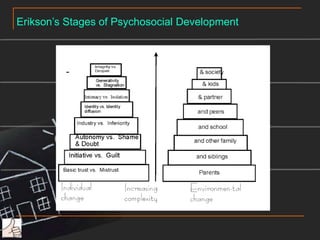
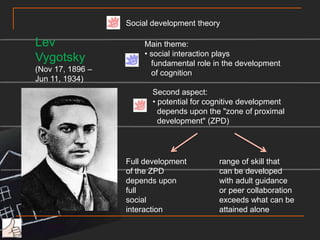
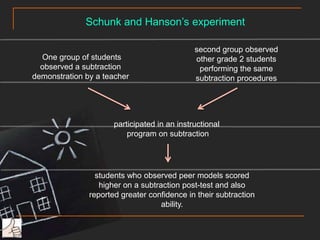
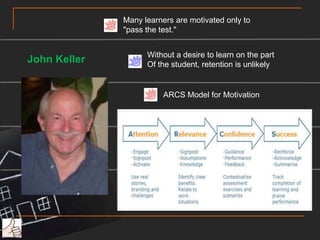
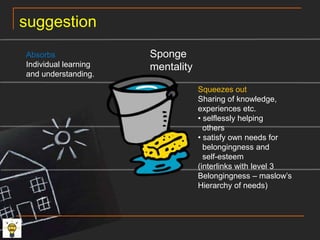
This document provides an overview and case scenario for an educational psychology course focusing on problem-based learning. It introduces the main characters of 11-year-old Andy, his family, and his teacher Ms. Wong. It then discusses several theories related to motivation, self-efficacy, social support, and learning including the works of Erikson, Pavlov, Bandura, Vygotsky, and Maslow. The document suggests applying principles like modeling, social persuasion, and addressing different levels of needs to support student learning and motivation. It also includes short reflections from two students on learning from others and the importance of a teacher in student development.