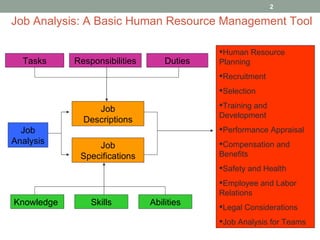
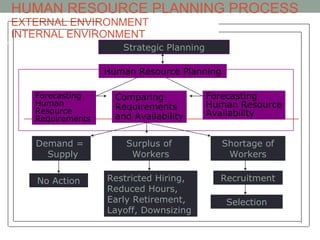
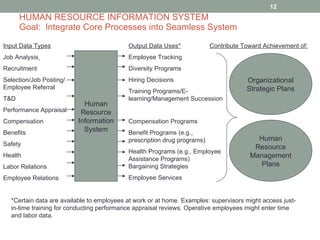
The document discusses key aspects of job analysis and human resource planning. It defines job analysis, job descriptions, job specifications, knowledge, skills and abilities. It also outlines the human resource planning process, including forecasting human resource requirements and availability, and addressing surpluses or shortages of workers. The role of human resource information systems in integrating core HR processes is also summarized.