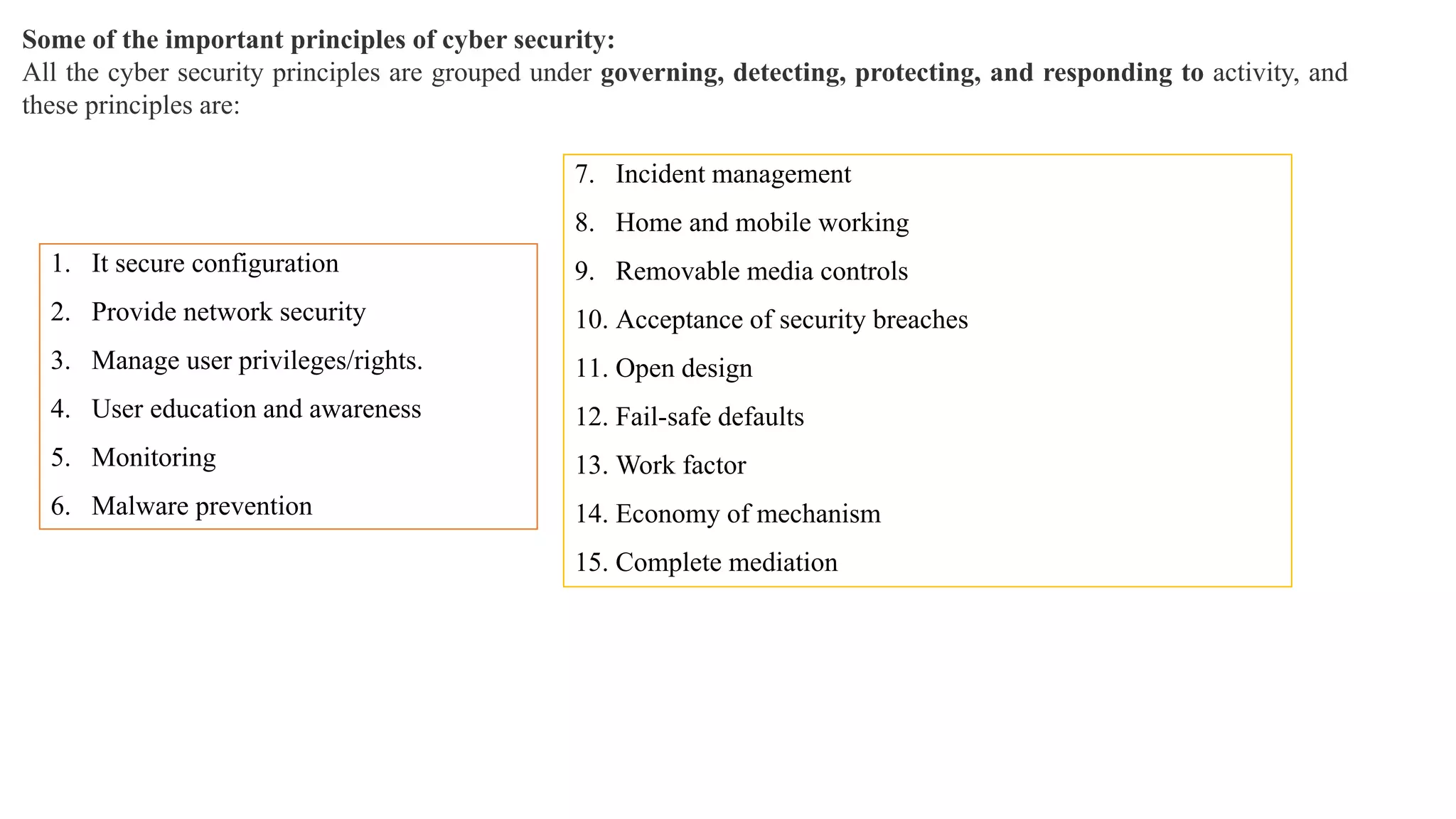
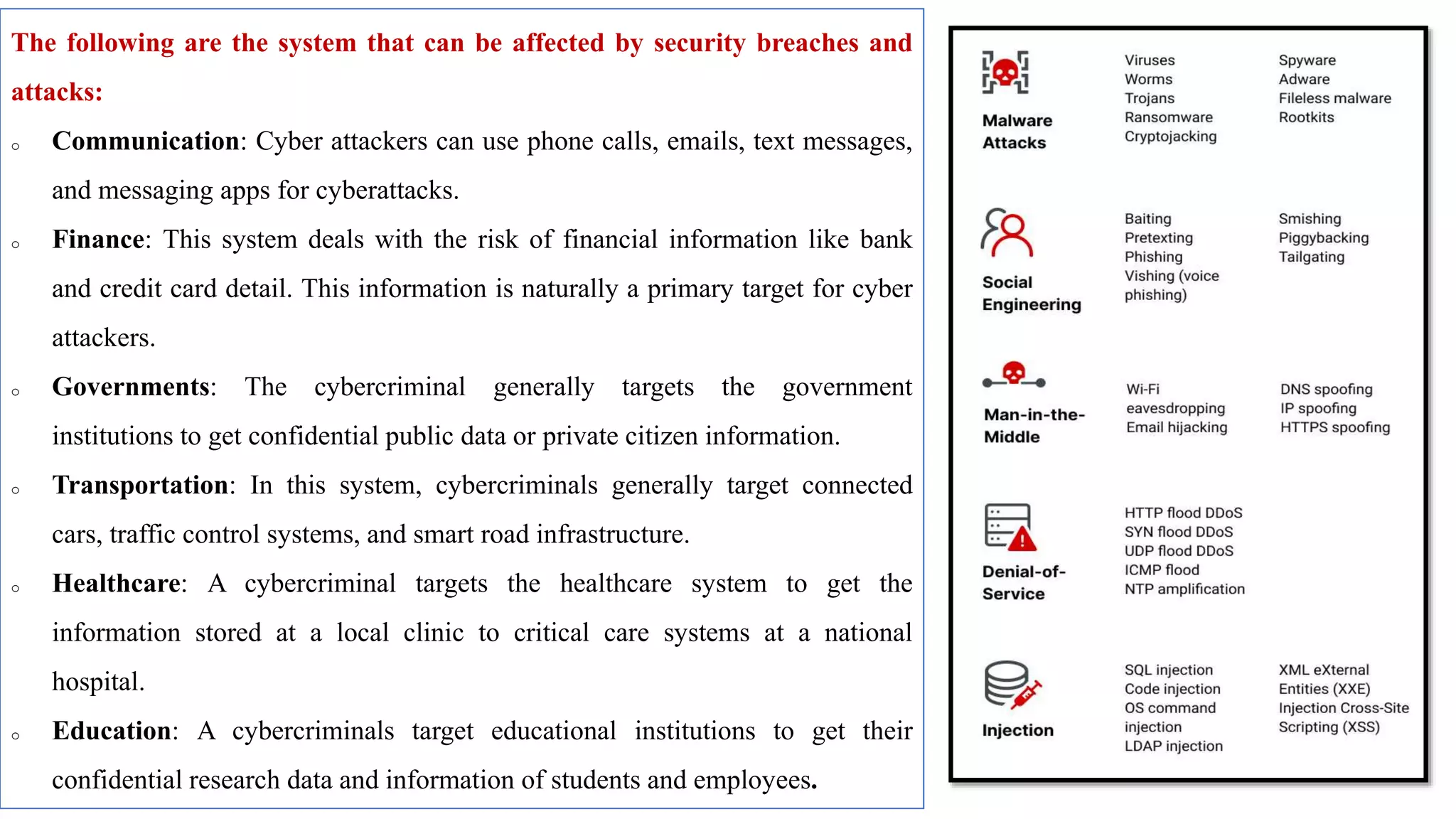
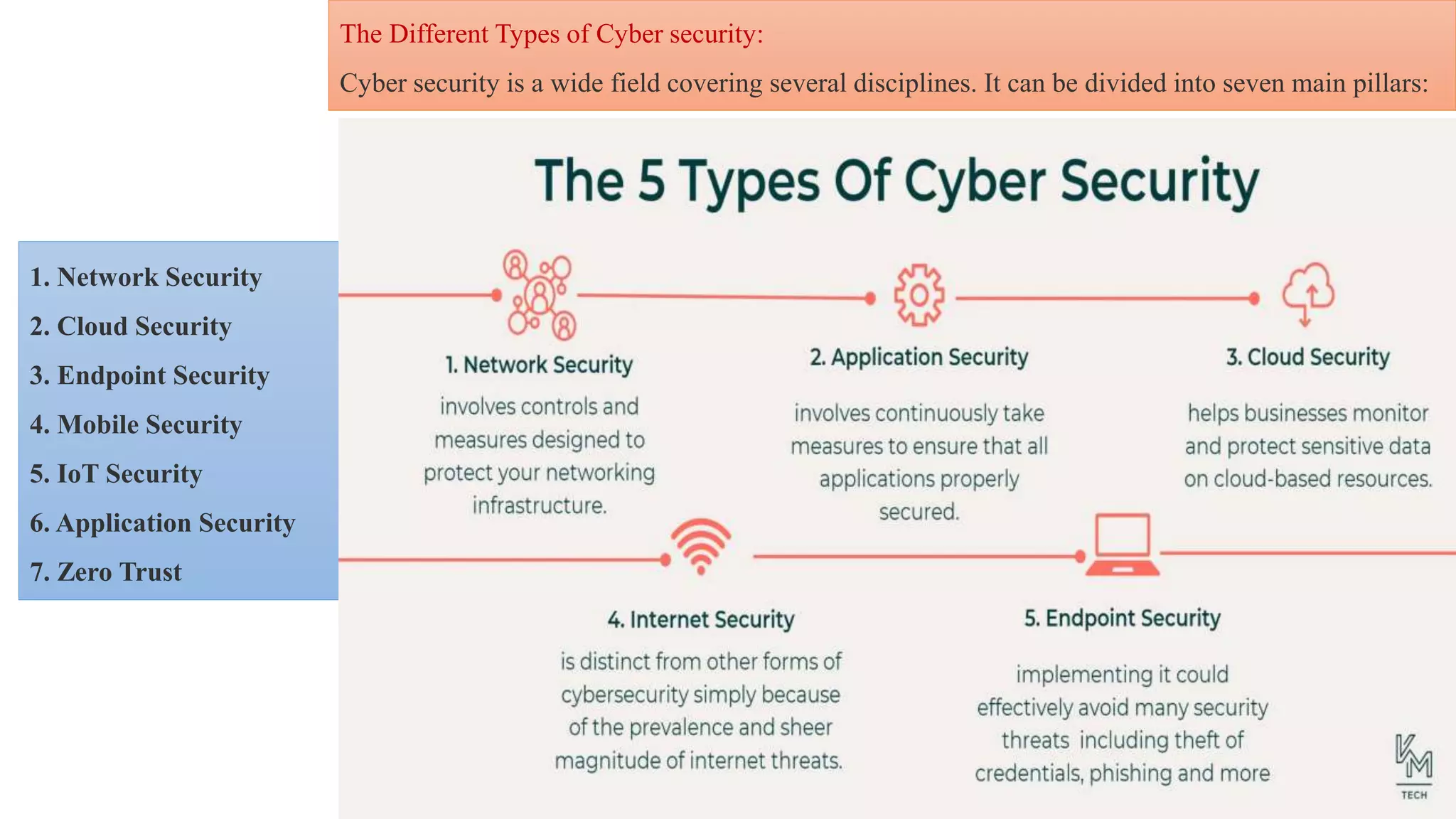
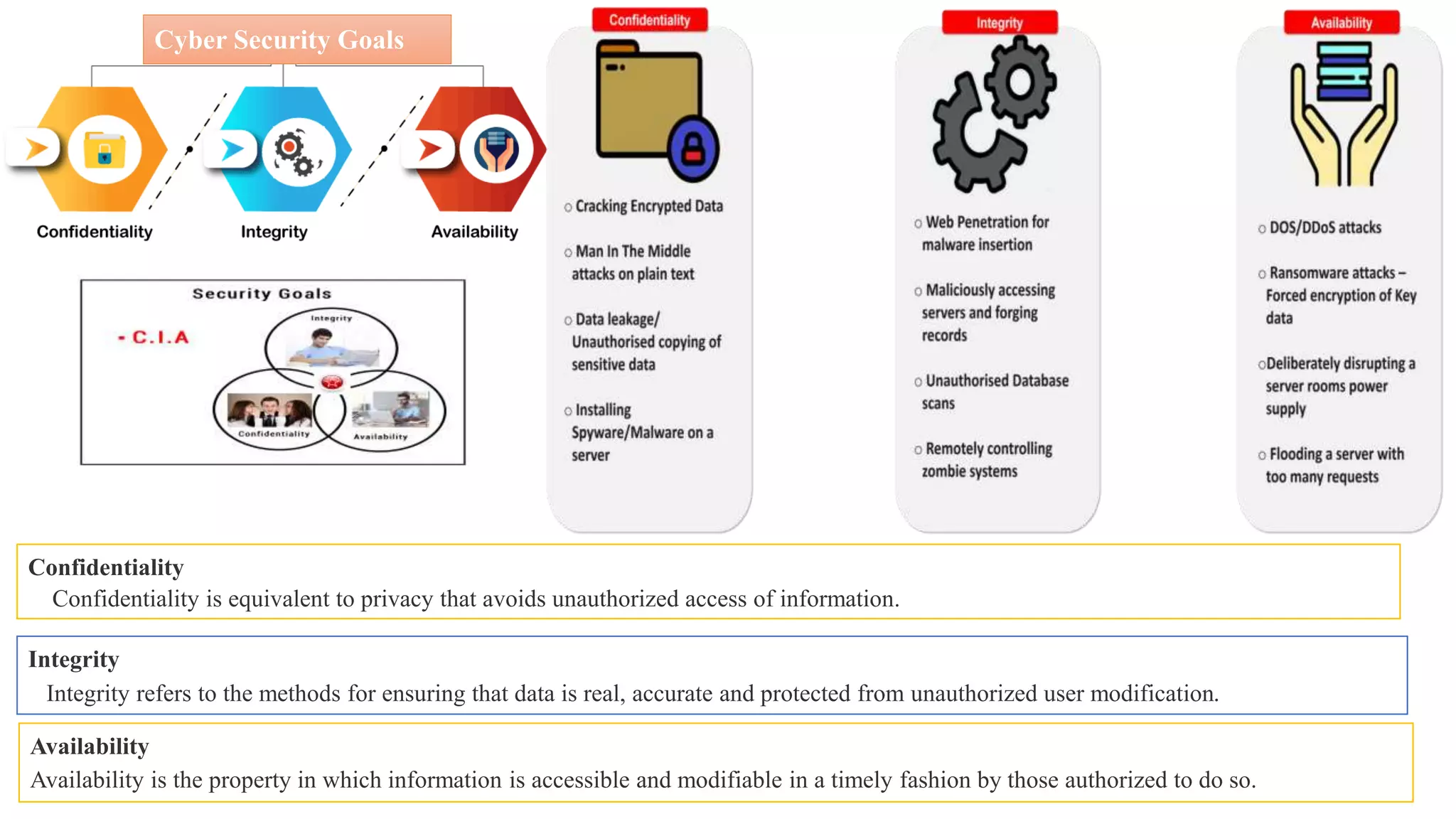
The document provides a comprehensive introduction to cyber security, detailing its importance, challenges, and various forms of cyber threats including cyber crime, cyber terrorism, and cyber espionage. It outlines essential principles and measures for protecting networks and systems from attacks while emphasizing the need for training and awareness among individuals and organizations. Additionally, it discusses the classification of cyber crimes and offers prevention strategies to mitigate risks associated with cyber threats.