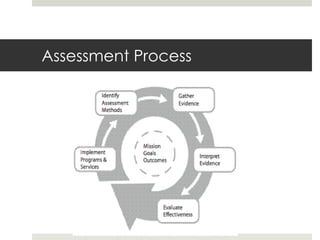
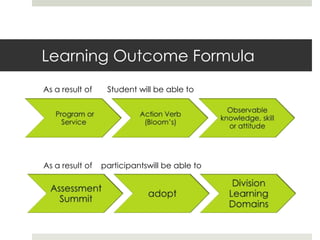
This document provides information on creating an assessment toolbox. It discusses learning outcomes and Bloom's taxonomy. Learning outcomes describe how a student will change due to a learning experience. They include knowledge, skills, attitudes, and habits students take away. The document also covers types of assessment like tracking participation, needs assessment, and outcomes assessment. Assessment tools in the toolbox include surveys, rubrics, focus groups, student work, and database/observation tools. The goal is to help participants understand assessment and choose appropriate tools to measure program impact based on learning outcomes.