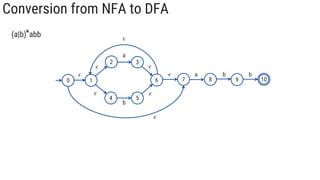
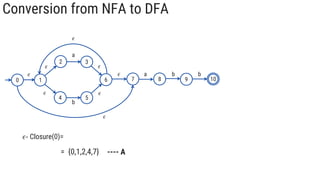
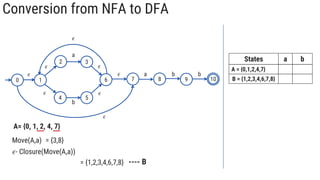
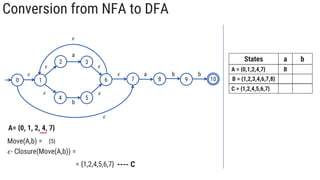
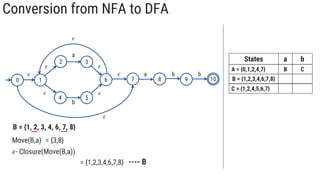
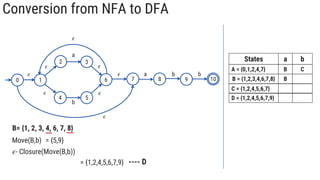
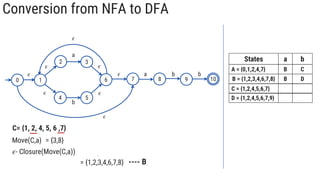
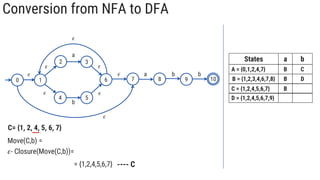
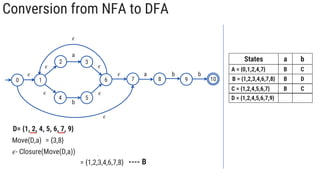
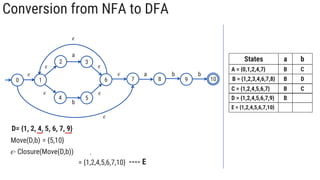
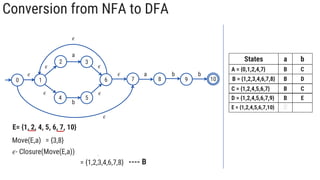
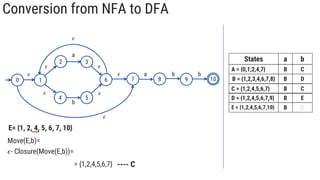
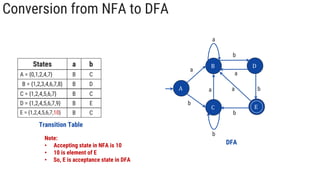
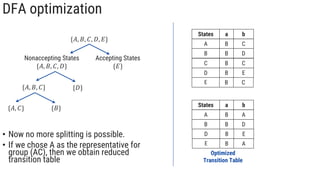
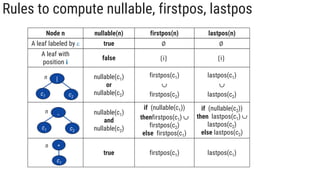
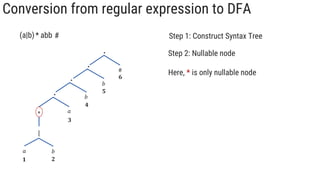
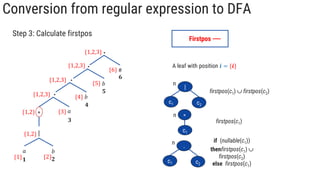
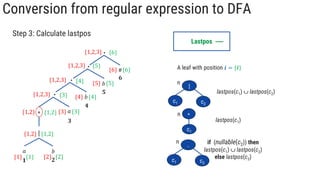
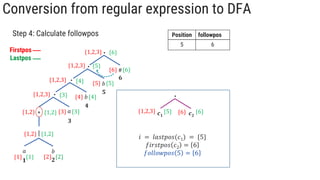
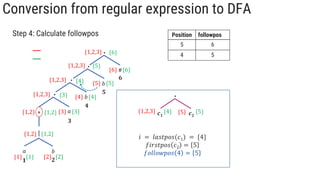
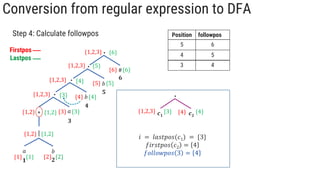
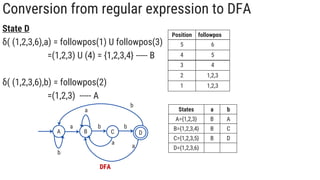
The document describes the subset construction algorithm for converting a non-deterministic finite automaton (NFA) to a deterministic finite automaton (DFA). The algorithm constructs the transition table for the DFA by iteratively taking the epsilon-closure of states reached on transitions and adding them as new DFA states until no new states are generated. An example conversion of an NFA to a DFA is shown step-by-step to demonstrate the algorithm.
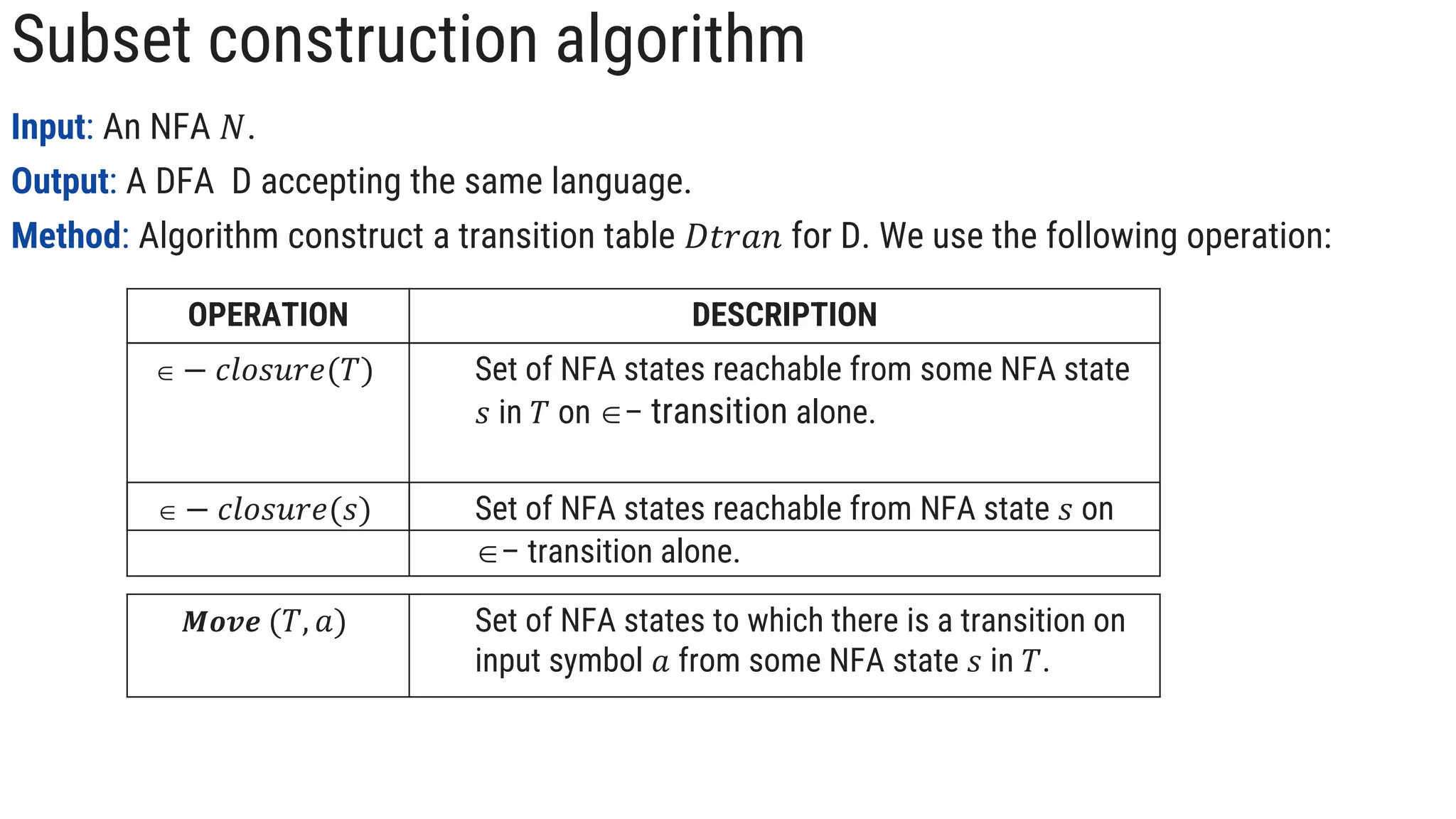
![Subset construction algorithm
initially − 𝑐𝑙𝑜𝑠𝑢𝑟𝑒(𝑠0) be the only state in 𝐷𝑠𝑡𝑎𝑡𝑒𝑠 and it is unmarked;
while there is unmarked states T in 𝐷𝑠𝑡𝑎𝑡𝑒𝑠 do begin
mark 𝑇;
for each input symbol 𝑎 do begin
𝑈 = 𝜖 − 𝑐𝑙𝑜𝑠𝑢𝑟𝑒 𝑚𝑜𝑣𝑒 𝑇, 𝑎 ;
if 𝑈 is not in 𝐷𝑠𝑡𝑎𝑡𝑒𝑠 then
add 𝑈 as unmarked state to 𝐷𝑠𝑡𝑎𝑡𝑒𝑠;
𝐷𝑡𝑟𝑎𝑛[ 𝑇, 𝑎 ] = 𝑈
end
end](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/4-regularexpressiontodeterministicfiniteautomatadirectmethod-05-05-2023-230707153605-a6b8dbff/85/4-Regular-expression-to-Deterministic-Finite-Automata-Direct-method-05-05-2023-pptx-2-320.jpg)