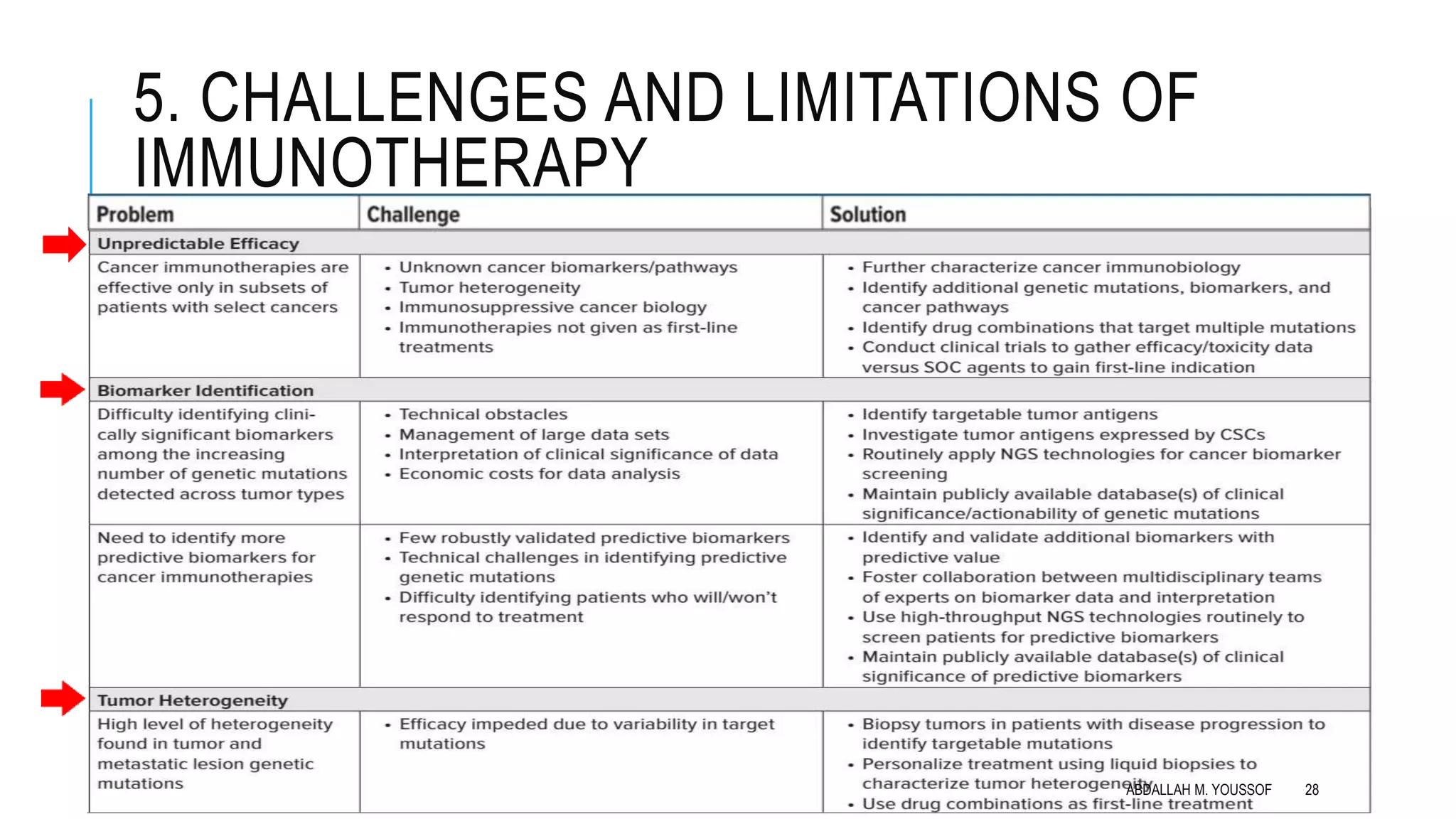
The document discusses current strategies for cancer immunotherapy, including monoclonal antibodies and cell-based immunotherapy. Monoclonal antibodies can target cancer cells directly via mechanisms like antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity. They can also be conjugated to toxins or radioactive particles for targeted delivery. Immune checkpoint blockers are a type of monoclonal antibody that blocks inhibitory receptors on T-cells to prolong anti-tumor responses. Cell-based immunotherapy includes adoptive T-cell therapy using tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes or chimeric antigen receptor T-cells that are genetically modified to target specific tumor antigens. Immunotherapy has advantages over other treatments in that it can target cancers throughout the body, is highly specific to cancer cells, and may provide durable, long-








![3. CURRENT STRATEGIES AND
AGENTS
3.1. Monoclonal Antibodies (mAbs): MOA of
ICBs Checkpoint ligand/receptor interactions can
be stopped by:
A. Blocking IC receptors such as
[Cytotoxic T-Lymphocyte
Associated Antigen 4 (CTLA-4) and
Programmed Death-1 (PD-1)] , or
B. Blocking IC ligands of tumor cells,
such as Programmed Death
Ligand-1& 2 (PD-L1and PD-L2).
R
L
CD28
ABDALLAH M. YOUSSOF 10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/immunotherapy-190414204640/75/Cancer-Immunotherapy-10-2048.jpg)