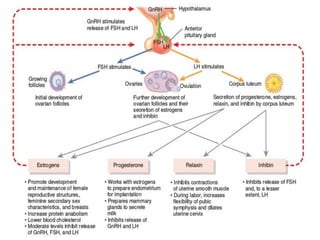
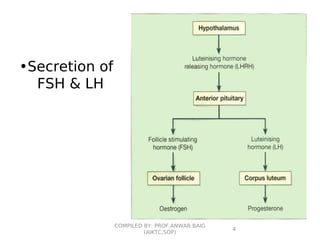
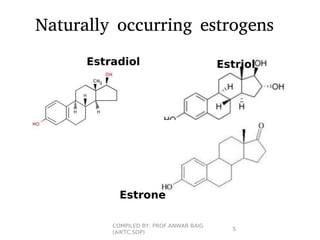
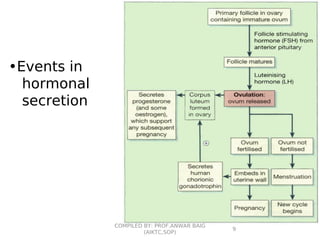
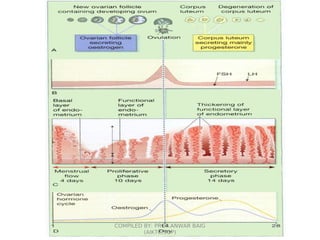
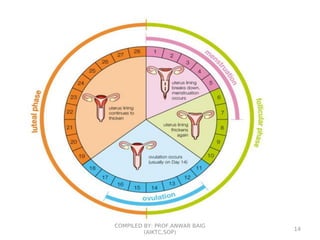
This document summarizes oral contraceptives, including their mechanism of action, methods of use, and formulation. It discusses how oral contraceptives work by suppressing ovulation through negative feedback inhibition of gonadotropins. It also describes the typical menstrual cycle and hormone levels throughout its phases. Common oral contraceptive formulations include combined estrogen-progesterone pills and sequential pills, which are taken in cycles to prevent pregnancy while allowing withdrawal bleeding. Side effects and precautions are also outlined.