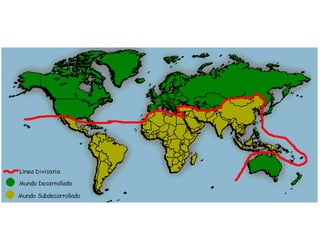
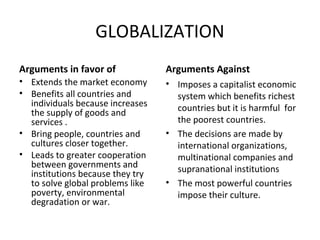
Globalization is a process of integration across geographical boundaries that affects economic, political, and cultural systems. It has created a global market where people, goods, ideas, information, and knowledge move between places thanks to new technologies like the Internet. The world is divided between developed and developing countries. There is controversy around globalization, with supporters like the IMF, WTO, G8, and G20 arguing it extends markets and benefits cooperation, while opponents like anti-globalization groups argue it imposes harmful capitalist systems and cultural dominance by powerful countries.