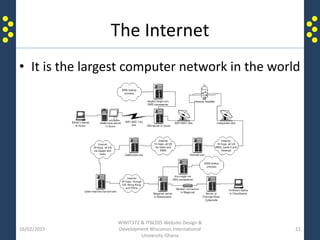
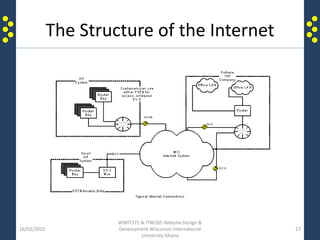
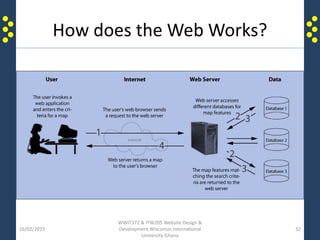
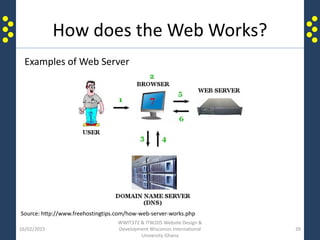
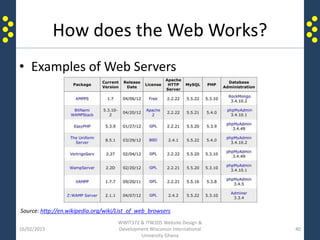
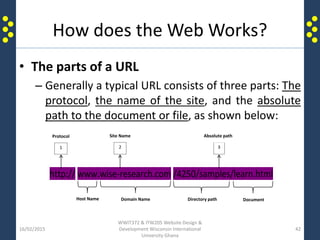
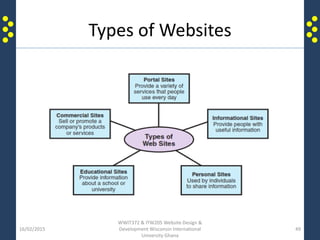
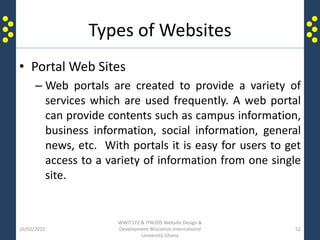
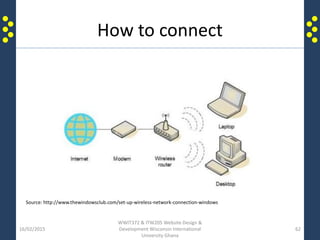
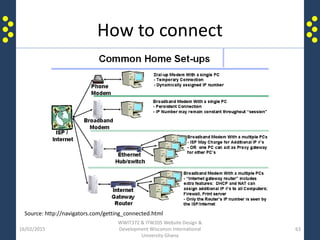
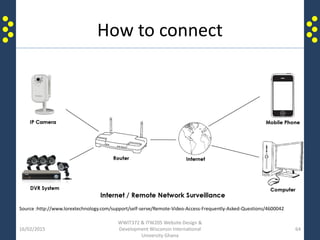
The document provides an introduction to the internet and the world wide web for a course on website design and development. It discusses the history of the internet and how it originated as a military network before becoming publicly available. It defines key terms like web browser, website, and homepage. It explains that the internet is the underlying infrastructure of hardware, while the world wide web is the software comprising hyperlinked web pages. The internet connects millions of computers and networks globally through protocols like TCP/IP, while the web is governed by HTTP and links files and documents stored on various computers.