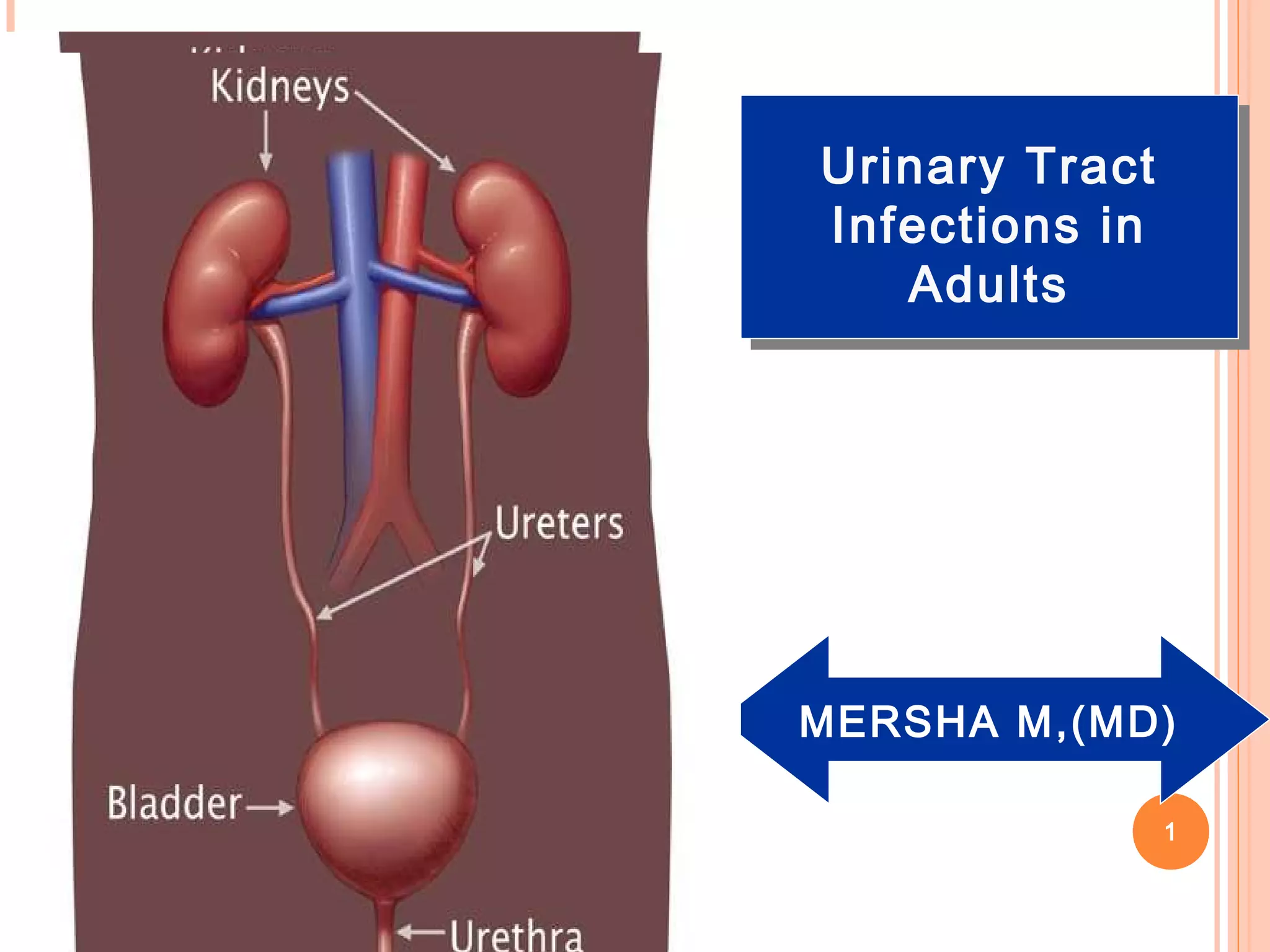
This document discusses urinary tract infections (UTIs) in adults. It begins by defining UTIs as the presence of microbial pathogens in the normally sterile urinary tract. It then covers the epidemiology of UTIs, noting that they primarily affect females and are caused most commonly by E. coli. The pathogenesis section explains that UTIs usually originate from gut flora and ascend the urinary tract. Clinical manifestations can include symptoms of lower or upper tract infections. Diagnosis involves urine culture thresholds above 100,000 CFU/ml typically. Treatment depends on the type and location of infection, with uncomplicated lower UTIs typically treated with a 3 day course of antibiotics and more serious pyelonephritis requiring longer intravenous treatment