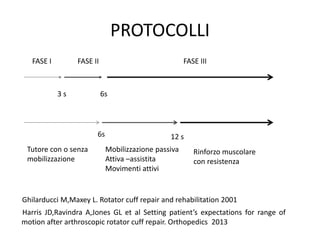
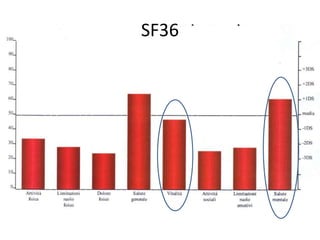
Il documento discute il processo di riabilitazione dopo la ricostruzione chirurgica della cuffia dei rotatori, evidenziando l'importanza di un approccio graduale e personalizzato. Vengono analizzati aspetti come l'attività fisica e la mobilizzazione, con riferimenti a studi su protocolli post-operatori. Il recupero ottimale della forza muscolare può richiedere fino a un anno di riabilitazione.