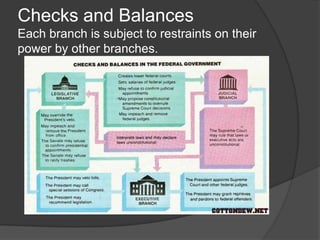
The U.S. Constitution was drafted in 1787 and established 6 major principles: popular sovereignty, where all political power comes from the people; limited government, where government is only given specific powers; separation of powers among the legislative, executive, and judicial branches; checks and balances to limit each branch's power; judicial review allowing courts to determine if laws abide by the Constitution; and federalism dividing power between central and regional governments.