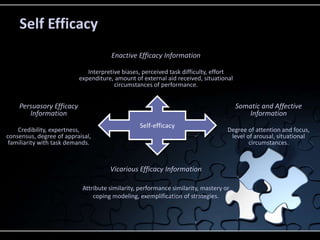
This document discusses sustaining organizational change through cultivating self-efficacy, fulfilling leadership functions, and continuous learning. It emphasizes that effective leadership involves enabling teams, providing compelling direction, and setting clear objectives. Leadership is discussed as a team function rather than an individual role. Key aspects of effective team leadership include creating the right conditions for teamwork, interdependence toward a shared goal, clear membership, and coaching teams over time. Organizational change is resisted by human nature, so leadership must provide inclusion and honest conversations. Coordination, commitment, competence, and creativity are important for organizational success. The document outlines steps for leading organizational change, including developing a new direction, identifying barriers, communicating involvement, and monitoring progress.