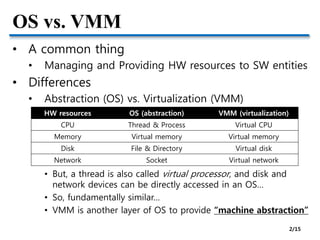
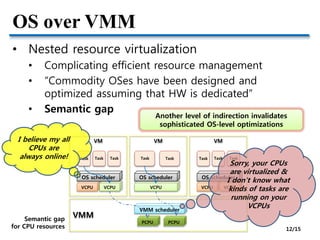
OS vs. VMM provides an overview of the similarities and differences between operating systems (OS) and virtual machine monitors (VMM). Both OS and VMM abstract hardware resources, but VMM provides virtualization while OS provides abstraction. Nested virtualization further complicates resource management by adding additional layers of indirection. Key issues in virtualization include trapping privileged OS operations, scheduling virtual CPUs, managing virtual memory translations, and achieving high performance I/O.

![CPU Virtualization
• Privileged level
• VMM makes OS step down to less-privileged layer
• VMM must trap and virtualize any OS’s attempt to
run privileged operations
OS
Application
VMM
OS
Application
OS VMM
[Issue] How to trap and virtualize OS’s privileged operations
3/15](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-150328170353-conversion-gate01/85/2-OS-vs-VMM-3-320.jpg)
![CPU Management
• Another scheduling layer: “VMM scheduler”
Virtual
CPU
OS VMM
[Issue] How to efficiently schedule virtual CPUs 4/15](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-150328170353-conversion-gate01/85/2-OS-vs-VMM-4-320.jpg)
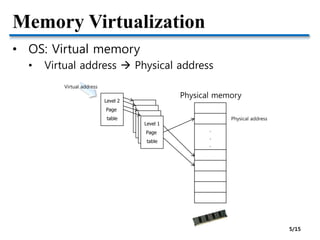
![Memory Virtualization
• VMM: “Virtualizing virtual memory”
• Virtual Physical Machine
Level 2
Page
table
Page
table
Page
table
Page
table
Level 1
Page
table
.
.
.
Machine memory
Virtual address
Physical
to
Machine
Pseudo physical
memory
Terminology
- Xen
Virtual (Pseudo) Physical Machine
- Others (general)
Guest-virtual Guest-physical Host-physical
[Issue] How to transparently and efficiently
manage additional memory translation 6/15](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-150328170353-conversion-gate01/85/2-OS-vs-VMM-6-320.jpg)
![Memory Management
• Memory sharing
• OS
• Parent-child copy-on-write sharing
• VMM
• No semantic of parent-child relationship
• Content-based page sharing invented by VMware [OSDI’02]
• Memory oversubscription (to be explained later)
VM 1 VM 2
Machine Memory
[Issue] How to efficiently use limited memory by avoiding
redundant and idle memory 7/15](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-150328170353-conversion-gate01/85/2-OS-vs-VMM-7-320.jpg)
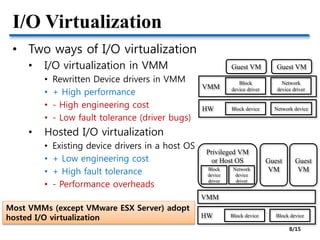
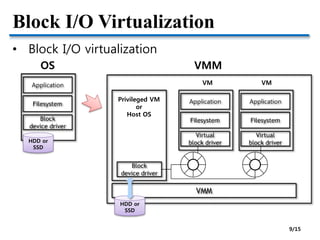
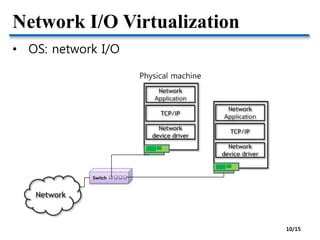
![Network I/O Virtualization
• VMM: Virtualizing network devices
VM VMPrivileged VM or Host OS
Virtual
switch
[Issue] How to achieve near-native I/O performance? 11/15](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-150328170353-conversion-gate01/85/2-OS-vs-VMM-11-320.jpg)
![Nested Virtualization
• IBM’s Turtles project [OSDI’10]
• Nesting is being continued…
• Nesting is being needed…
• Cloud of cloud
• Gang migration
• Hypervisor development
Guest VMM
Guest
VM
Host VMM
HW
Guest VMM
Guest
VM
Guest
VM
Guest
VM
Microkernels Meet Recursive Virtual Machines [OSDI’96]
13/15](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-150328170353-conversion-gate01/85/2-OS-vs-VMM-13-320.jpg)
![Nested Virtualization is Not New
• Theoretical analysis
• [IEEE Computer’74], [Commun. ACM’74], [SIGOPS rev’75]
• Hardware architecture
• [ACM’75]
• Nested virtualization on IBM z/VM
• [IBM system journal’91]
• Microkernel-based nested virtualization
• [OSDI’96]
• Nested virtualization on KVM with AMD
• [Linux Plumbers Conference’09]
• Nested virtualization on Xen
• [Xen summit’09]
• Blue Pill
• [Blackhat’09]
14/15](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-150328170353-conversion-gate01/85/2-OS-vs-VMM-14-320.jpg)
