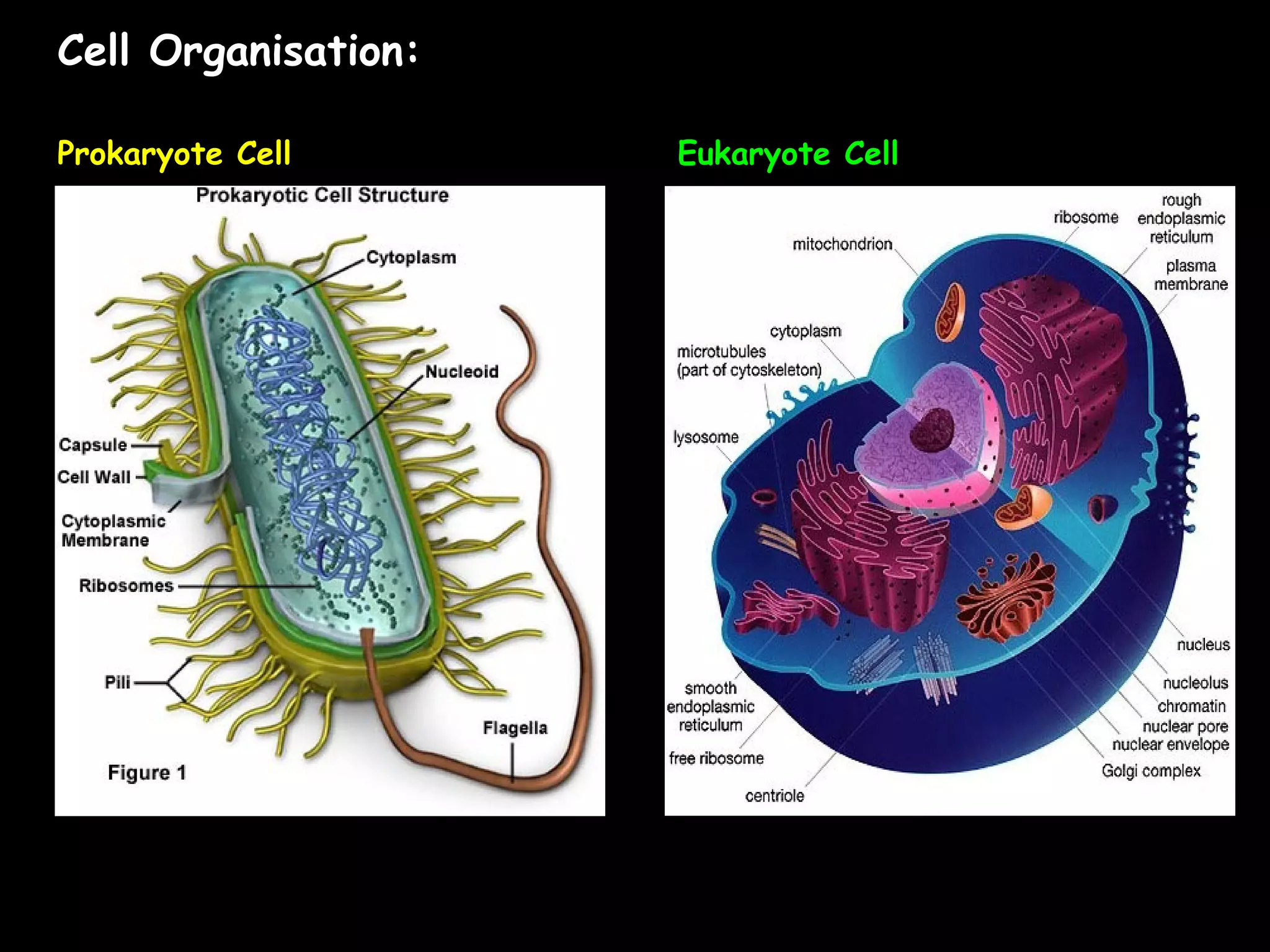
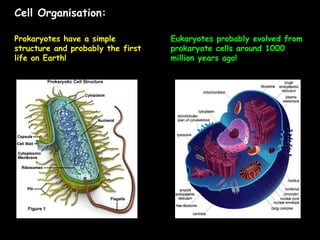
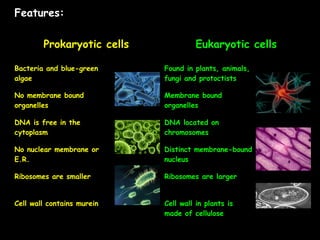
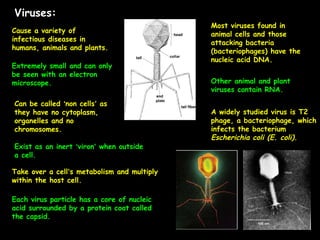
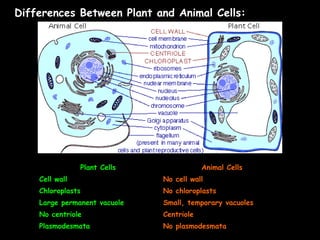
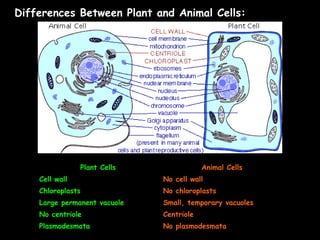
This document summarizes key differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, viruses, and plant and animal cells. Prokaryotic cells like bacteria have no membrane-bound organelles and DNA in the cytoplasm, while eukaryotic cells evolved later and have organelles like the nucleus. Viruses are non-living particles that take over host cell metabolism to multiply, each having a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein coat. Plant cells have cell walls made of cellulose, chloroplasts, large permanent vacuoles, and plasmodesmata connecting cells, while animal cells lack these features.