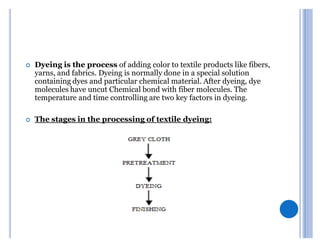
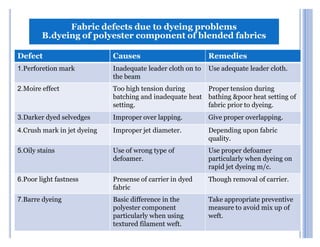
This document summarizes a presentation on dyeing problems and remedies. It discusses common problems that occur during different stages of the dyeing process like pretreatment, dyeing and printing, and finishing. Pretreatment problems account for 21% of issues and are a major cause of other dyeing problems. The document outlines specific problems at each stage and their potential causes. It then provides recommendations for remedies, including using specialty chemicals, controlling temperature and tension carefully, and conducting lab tests. Overall, the key messages are that proper pretreatment is critical to avoid issues in dyeing, and that identifying the root cause of any problem is important before determining a solution.