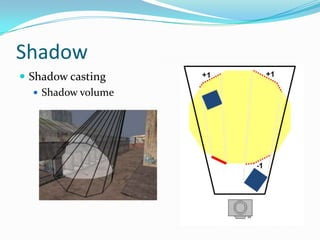
The document discusses techniques for real-time rendering of scenes with complex geometry and dynamic lights using modern GPU features. It describes using a deferred shading scheme with multiple render targets to support massive dynamic light sources. Key techniques discussed include fast shadow calculation in deferred shading, screen space ambient occlusion, shadow mapping/volumes, edge-based anti-aliasing, and screen space occlusion culling to improve performance. A multi-threading layout is proposed to map the rendering passes to GPU kernels for parallel processing of image buffers.