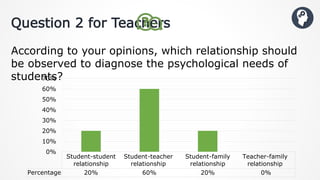
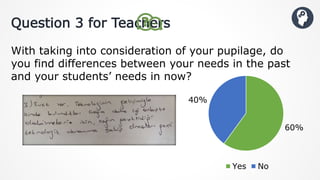
The document discusses the significance of understanding students' basic psychological needs to improve their behavior and academic performance. It reviews various theories and perspectives on psychological needs, identifies factors contributing to academic failure, and suggests methods for teachers to better engage with students. The document concludes with recommendations for creating supportive learning environments and emphasizes the importance of teacher-student relationships.