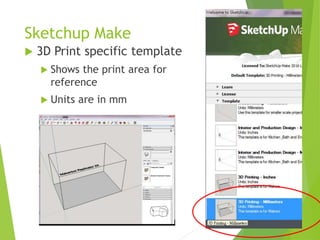
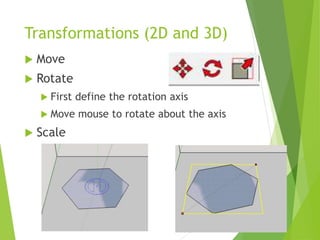
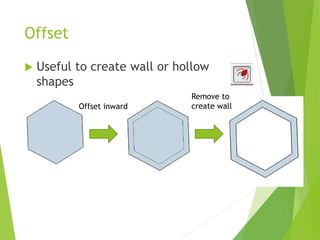
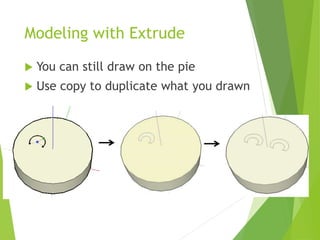
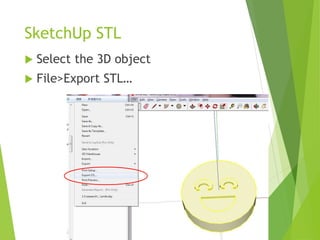
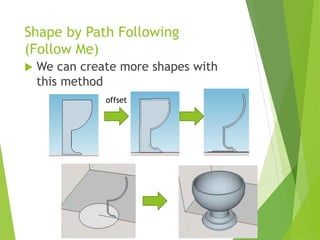
The document outlines a 3D printing workshop led by Dr. Raymond Pang at the Caritas Institute of Higher Education, providing an overview of 3D printing technologies, applications, and hands-on experience with a 3D printer. It covers various methods of 3D printing, including stereolithography, selective laser sintering, and fused deposition modeling, as well as software and materials used in printing. Additional resources for 3D modeling are also mentioned, along with step-by-step instructions for preparing and printing 3D objects.