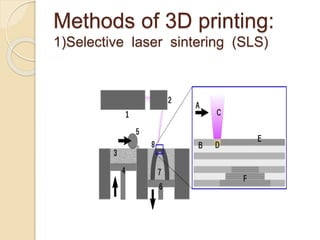
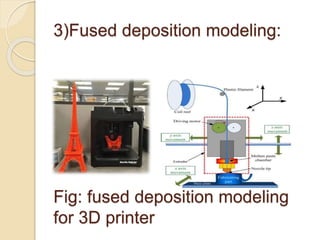
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is a process of making 3D solid objects from a digital file by successively adding material layer by layer. There are two main types of manufacturing: additive and subtractive. Additive manufacturing builds objects by adding layers of material, while subtractive manufacturing cuts material away from a solid block. Common 3D printing methods include selective laser sintering, stereolithography, and fused deposition modeling. Materials used include plastics and metals. Applications of 3D printing include manufacturing tools, medical devices, prototypes, and more. The technology offers advantages like customization, rapid production, and low costs.