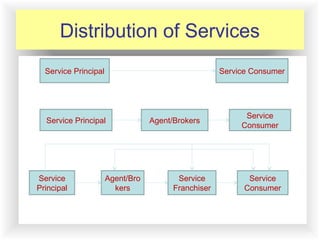
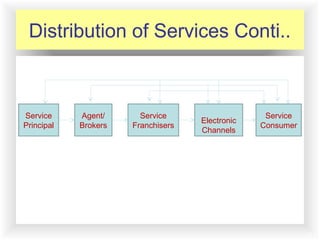
The document discusses objectives and strategies for distribution channels of services. It outlines 6 key objectives: increase availability and customer satisfaction, ensure promotion, obtain market information, increase cost-effectiveness, and maintain flexibility. It categorizes service transactions and discusses distribution strategies like extensive, selective, and exclusive distribution. The document also covers factors in selecting service locations, using direct distribution or intermediaries like franchising, agents, brokers, and electronic channels. It provides benefits and challenges of these distribution methods and offers strategies for effective channel management.