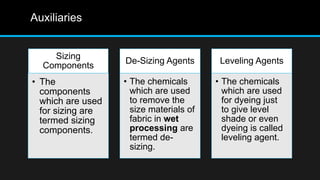
Textile auxiliaries are chemicals that enable textile processing operations like preparation, dyeing, and printing to be carried out more effectively. They help stabilize dye baths, improve dye exhaustion and levelness, and enhance fastness properties. Common auxiliaries include wetting agents, detergents, emulsifiers, sizing components, de-sizing agents, and leveling agents. Pretreatment processes like desizing, scouring, and bleaching also rely on auxiliaries to improve fabric properties before dyeing. Reactive dyeing specifically uses reactive dyes along with dispersing agents, leveling agents, and anti-creasing agents.