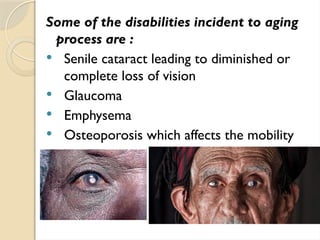
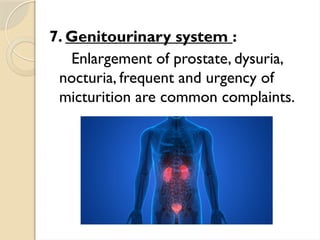
The document discusses health problems faced by the elderly, including age-related diseases, chronic illnesses, and psychological issues. It emphasizes the importance of lifestyle factors such as diet, exercise, and social engagement in promoting healthy aging. Additionally, it outlines national policies and programs in India aimed at supporting older adults, including pensions, healthcare facilities, and community support initiatives.