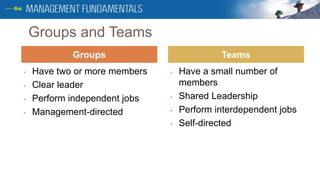
1. The document discusses different types of groups and teams in organizations, including formal vs informal groups, functional vs cross-functional groups, and command vs task groups.
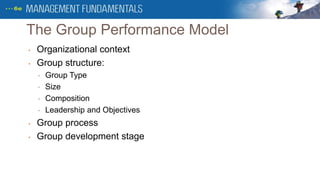
2. It also covers factors that impact group performance like group size, composition, leadership, objectives, processes, roles, and norms.
3. Group processes include the stages of forming, storming, norming, performing, and adjourning. The document discusses appropriate management styles at each stage and the differences between managing groups vs leading teams.