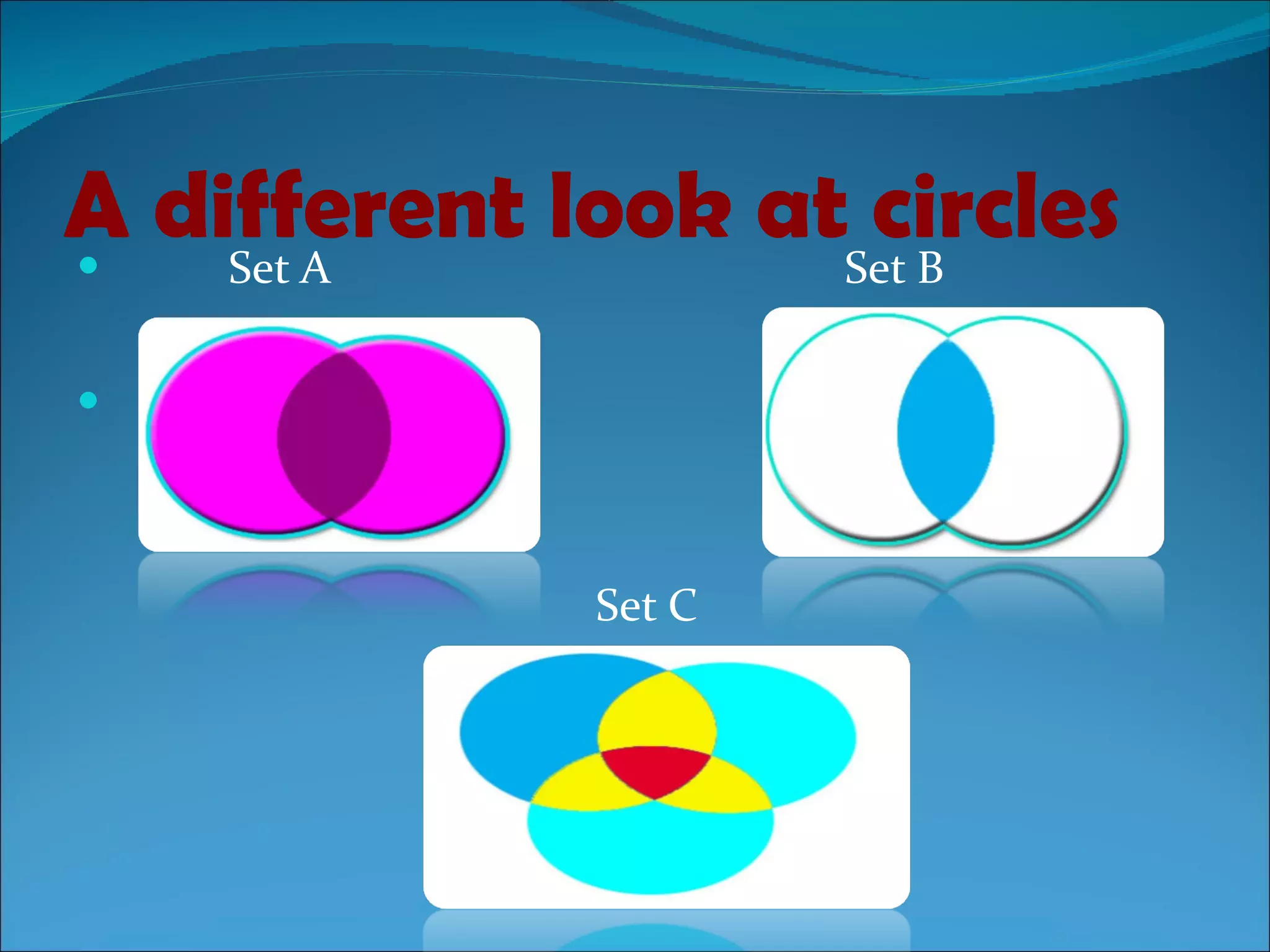
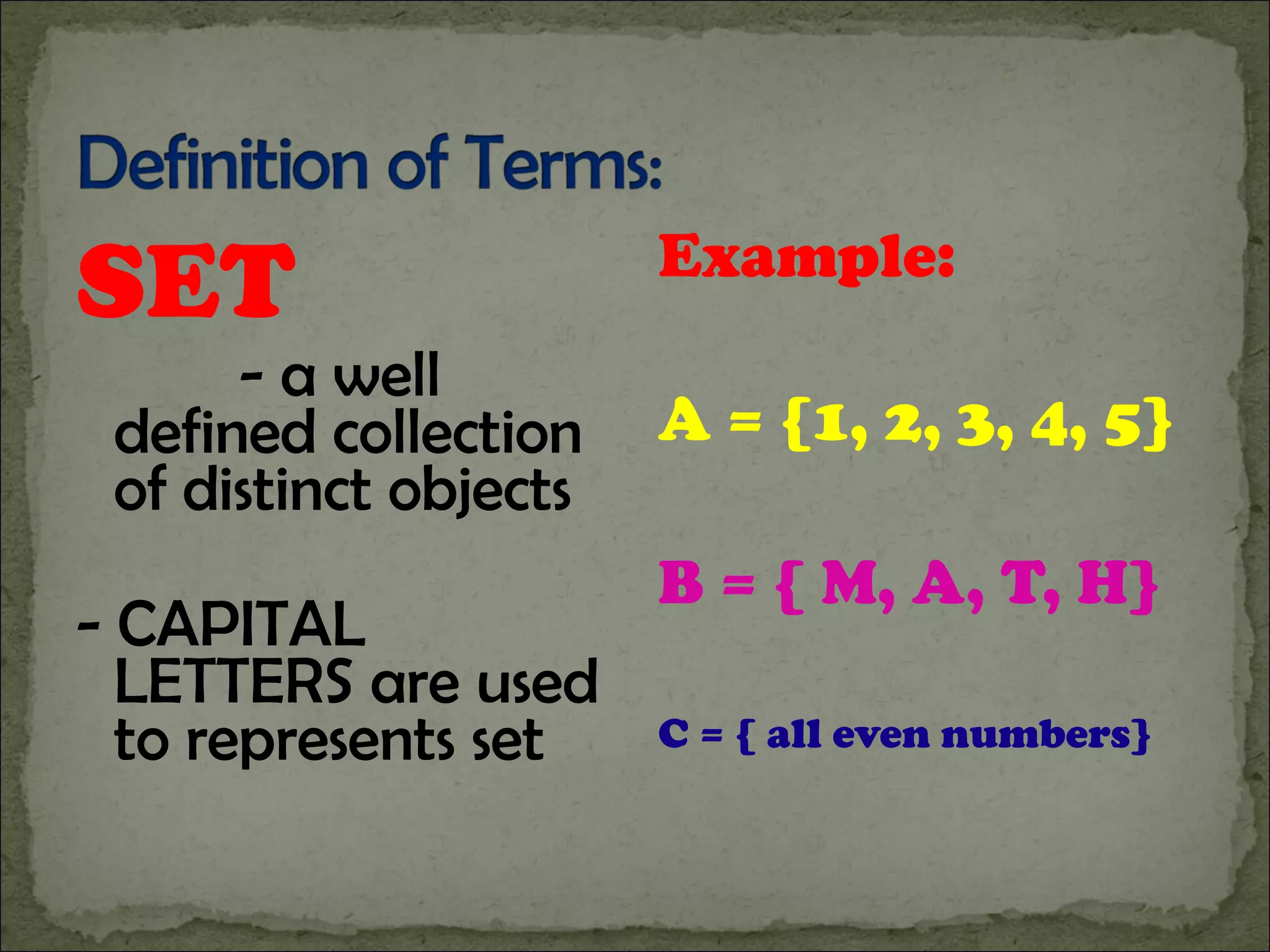
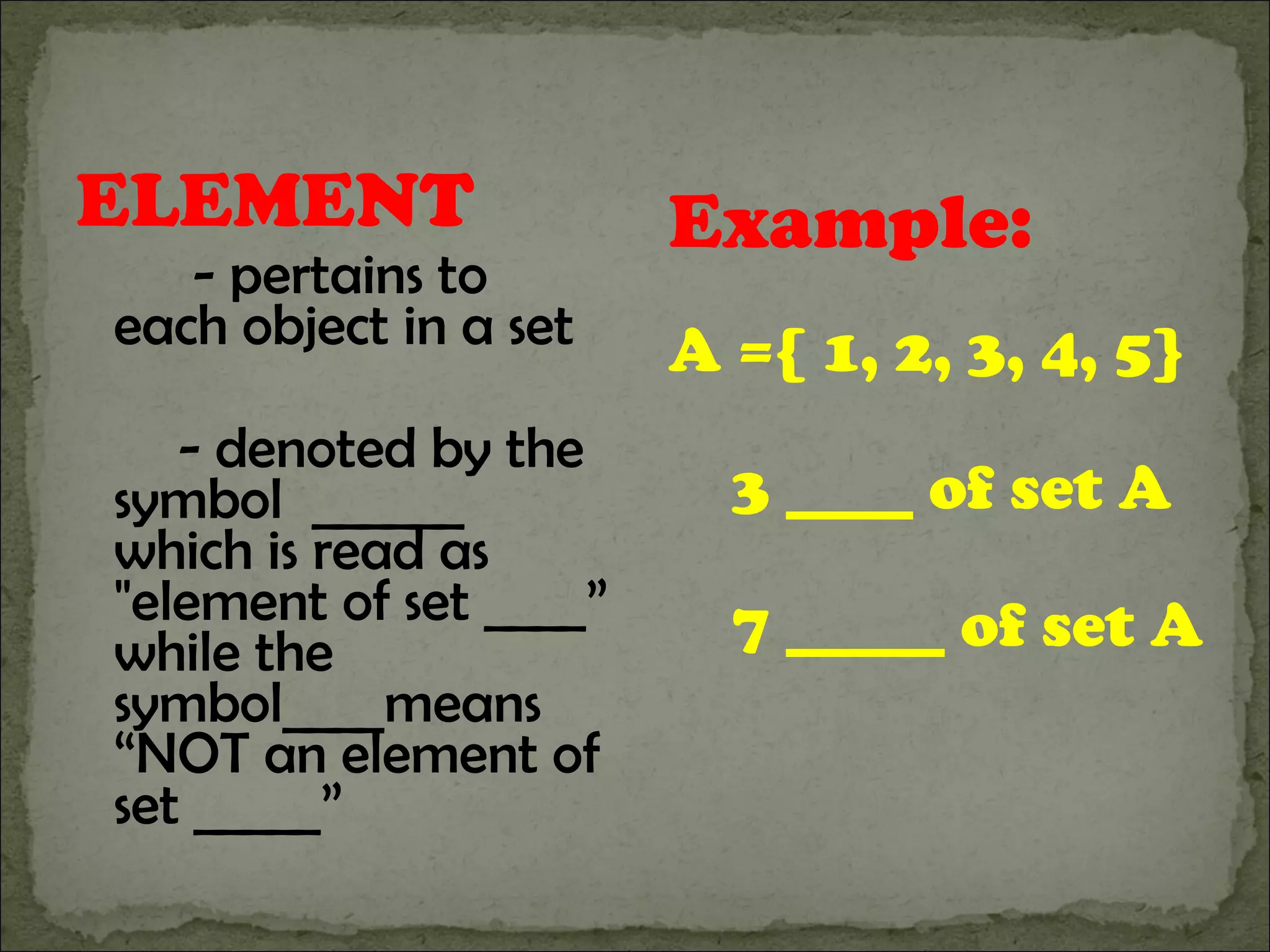
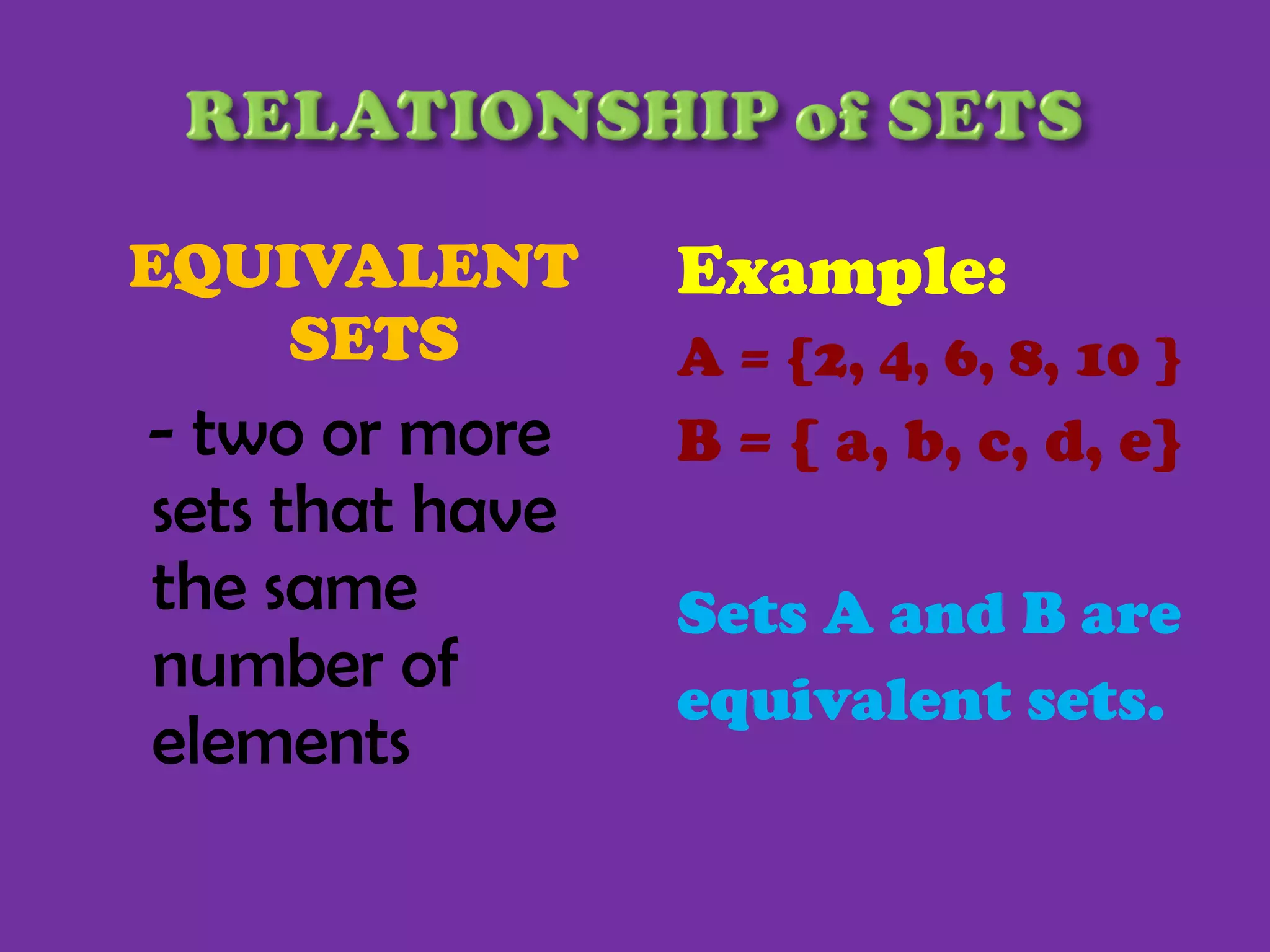
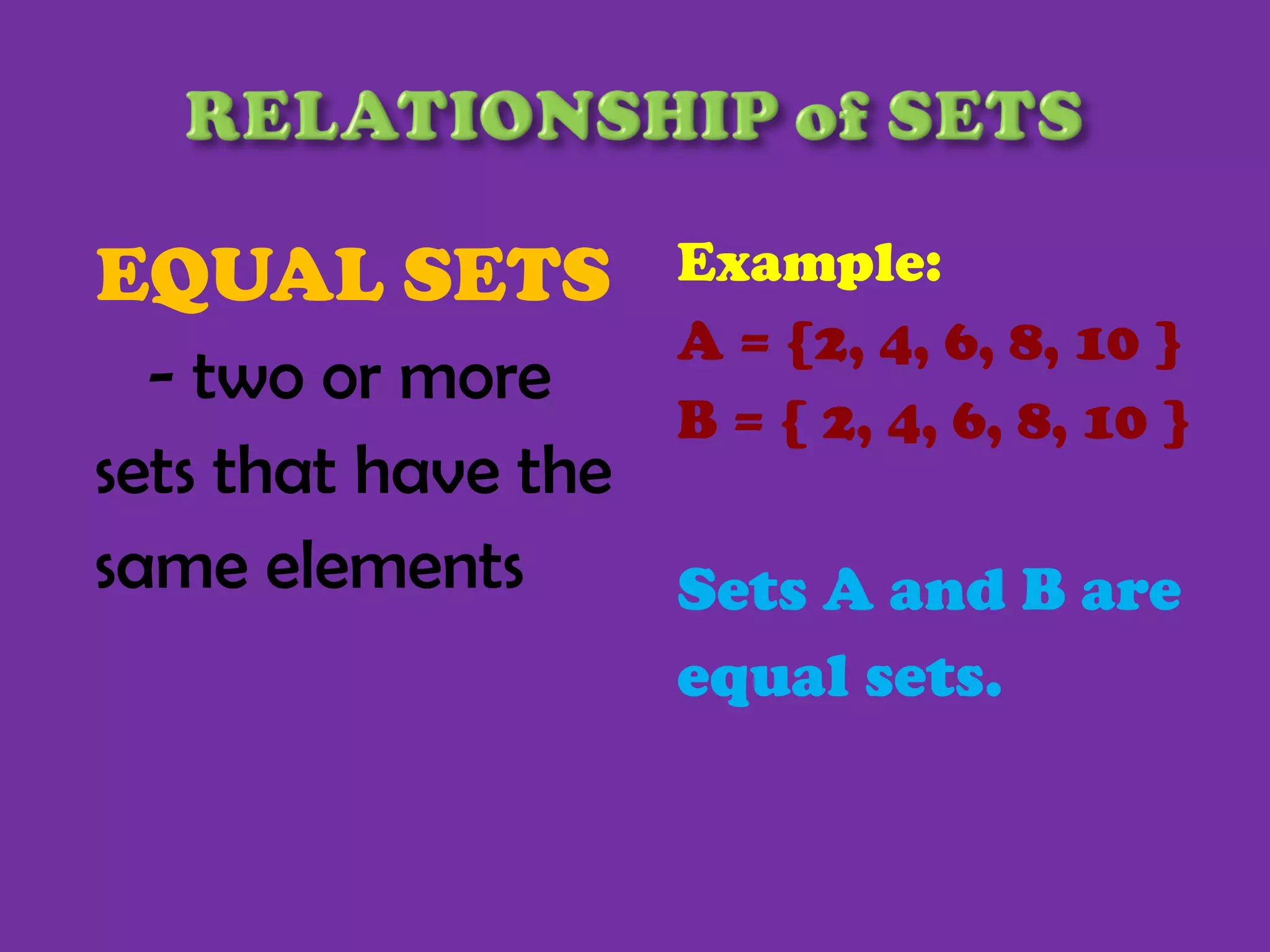
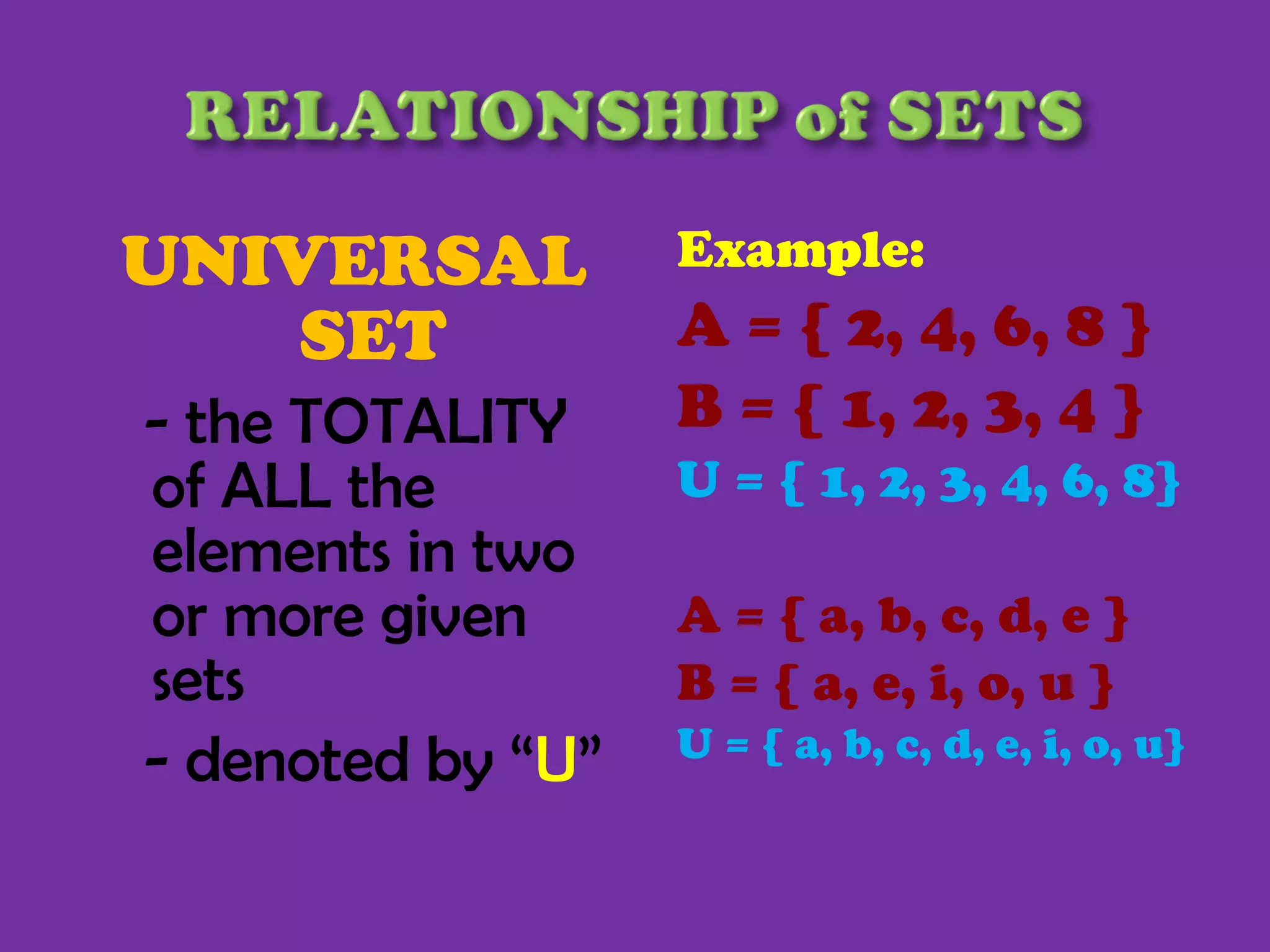
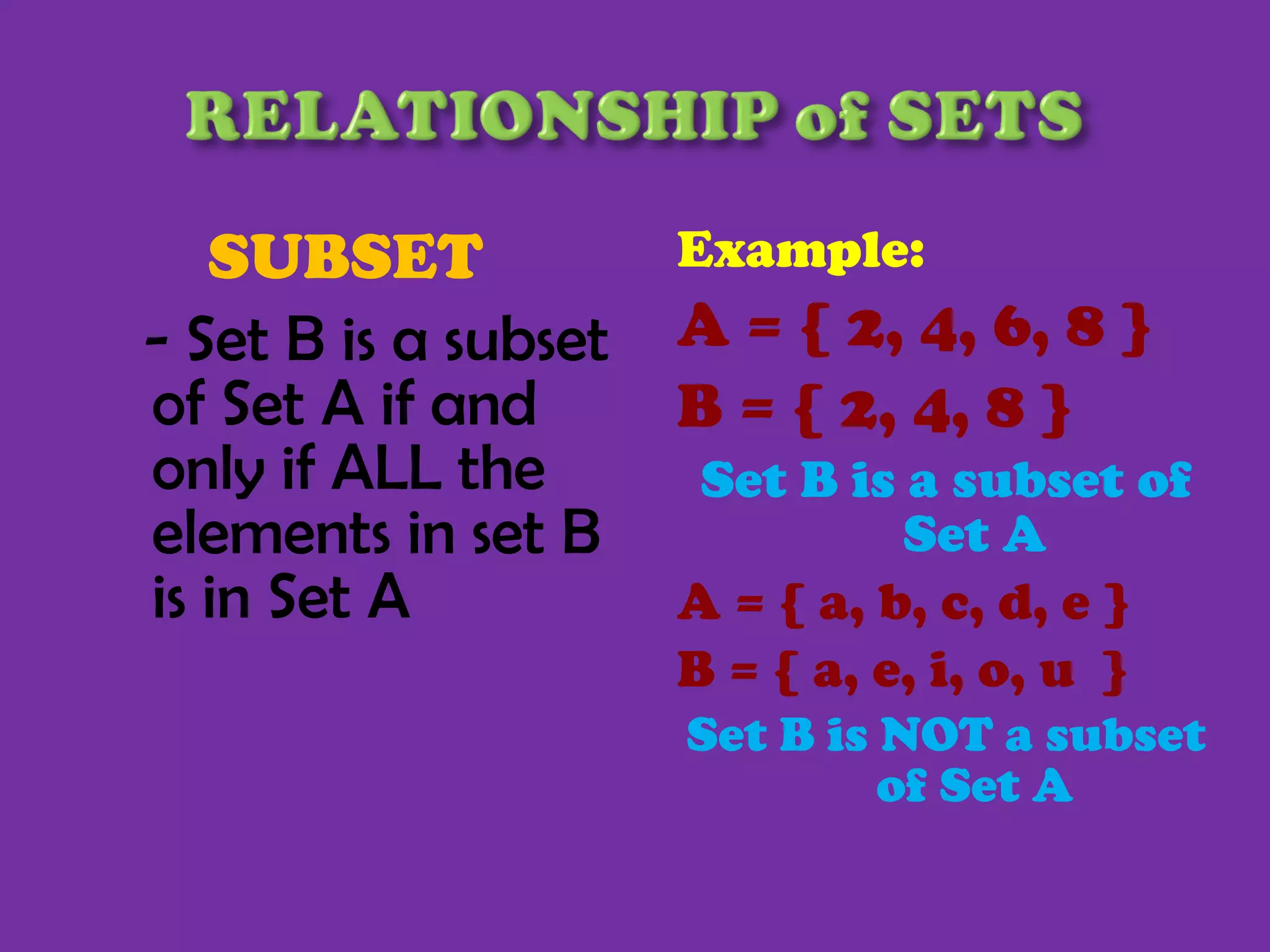
1) The document defines basic set terminology including sets, elements, subsets, finite and infinite sets, empty sets, equivalent sets, equal sets, and the universal set.
2) It provides an example of a situation where 80 students brought sandwiches, drinks, and canned goods to an outing, with various numbers of students bringing each item.
3) The key question is how many students did not bring any of the 3 kinds of items (sandwiches, drinks, canned goods).