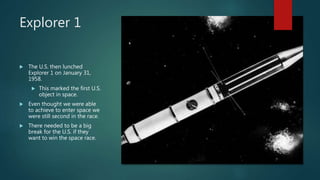
The Space Race between the United States and Soviet Union lasted from 1955 to 1975. It began with the Soviet launch of Sputnik 1 in 1957, making them the first to reach space. This spurred the US to create NASA and launch their own satellites to catch up. The Space Race culminated in the US Apollo 11 mission in 1969 which landed the first humans on the Moon, achieving the goal that ultimately declared the US the winner of the Space Race.