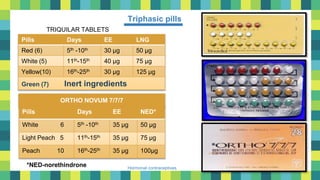
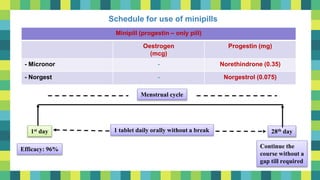
Hormonal contraceptives provide effective birth control through the use of hormones that prevent ovulation. Oral contraceptive pills are the most commonly used hormonal method and contain synthetic estrogens and progestins. Combined oral contraceptive pills are taken daily for 21 days followed by a 7 day break. Progestin-only pills must be taken daily without breaks and are less effective than combined pills. Long-acting reversible methods include intrauterine devices and injectable contraceptives administered every 3 months. Emergency contraceptive pills can prevent pregnancy if taken within 3-5 days after unprotected sex. Hormonal contraception is highly effective and reversible but some methods can cause irregular bleeding or other side effects.


![3
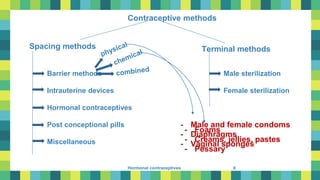
History of contraception
- Condoms are named after Dr Condum, who started the act to stop illegal Offsprings
[condus – receptacle]
- Pebbles were inserted in the uteri of camels to prevent
pregnancies during long journies in the desert by arabs and turks
- Intrauterine devices were introduced in germany by
Ernst Grafenberg made up of silkworm gut and silver wire
- Rock and Pincus ( 1955) announced the successful use of an oral progestin for contraception](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/adrew2-220814185936-c0498e61/85/adrew2-pdf-3-320.jpg)







![16
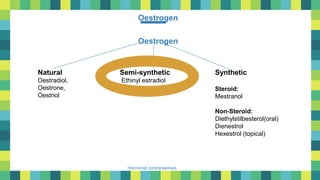
Hormonal contraceptives
Progesterone derivatives: 19- nortestosterone:
1]Older 1]
Medroxyprogesterone acetate
Dydrogesterone (Duphaston)
Hydroxyprogesterone Caproate/ Acetate
Megestrol
2]Newer: 2]Newer:
Nomegestrol Desogestrel
Norgestimate
Gestodene
Older
Lynestrenol
Levonorgestrel
Allylestrenol
Norethindrone (Norethisterone)
Norethynodrel
Progestins
Androgenic
Antiovulatory](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/adrew2-220814185936-c0498e61/85/adrew2-pdf-16-320.jpg)

















![37
Hormonal contraceptives
Injectable contraceptives
C] DMPA-SC
- A new lower-dose formulation of DMPA, depo-subQ provera 104
is injected under the skin rather than in the muscle.
- It contains 104 mg of DMPA rather than the 150 mg in the intramuscular
formulation.
- Like the intramuscular formulation, DMPA-SC is given at 3-month intervals.
- DMPA-SC is just as effective as the formulation injected into the muscle, and the patterns of bleeding
changes and amount of weight gain are similar.
- Injections of DMPA-SC are given in the upper thigh or abdomen. DMP A-SC should not be injected
intramuscularly, and the intramuscular formulation should not be injected subcutaneously.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/adrew2-220814185936-c0498e61/85/adrew2-pdf-37-320.jpg)

![40
Hormonal contraceptives
Implants
- These are drug delivery systems implanted under the skin, from which the steroid is released
slowly over a period of 1-5 year,.
They consist of either-
(a) Biodegradable polymeric matrices-do not need to be removed on expiry.
(b) Nonbiodegradable rubber membranes-have to be removed on expiry.
1] NORPLANT](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/adrew2-220814185936-c0498e61/85/adrew2-pdf-40-320.jpg)
![41
Hormonal contraceptives
Implants
1] NORPLANT: A set of 6 capsules each containing 36 mg levonorgestrel (total 216 mg) for subcutaneous
implantation is available in some countries. but has been discontinued in the USA.
It works for up to 5 years.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/adrew2-220814185936-c0498e61/85/adrew2-pdf-41-320.jpg)

















