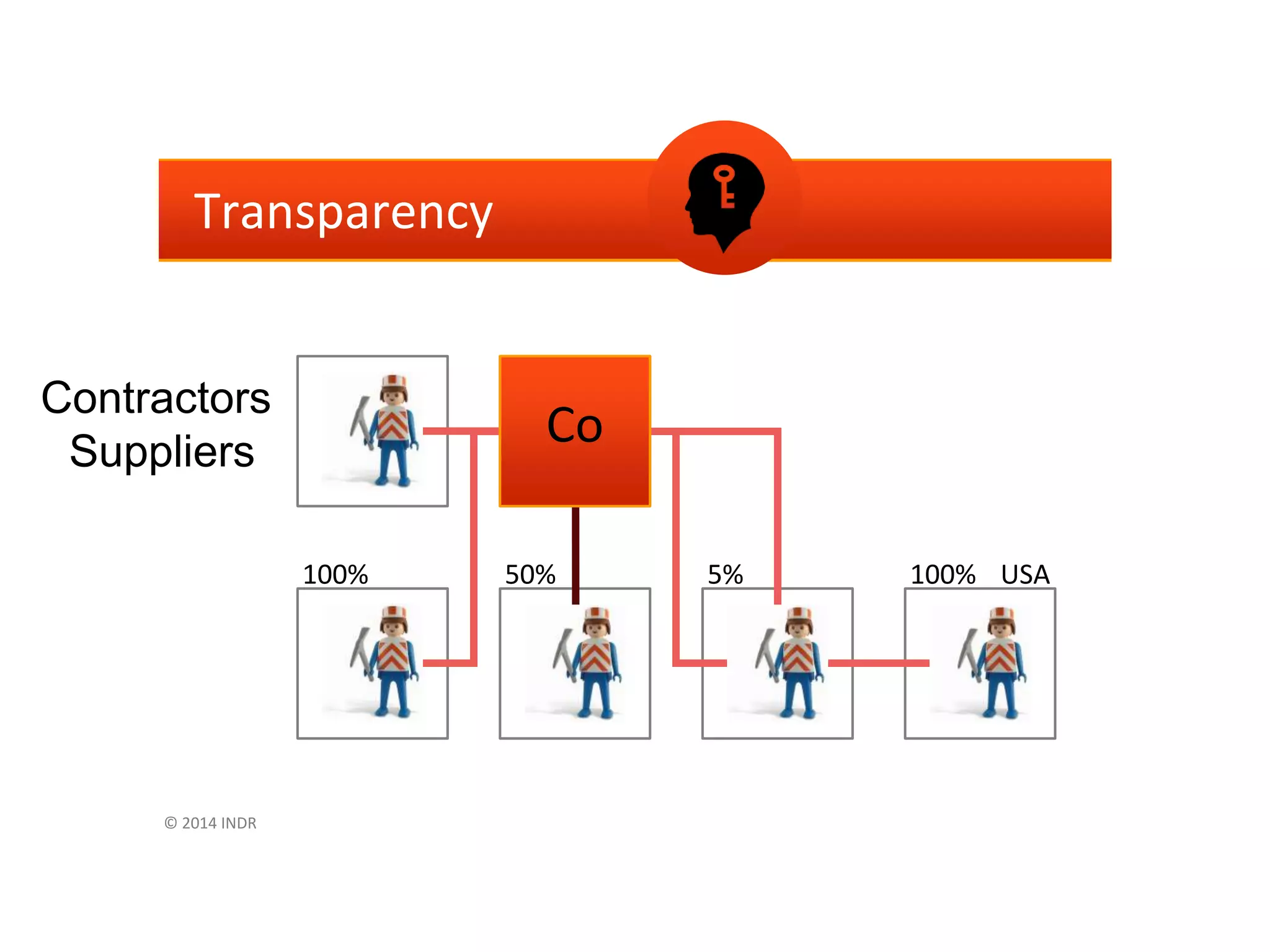
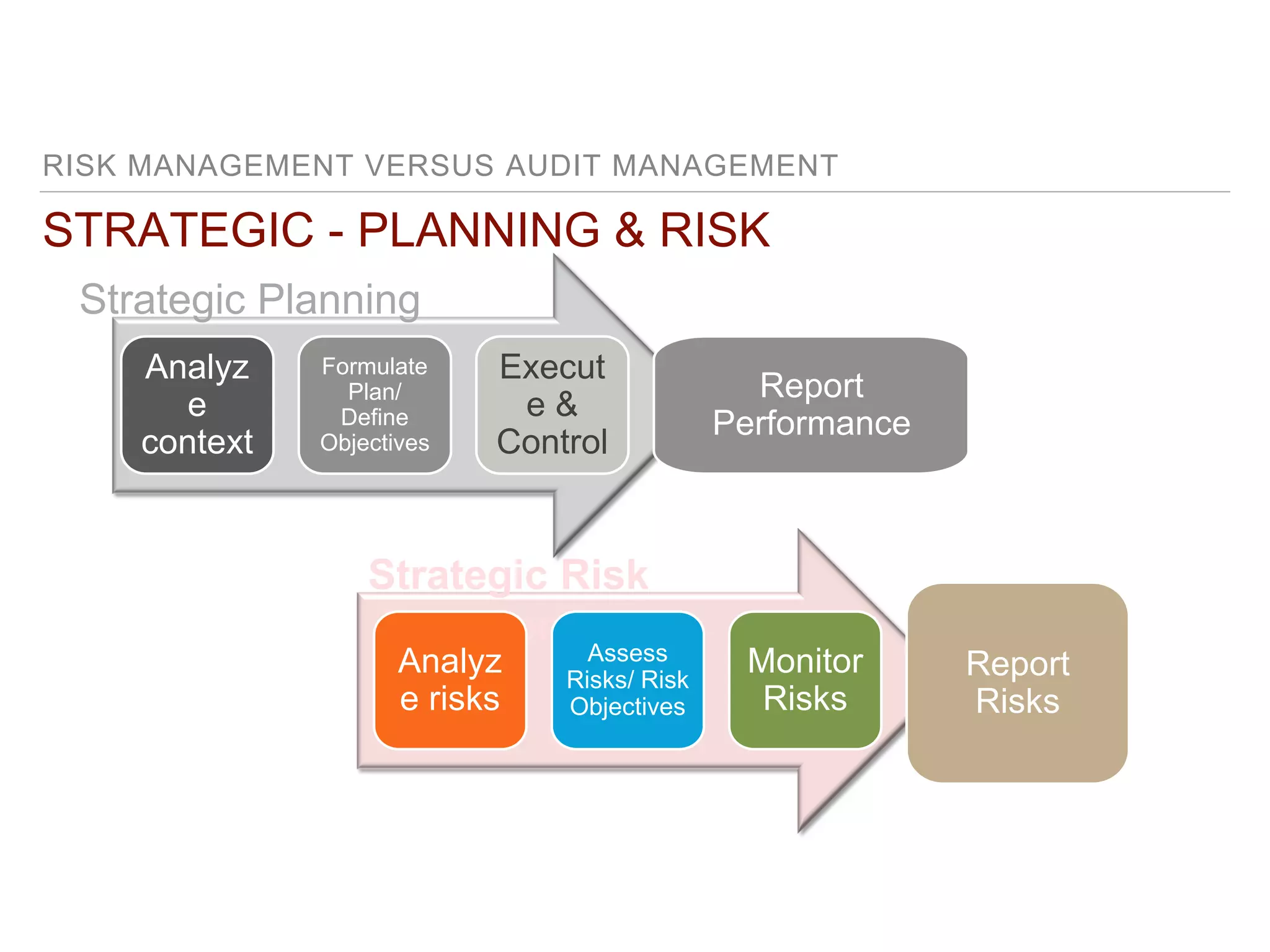
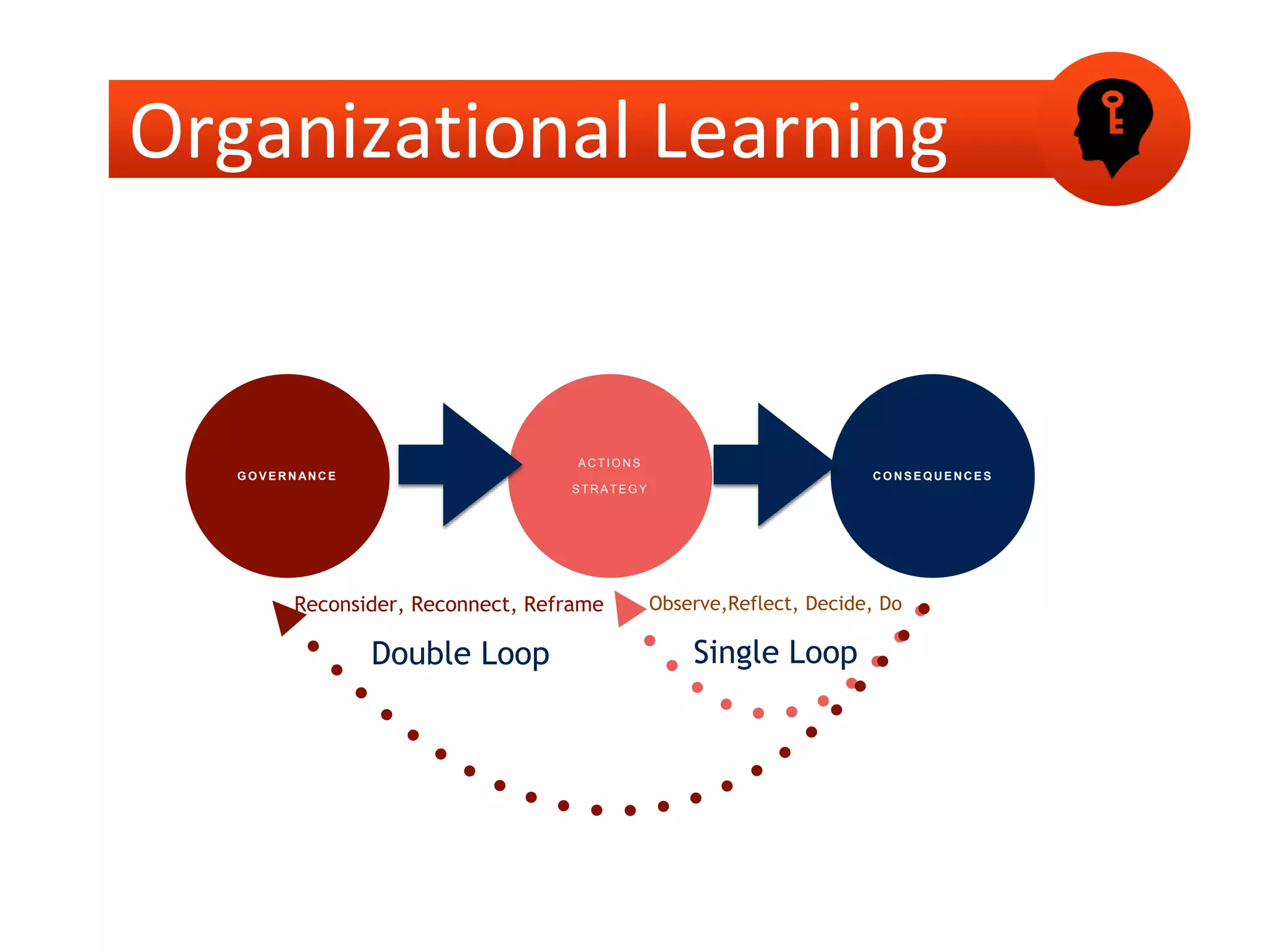
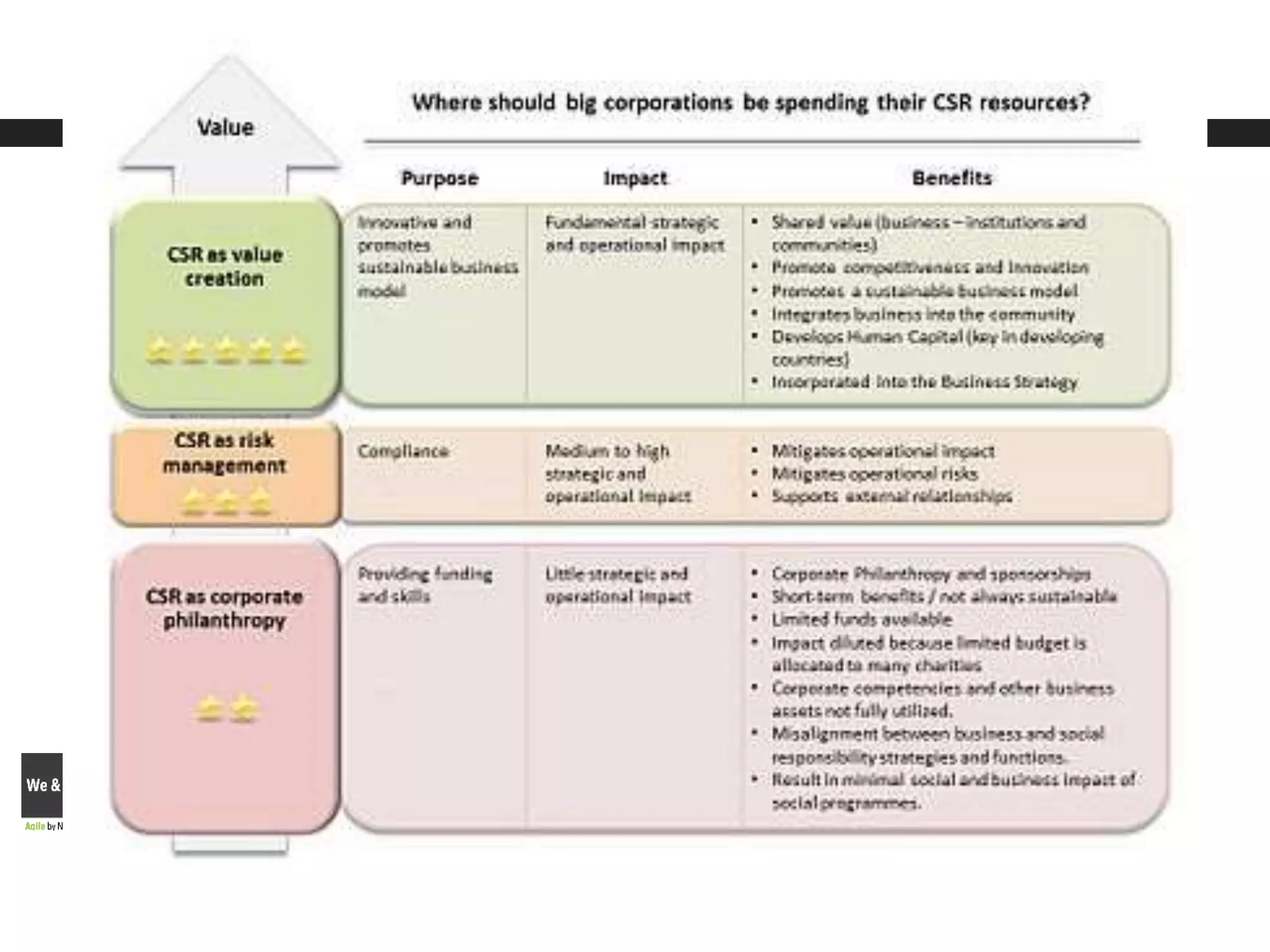
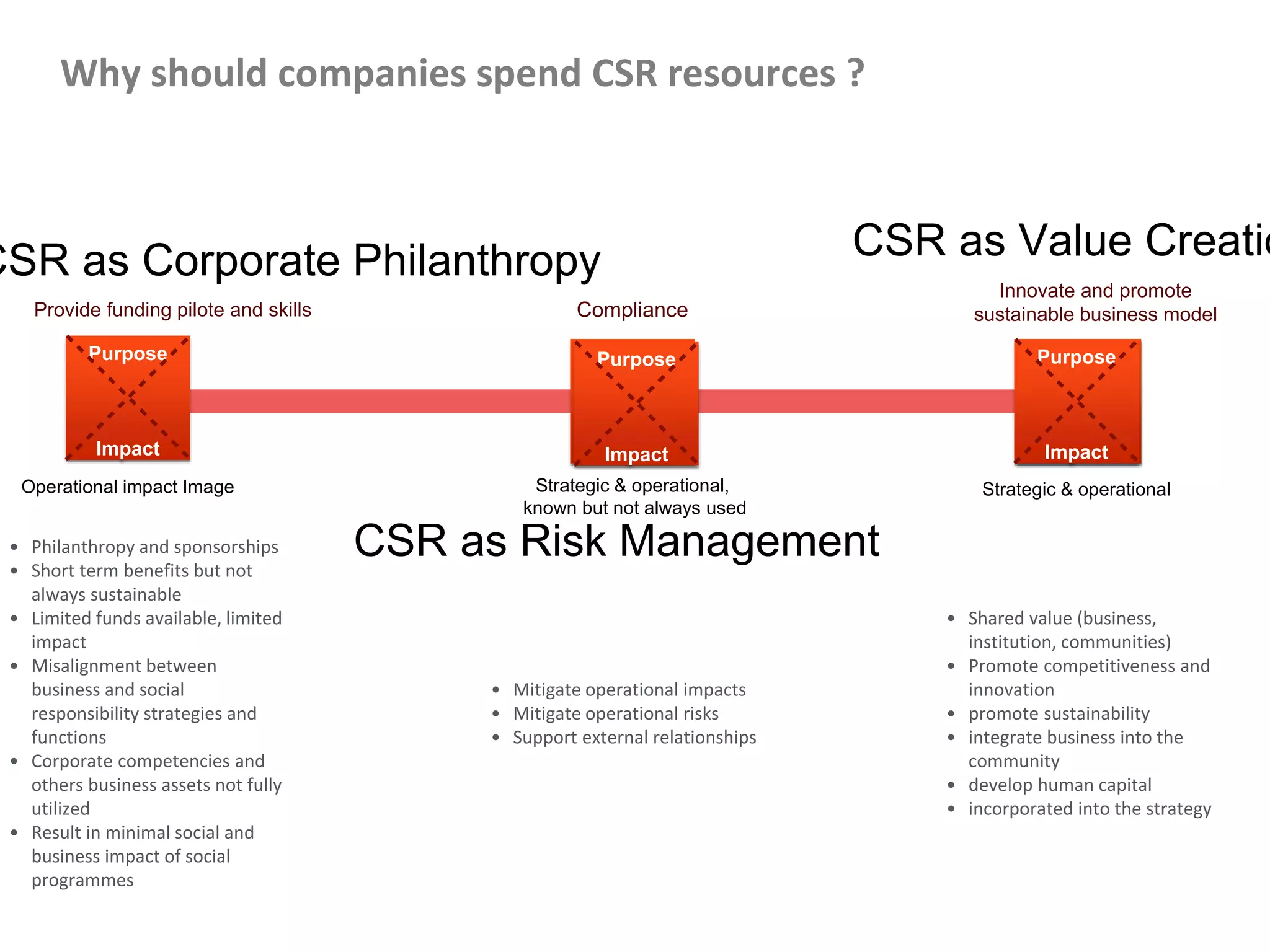
This document outlines steps for measuring and reviewing corporate social responsibility (CSR). It discusses mapping interested parties and their relationships. Objectives and key performance indicators (KPIs) should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant and time-bound. Continual improvement involves implementing an action plan with objectives and KPIs, monitoring and controlling progress, and reporting KPI results to drive further actions. The CSR strategy should be integrated with the company's overall strategy. Risk management is also important for CSR. Creating shared value by enhancing competitiveness and advancing social conditions is discussed as a purpose of CSR.