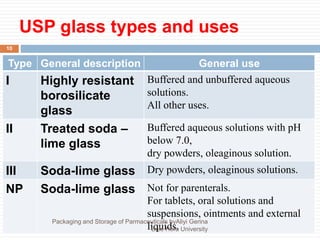
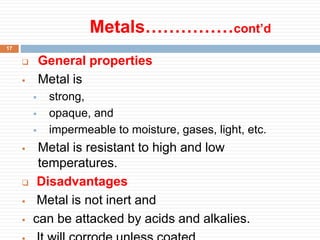
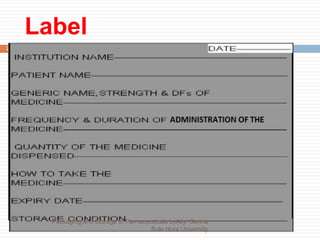
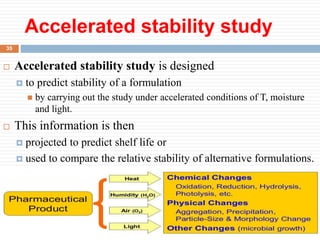
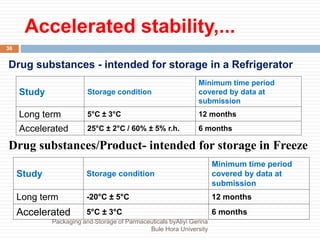
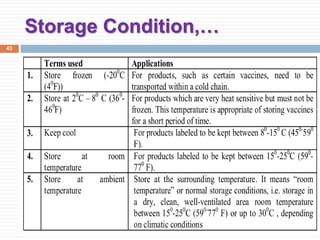
This document discusses packaging and storage of pharmaceuticals. It covers various packaging materials like glass, plastics, and metals. It describes primary and secondary packaging as well as different types of containers, closures, and labeling requirements. The document also discusses stability studies, storage conditions, and establishing beyond-use dates to ensure pharmaceuticals maintain quality until the expiration date.
![Bule Hora University
College of Health and Medical Sciences
Department Of Pharmacy
INTEGRATED PHYSICAL PHARMACY AND PHARMACEUTICS I
CHAPTER 5
Packaging and storage of
pharmaceuticals
By: Aliyi Gerina [BSc, B.pharm]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch5-220220075933/75/Ch5-packaging-of-pharmaceuticals-1-2048.jpg)