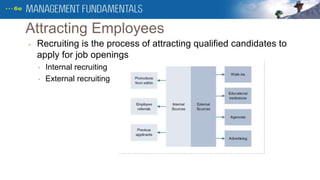
This document summarizes key aspects of human resources management. It discusses harassment and job analysis procedures. It also outlines the employee attracting process, including internal and external recruiting methods. The selection process and new employee orientation and training programs are described. Additional topics covered include job evaluation, benefits, health and safety standards, labor unions, and procedures for terminating employees.