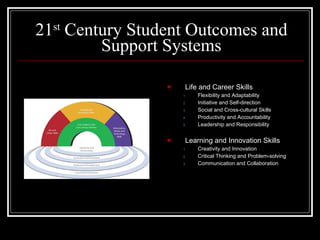
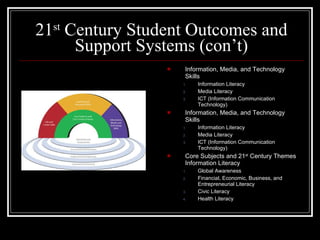
The document discusses 21st century skills learning, focusing on the three C's of communication, creativity/innovation, and critical thinking. It provides examples of how tools like Twitter, blogs, and social bookmarking can be used to teach these skills and foster collaboration. Project-based learning and online conferences are presented as ways to engage students in problem solving and challenges.