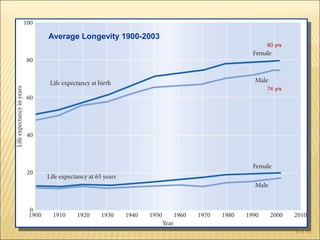
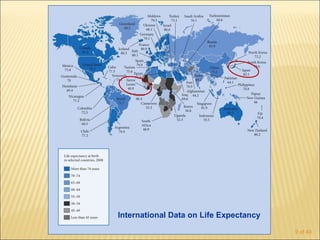
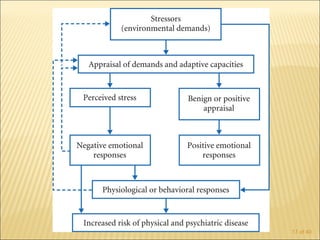
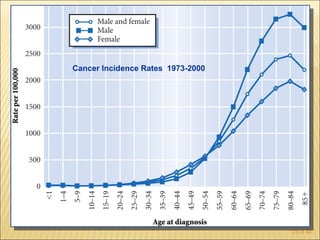
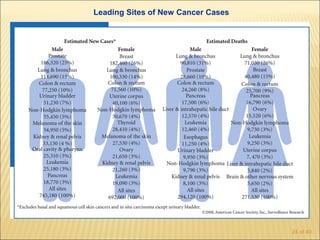
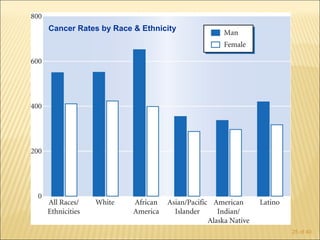
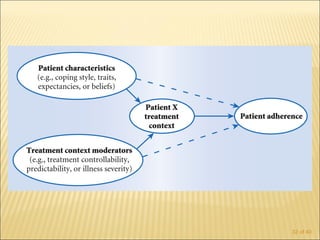
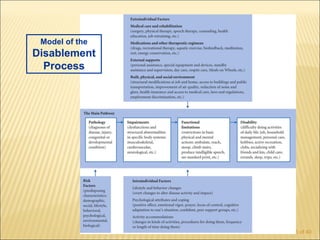
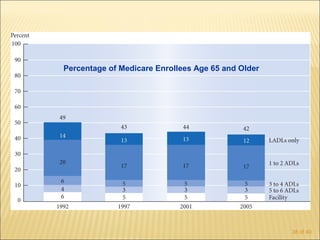
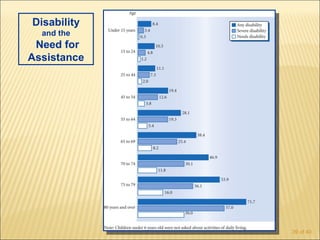
The document discusses factors that influence functional health and disability in older adults. It presents a model of the disablement process and examines how chronic conditions, socioeconomic status, gender, and ethnicity can impact functional limitations and the need for assistance with daily activities. Common causes of disability in older adults include cerebrovascular disease, arthritis, smoking, physical inactivity, and depression.