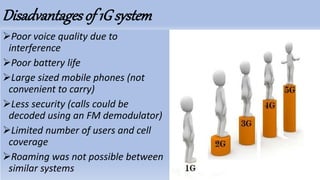
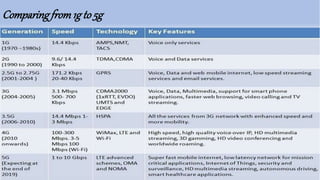
The document covers the evolution and architecture of wireless technology from 1G to 5G, highlighting major advancements in each generation. 5G, deployed widely since 2019, offers significant improvements such as ultra-fast internet speeds up to 10 Gbps, low latency, and increased bandwidth for connected devices. It utilizes an intelligent architecture with small cells and cloud-based infrastructure for enhanced efficiency and future compatibility.