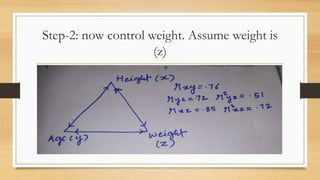
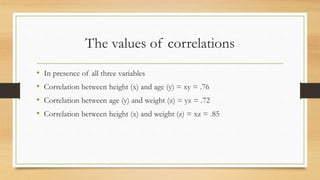
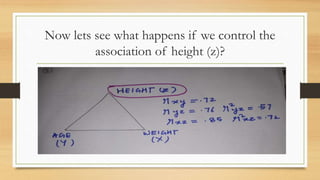
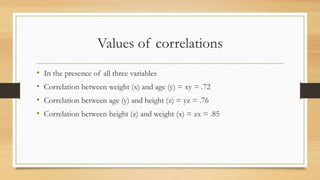
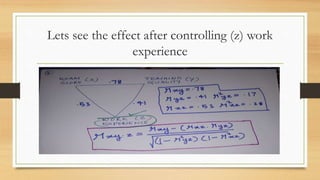
Partial correlation measures the strength and direction of the linear relationship between two continuous variables while controlling for one or more additional continuous variables. The document illustrates partial correlation with examples involving height, weight, and age of children, showing how controlling for different variables changes correlation coefficients. It also discusses cases with reading ability and teaching quality, demonstrating the limited direct relationships revealed by controlling covariates.