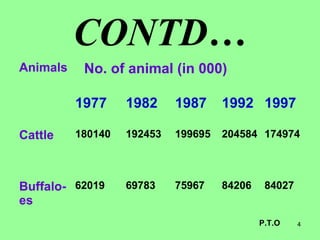
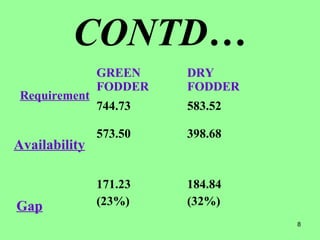
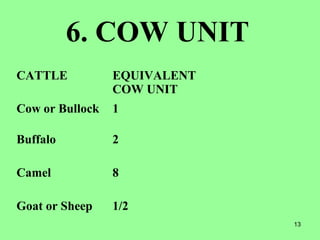
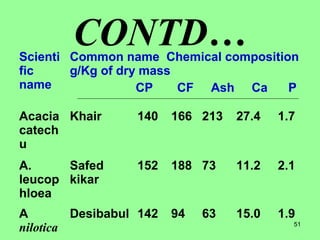
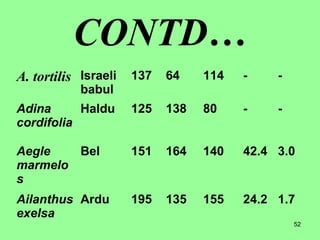
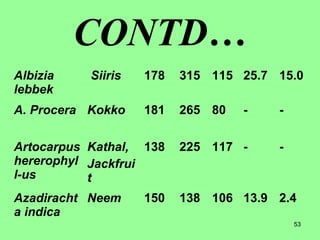
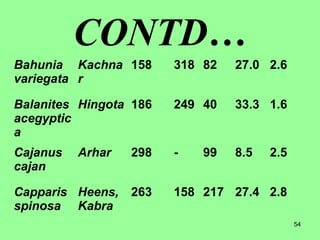
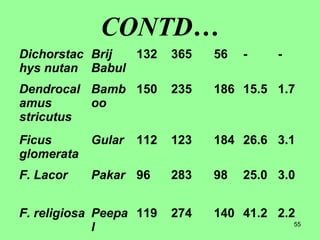
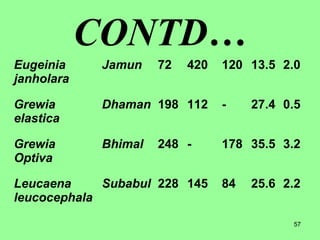
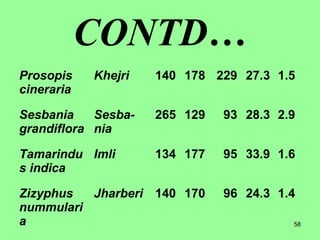
This document provides information on cattle fodder requirements and availability in India. It discusses livestock population trends from 1977 to 1997, with cattle and buffaloes as the dominant livestock. The key factors affecting livestock population are also examined. There are significant gaps between the estimated green and dry fodder requirements versus availability. Forests play an important role in meeting around 30% of fodder demand. The document also defines grazing land types and carrying capacity, and lists and describes various important fodder grasses and shrubs found across India.