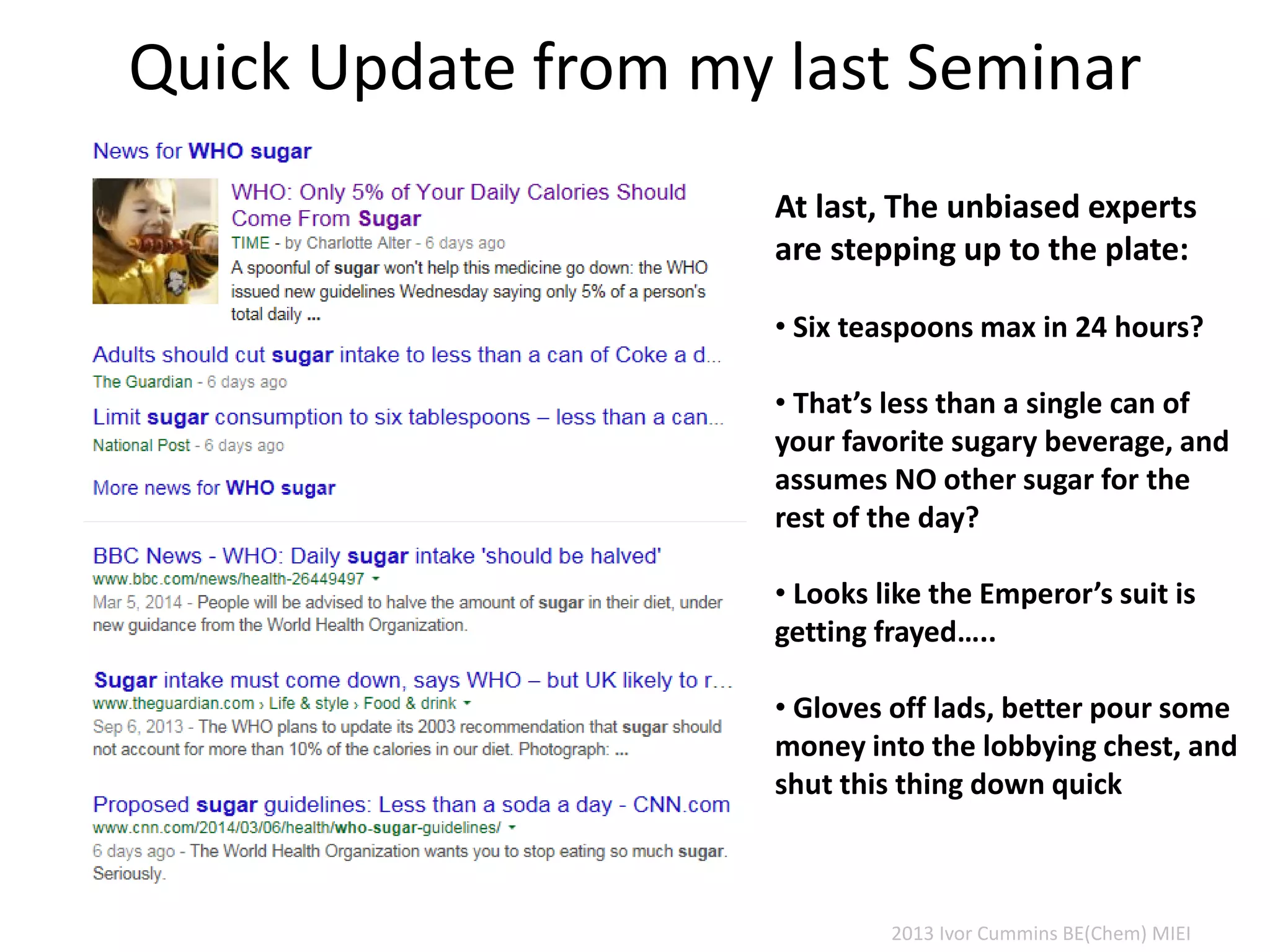
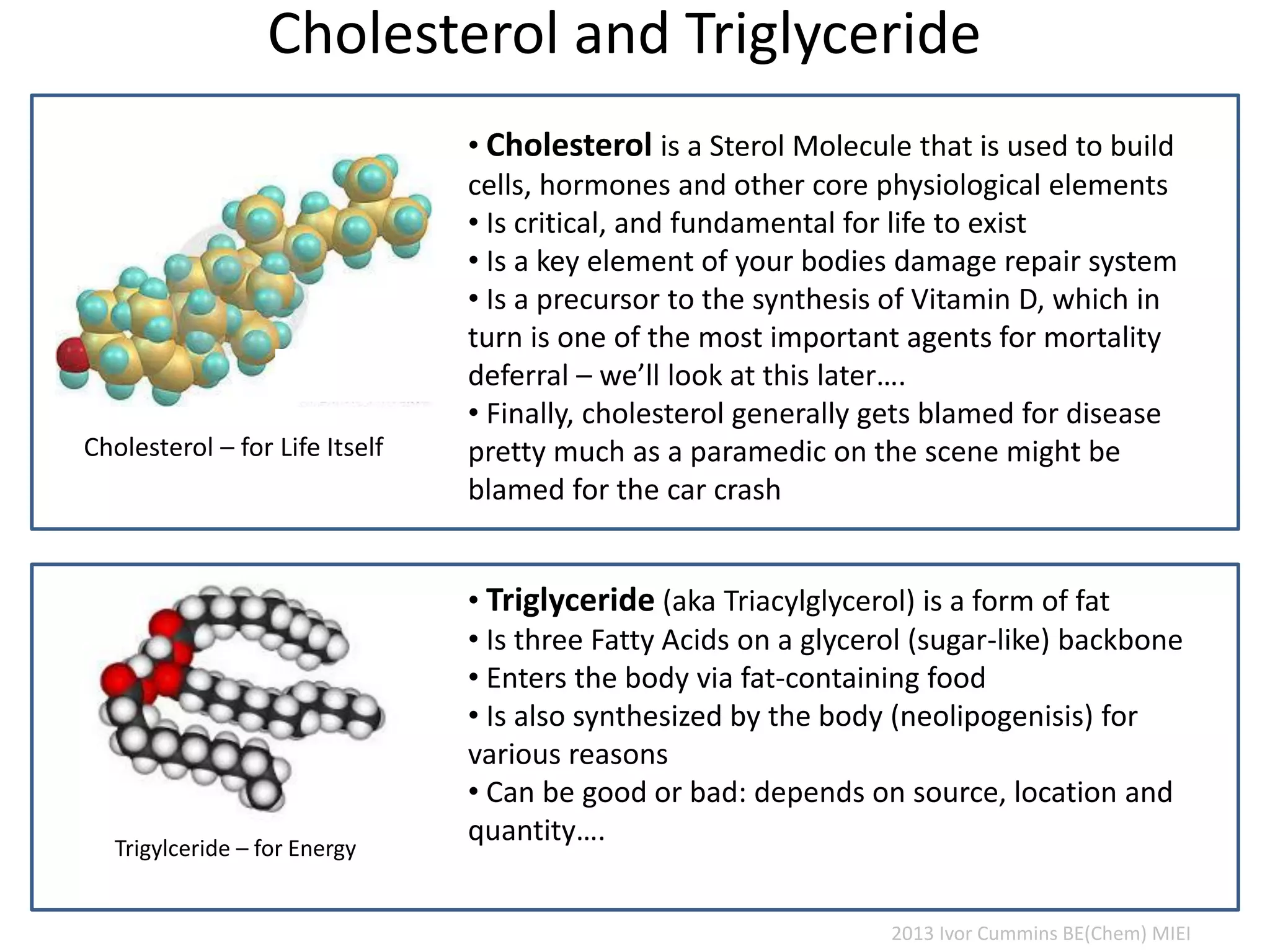
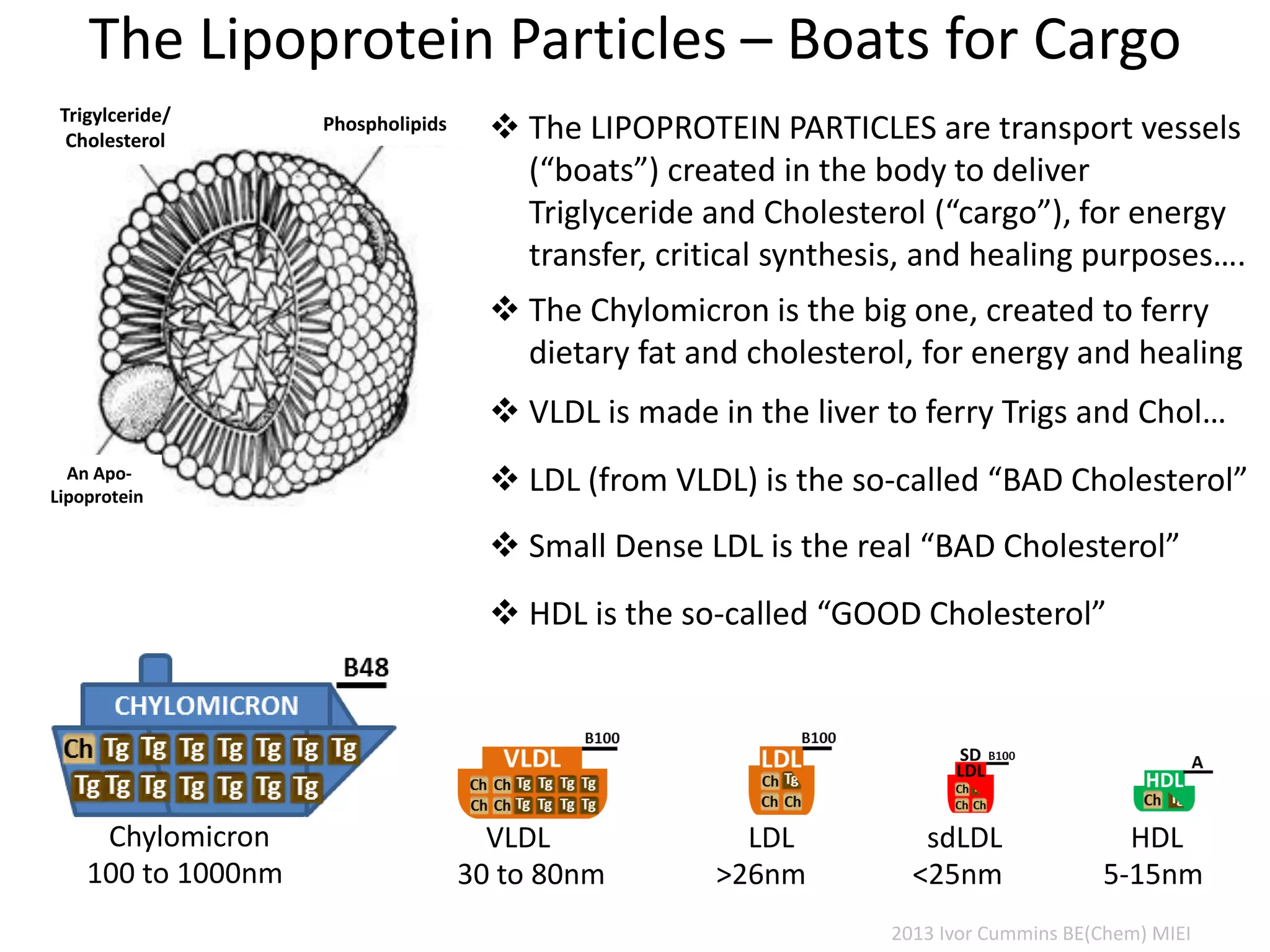
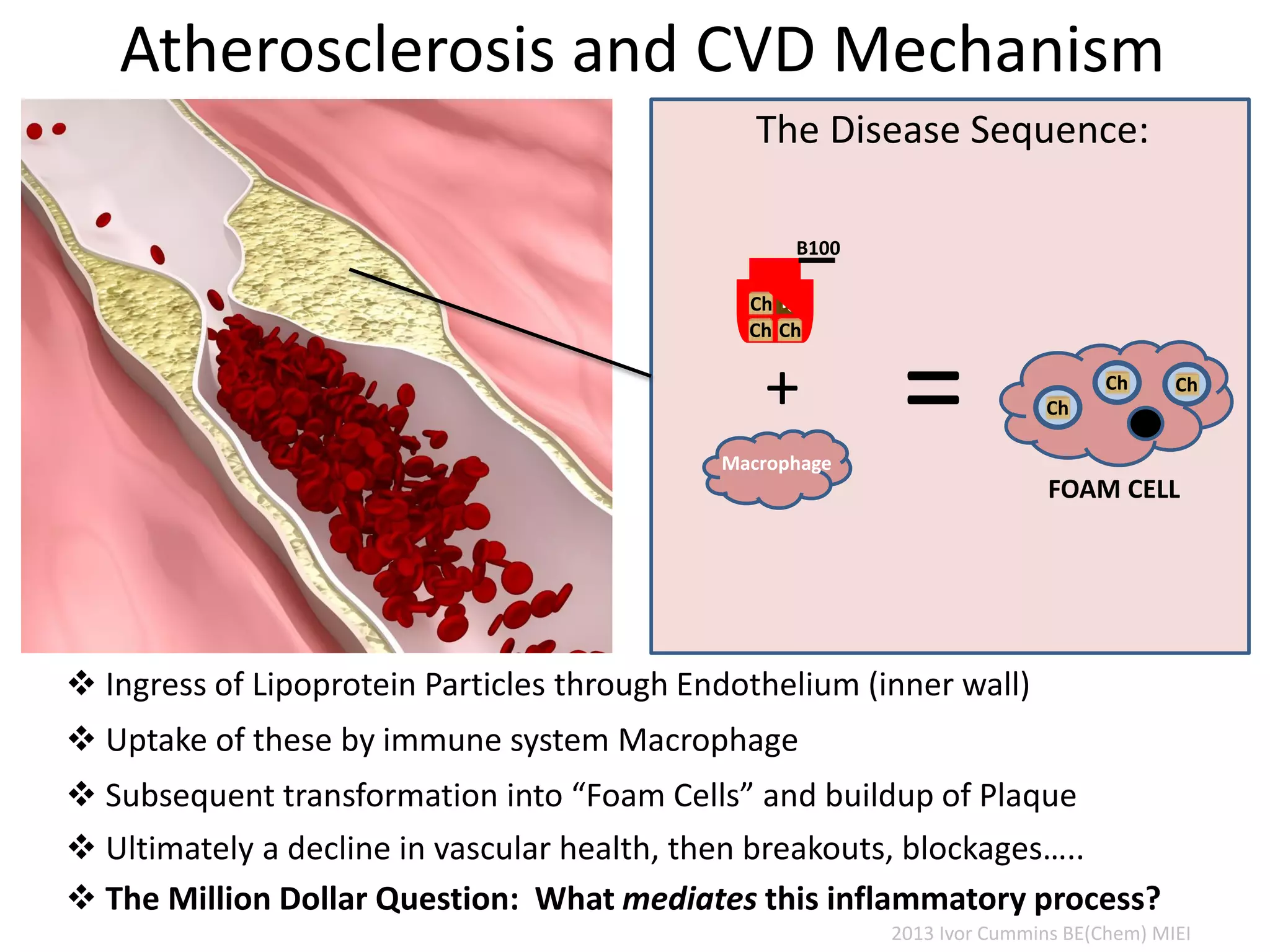
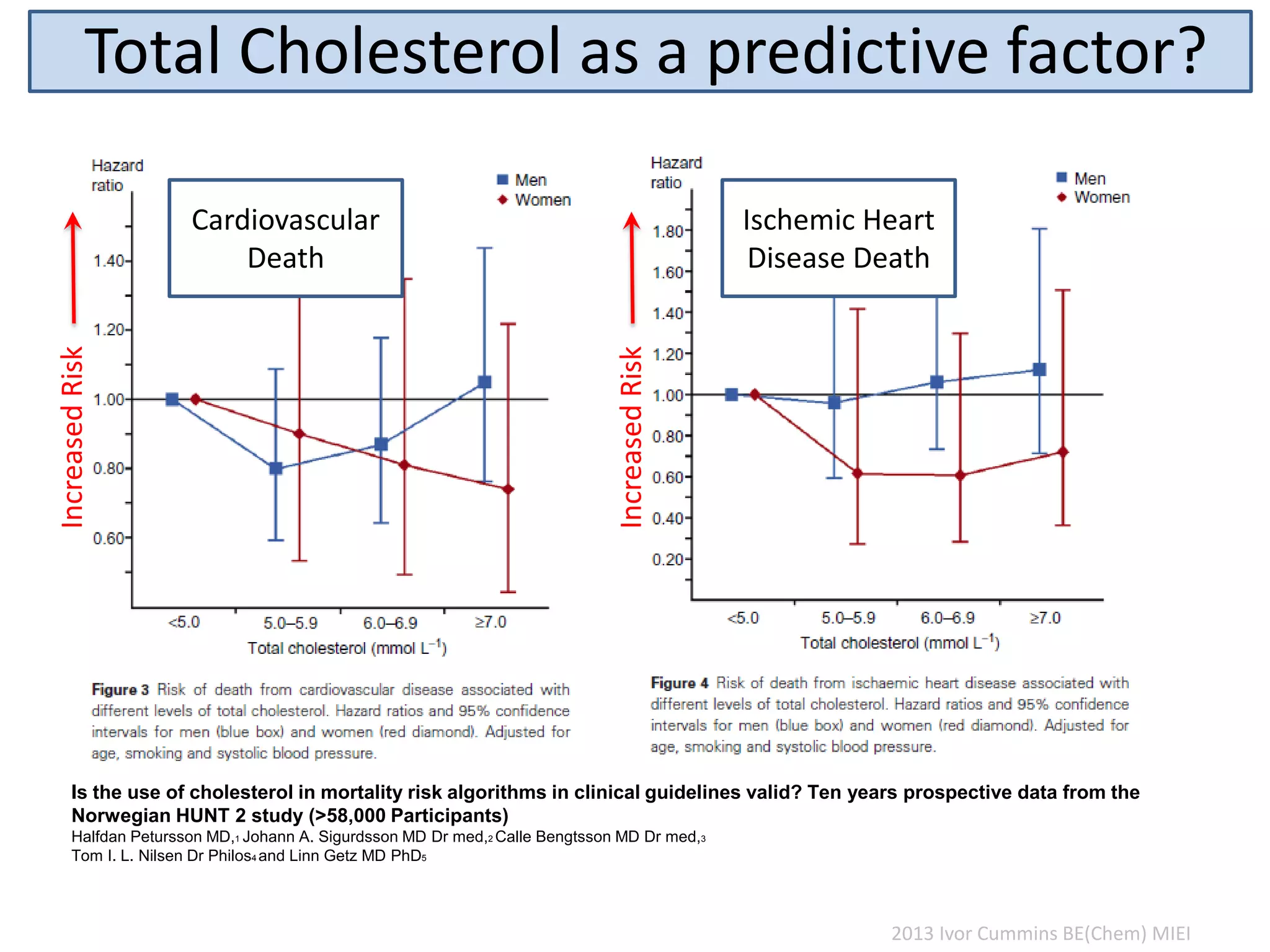
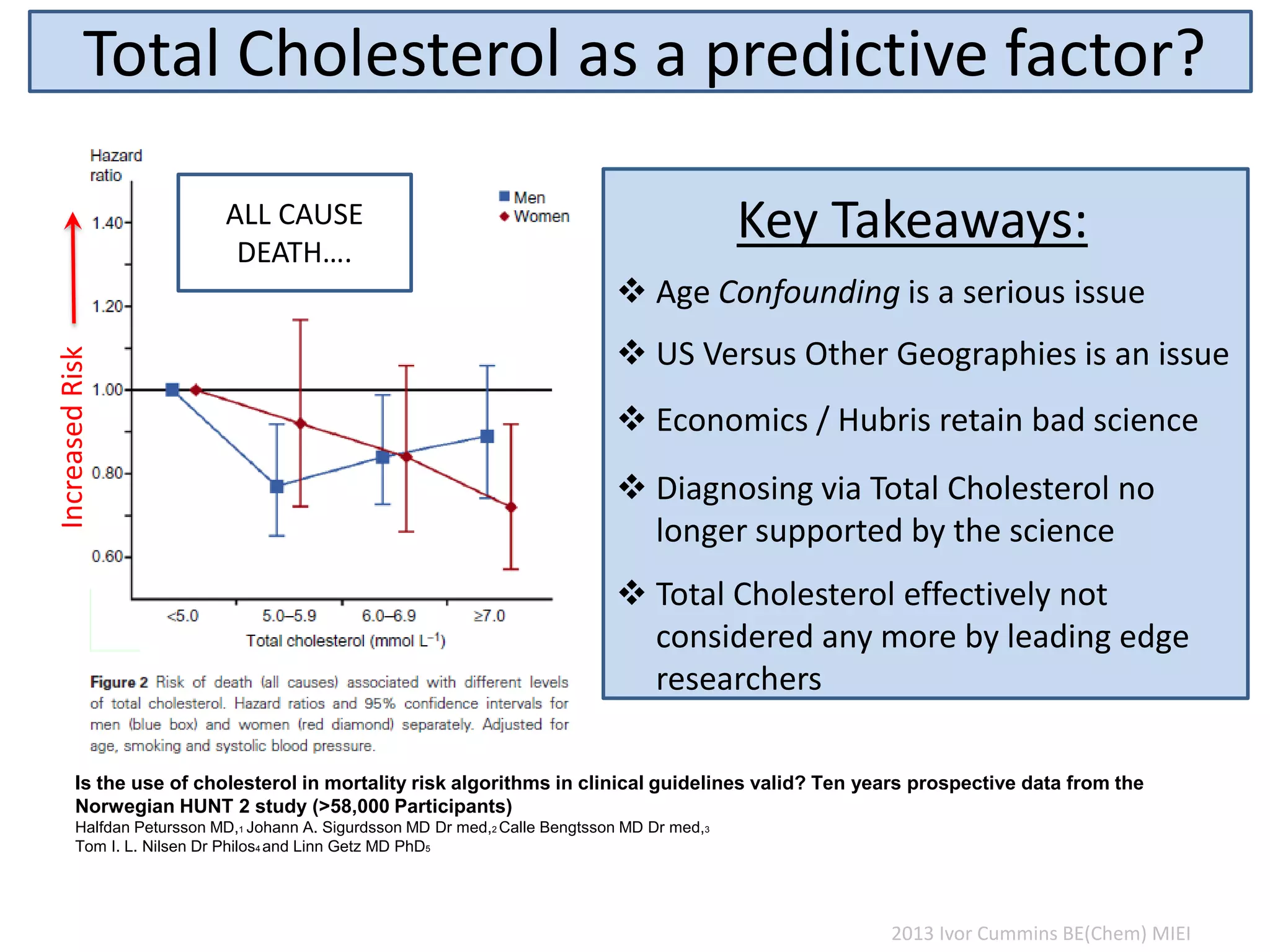
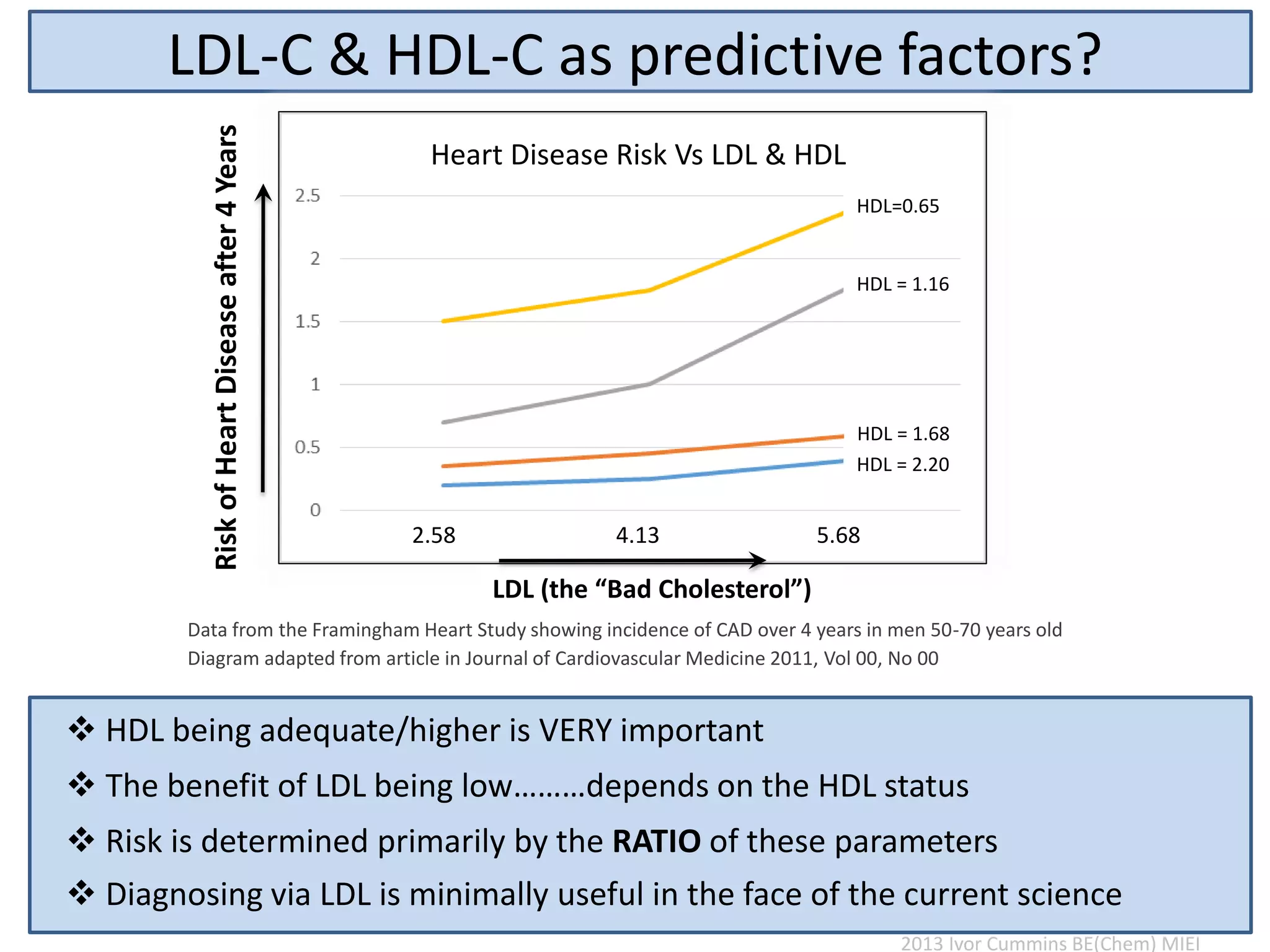
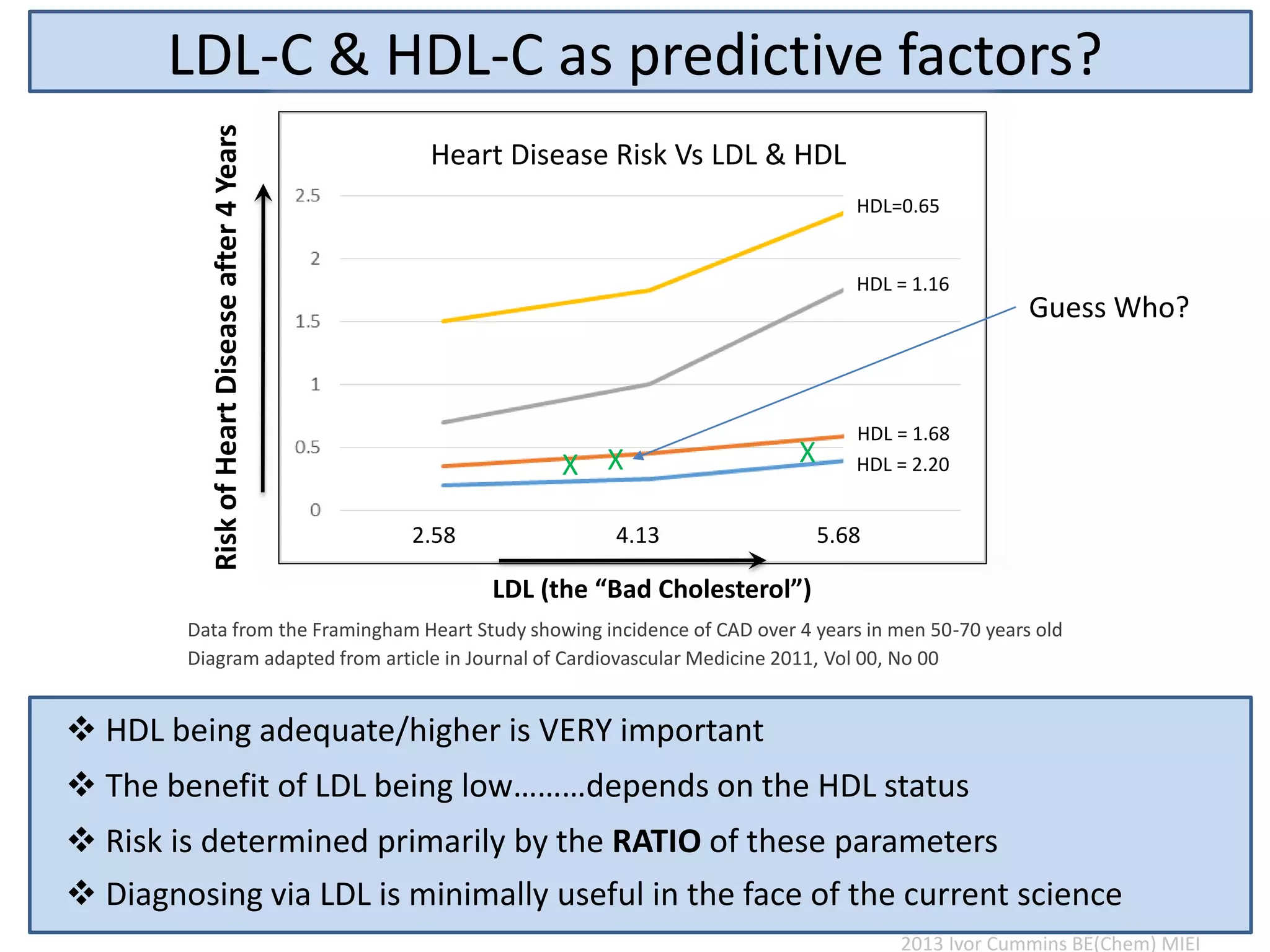
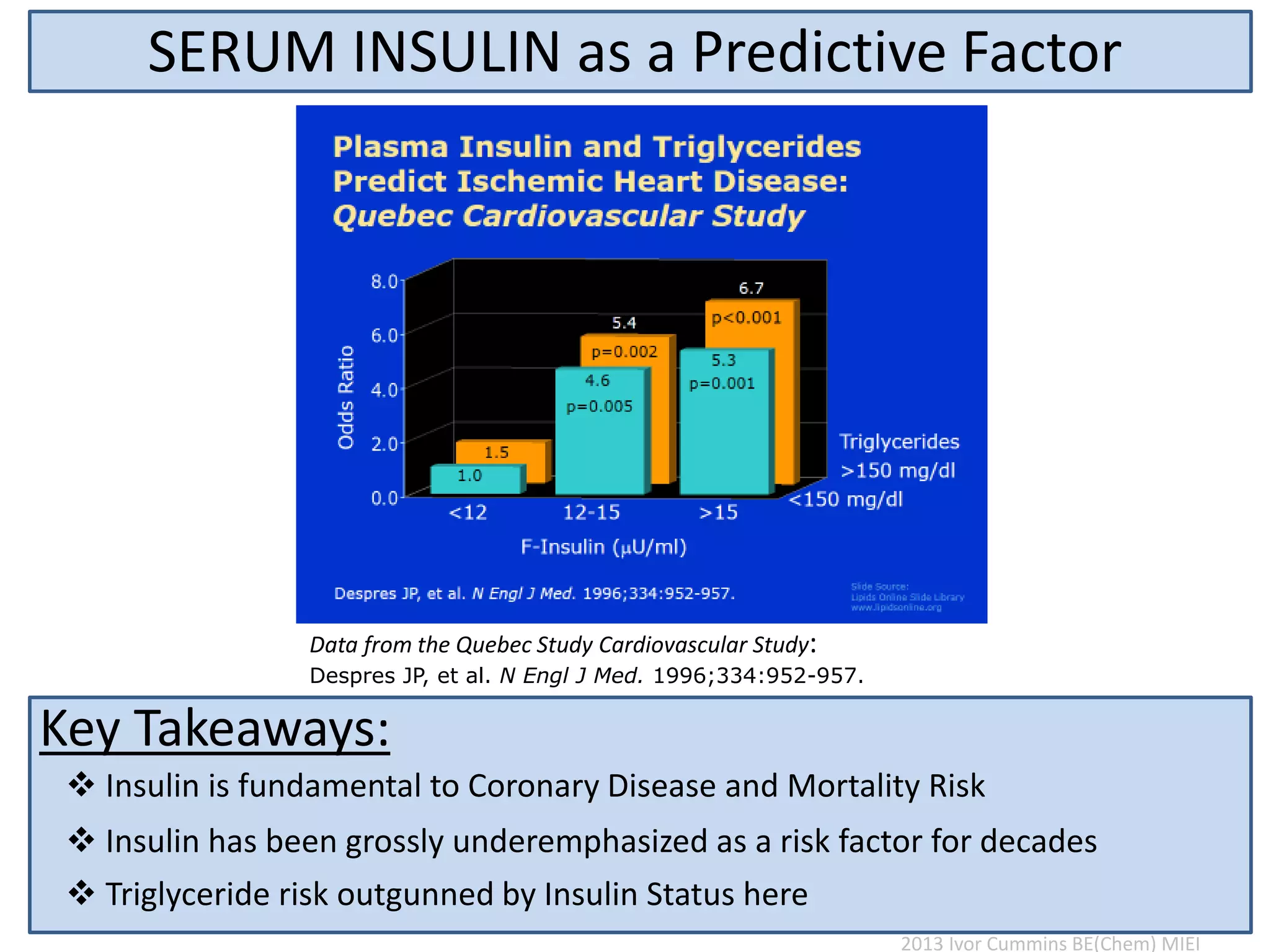
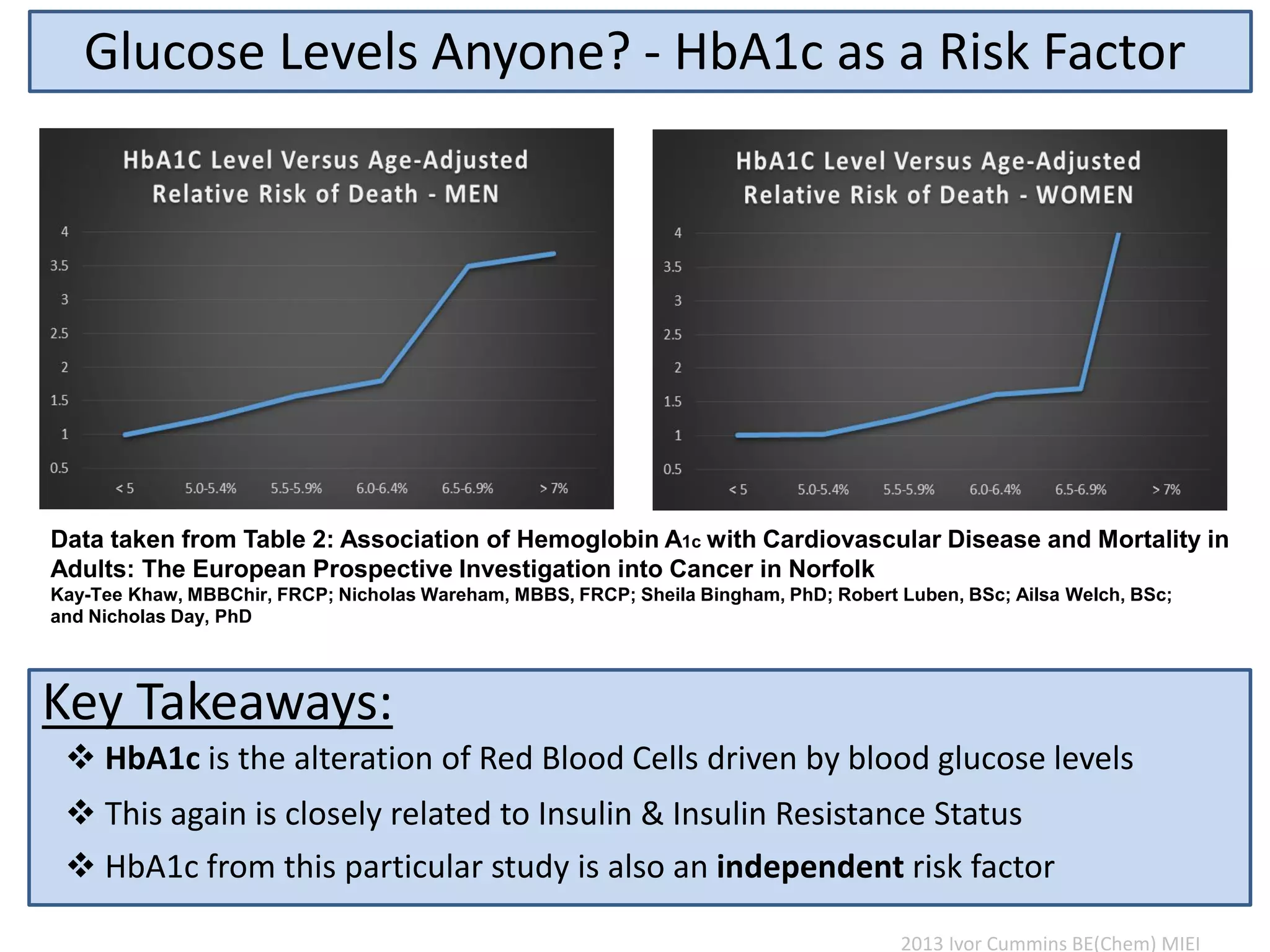
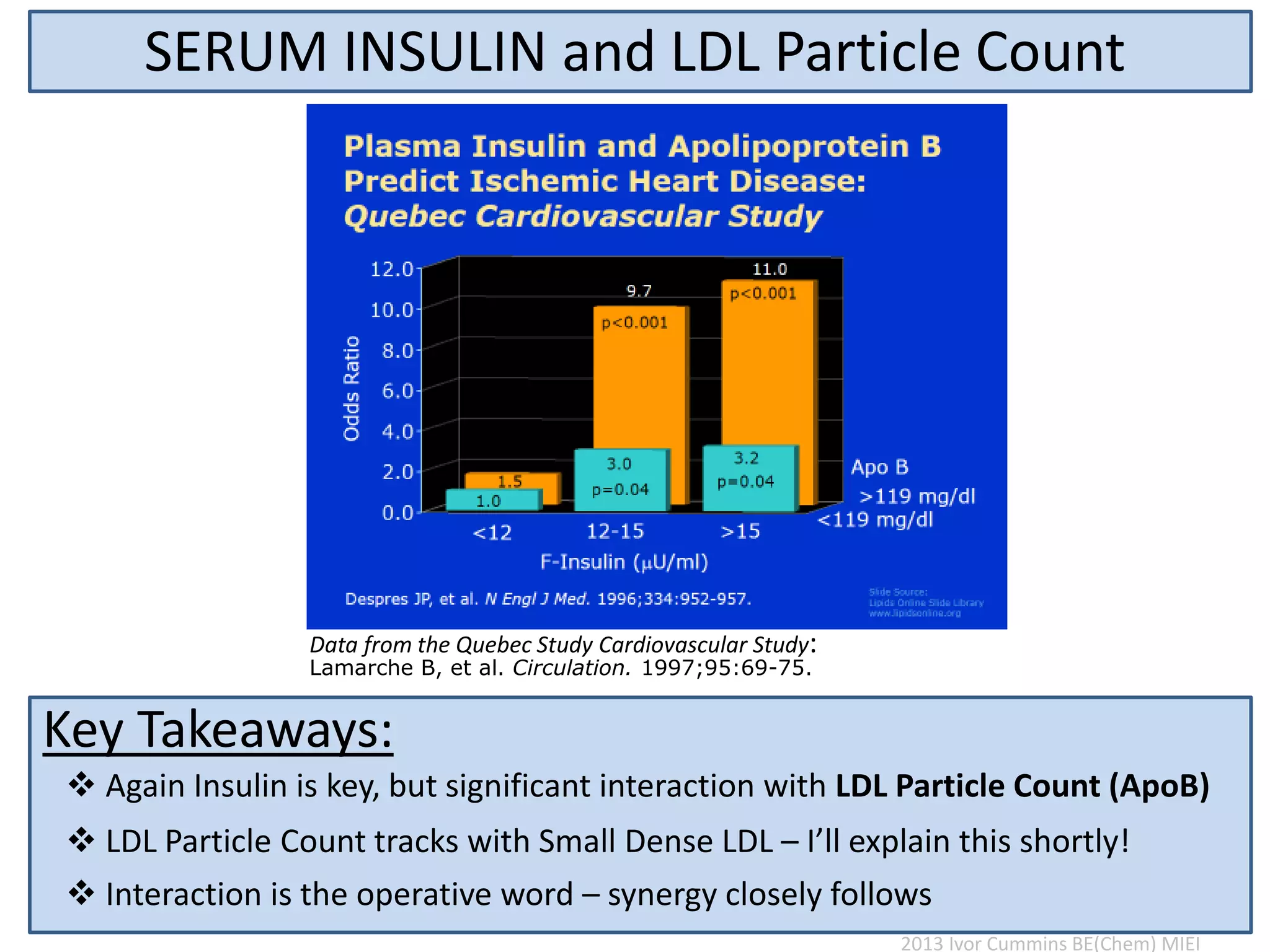
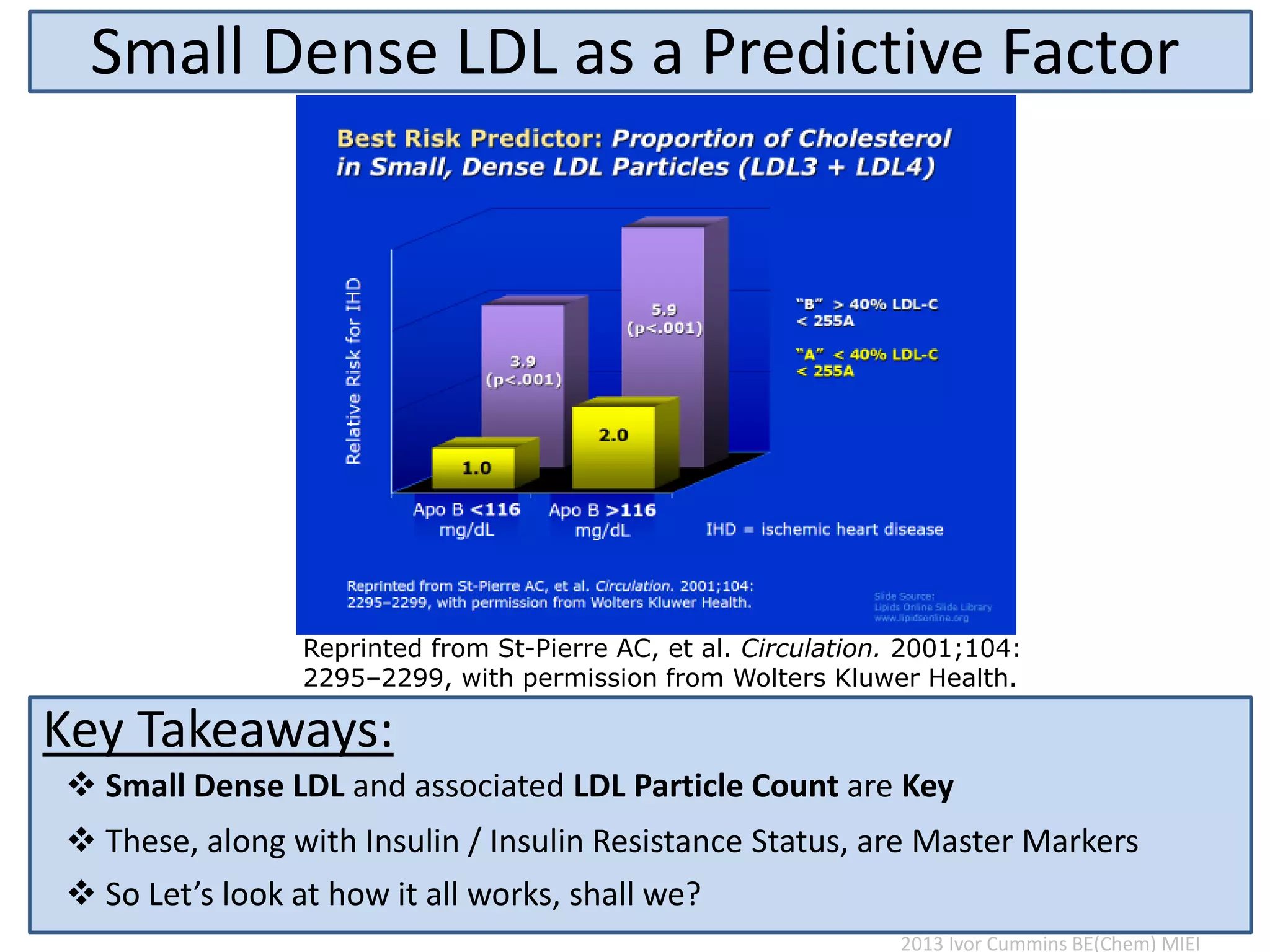
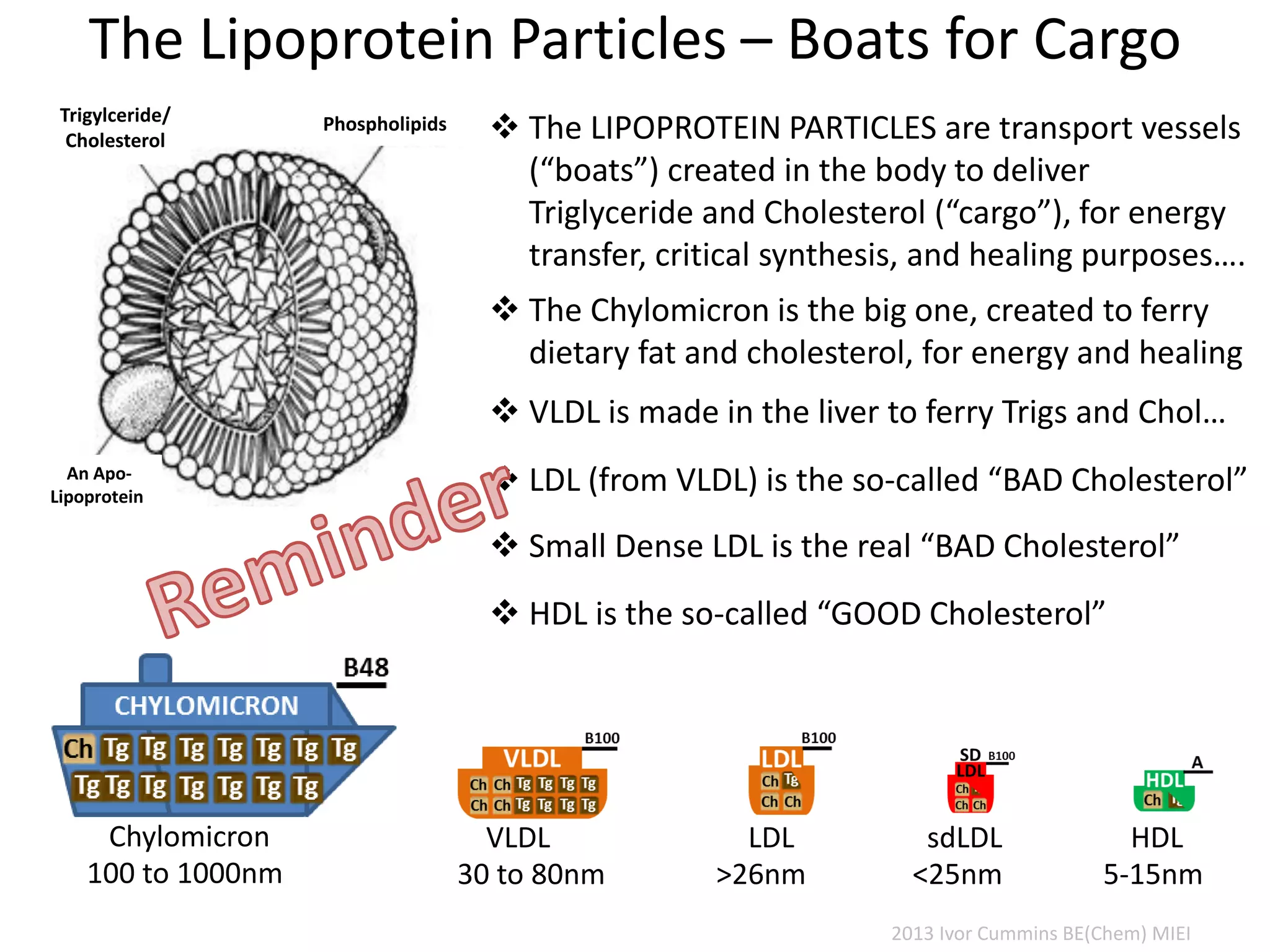
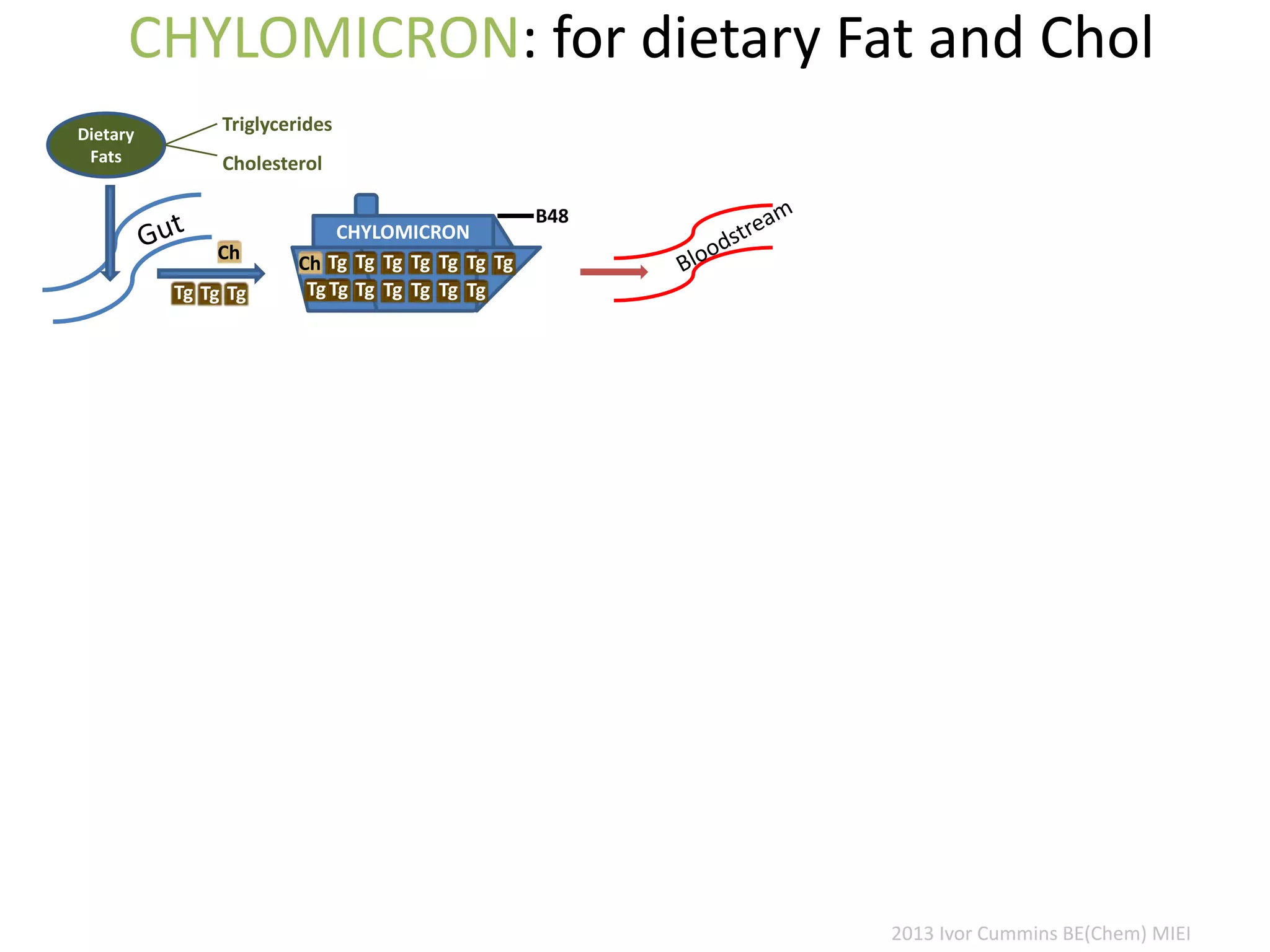
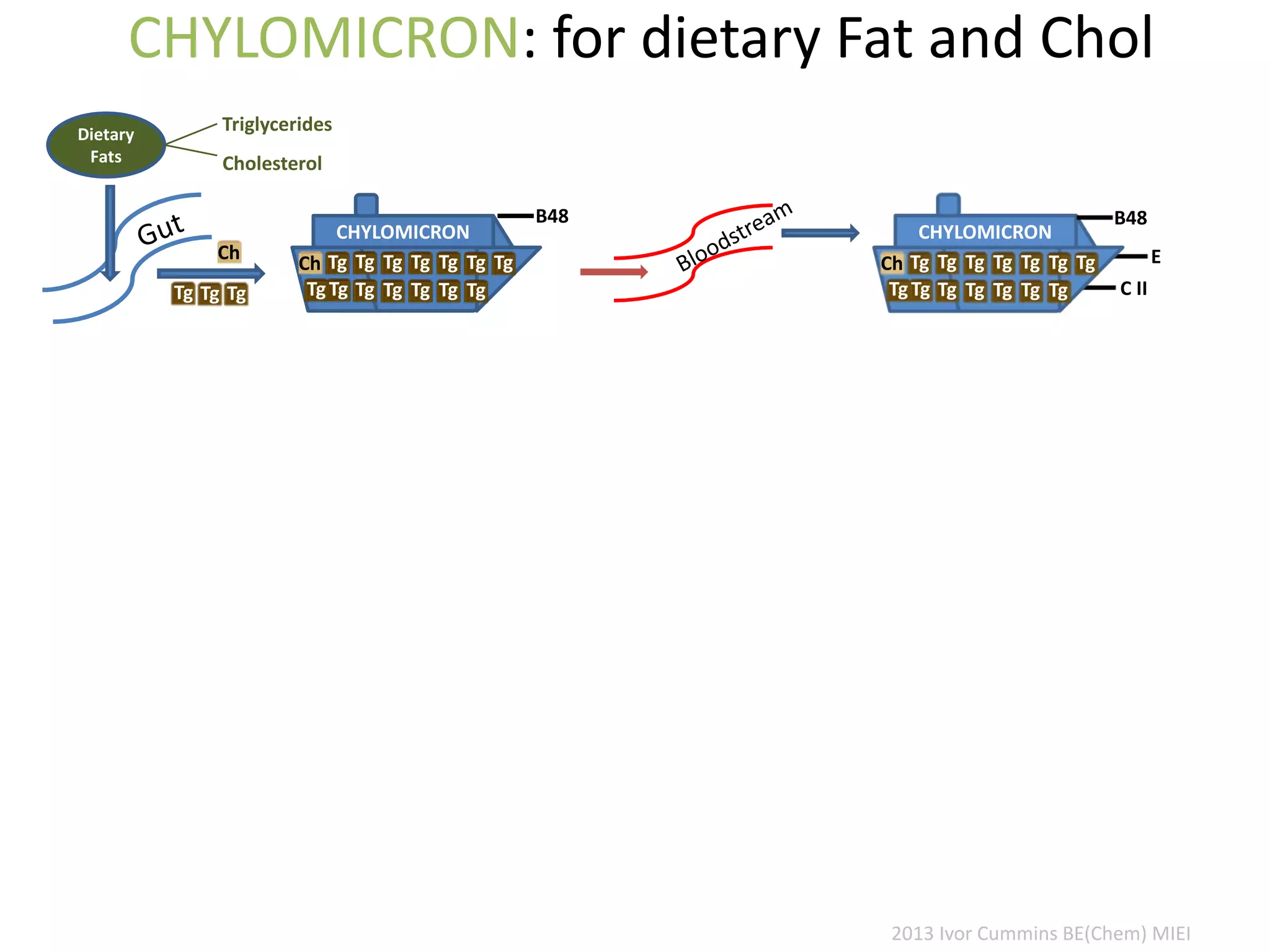
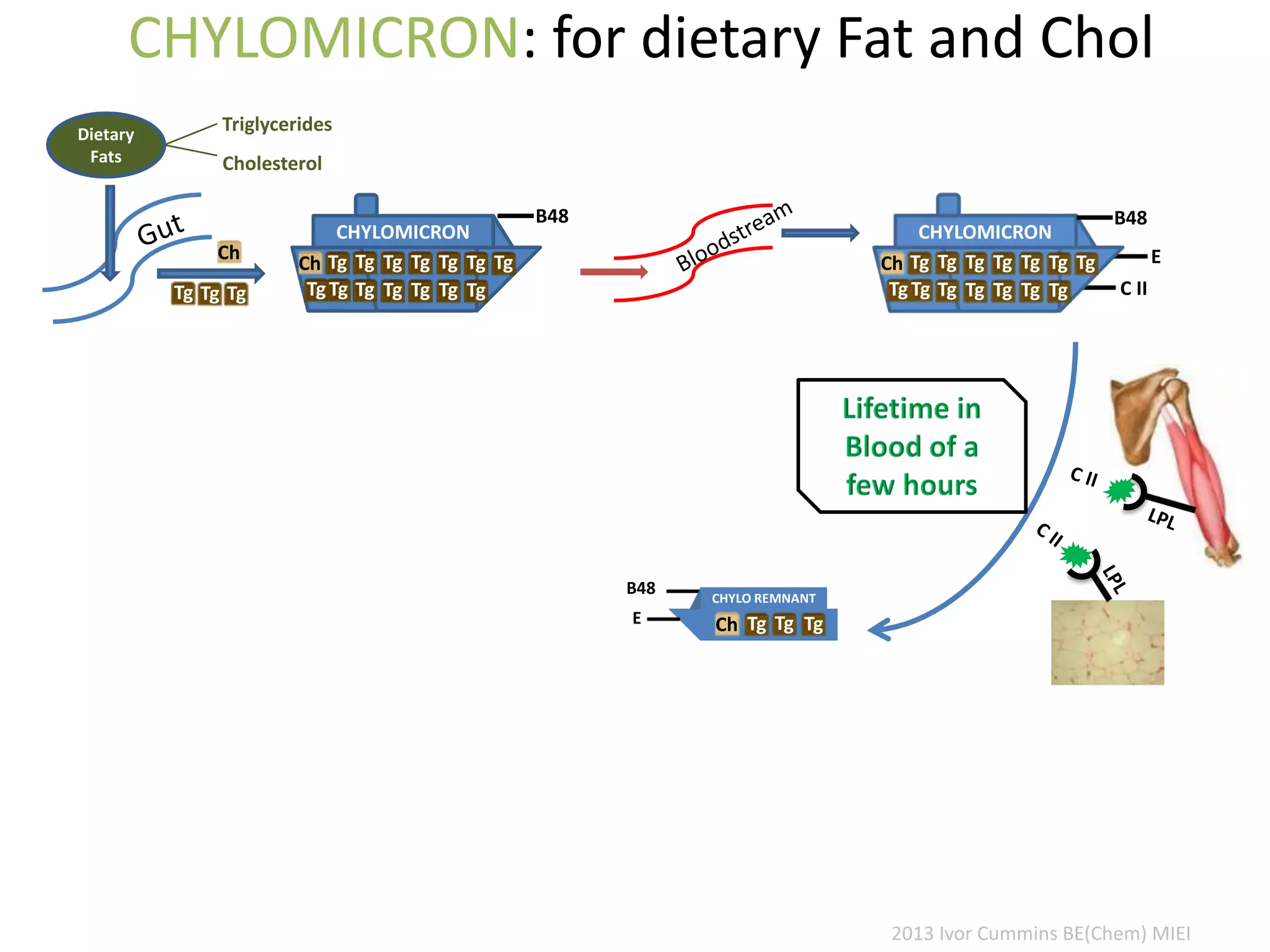
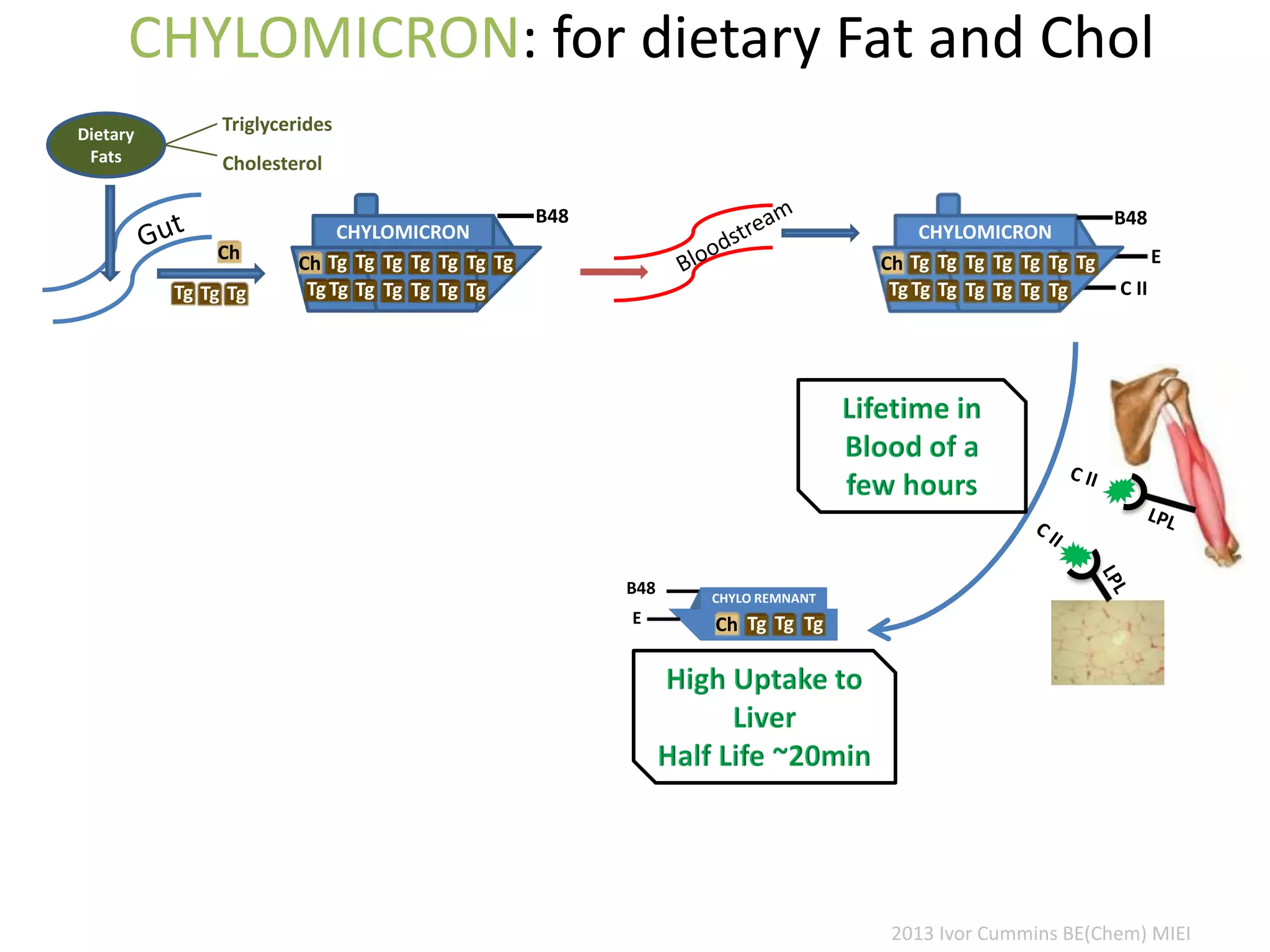
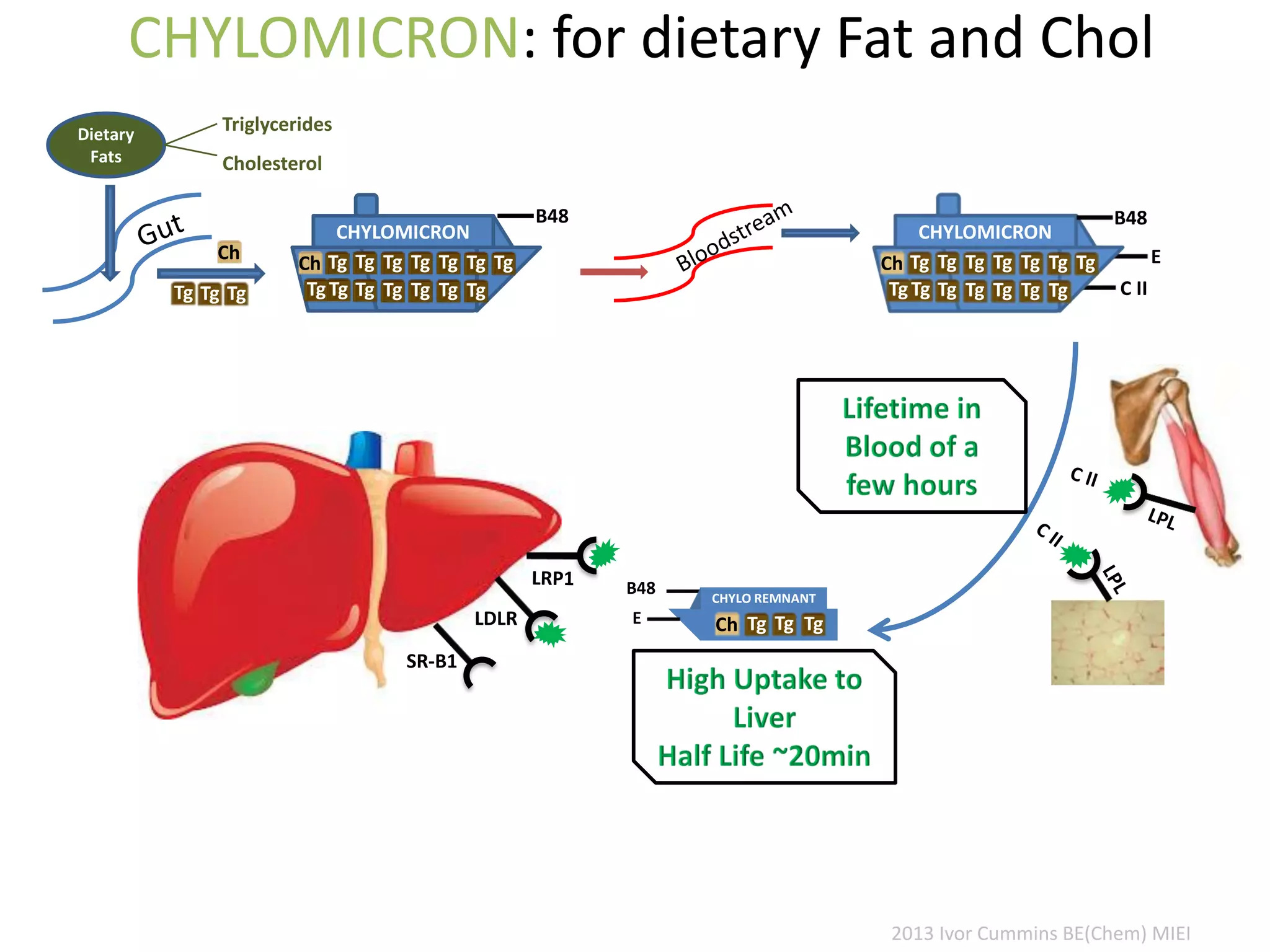
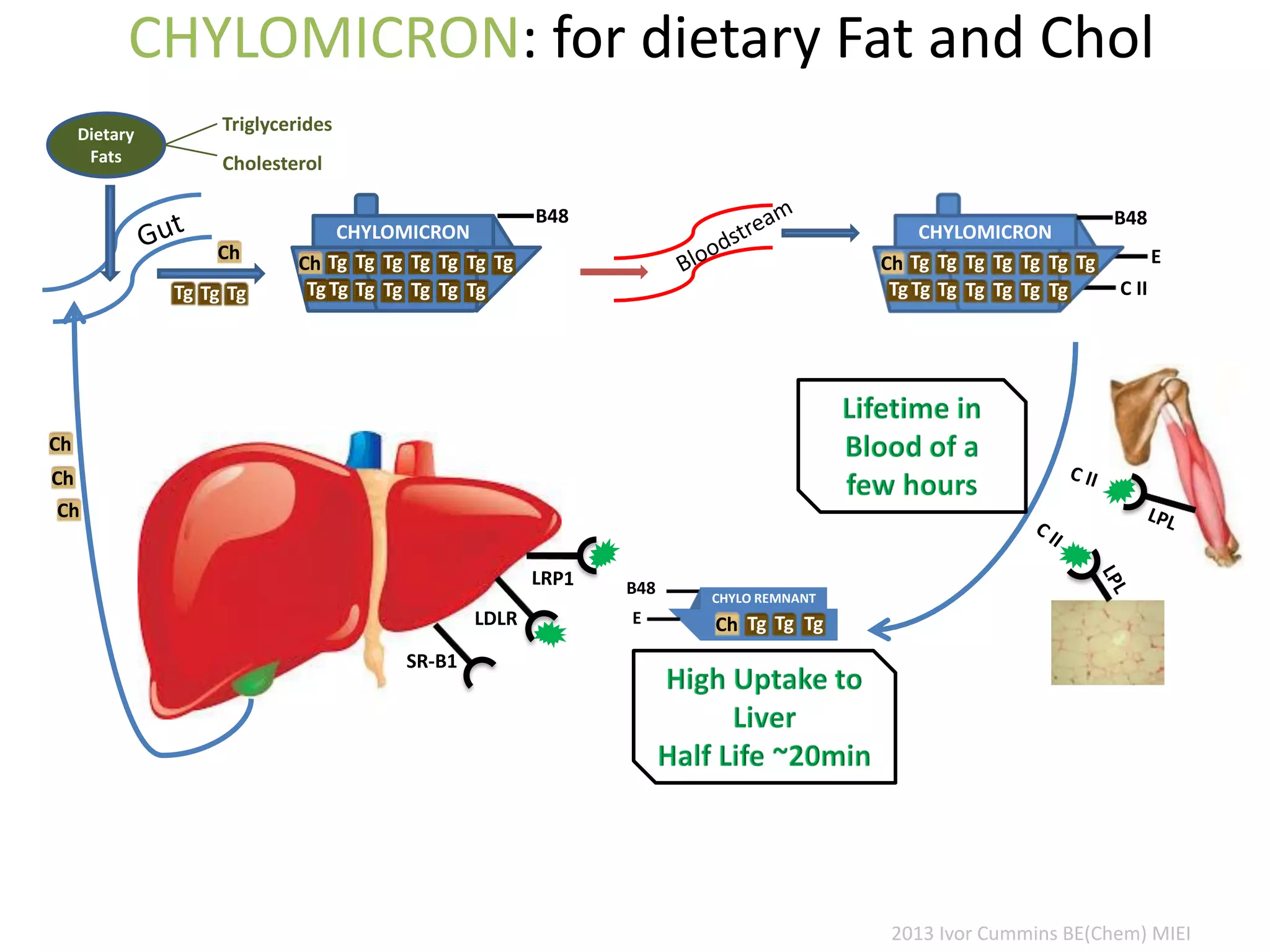
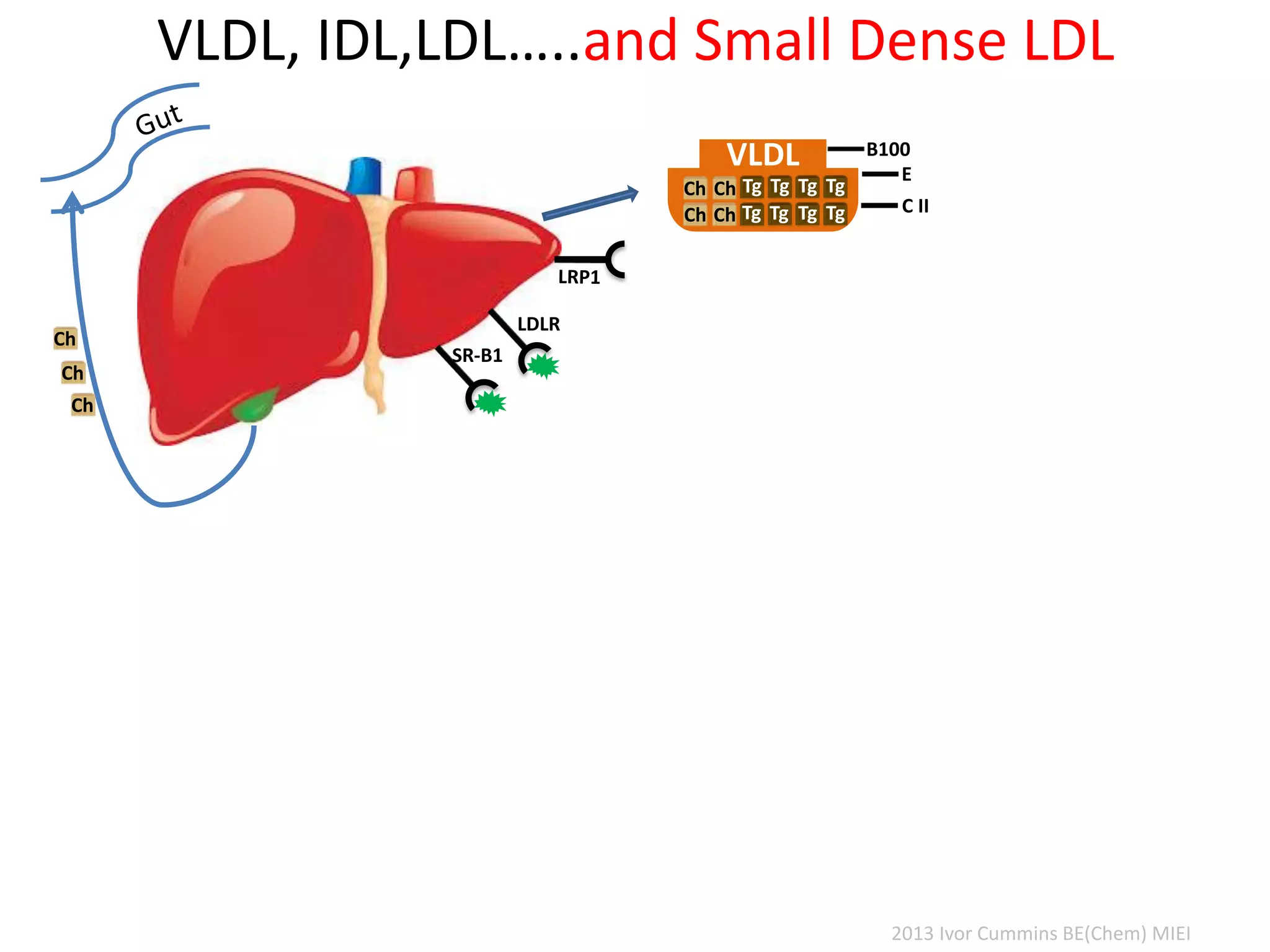
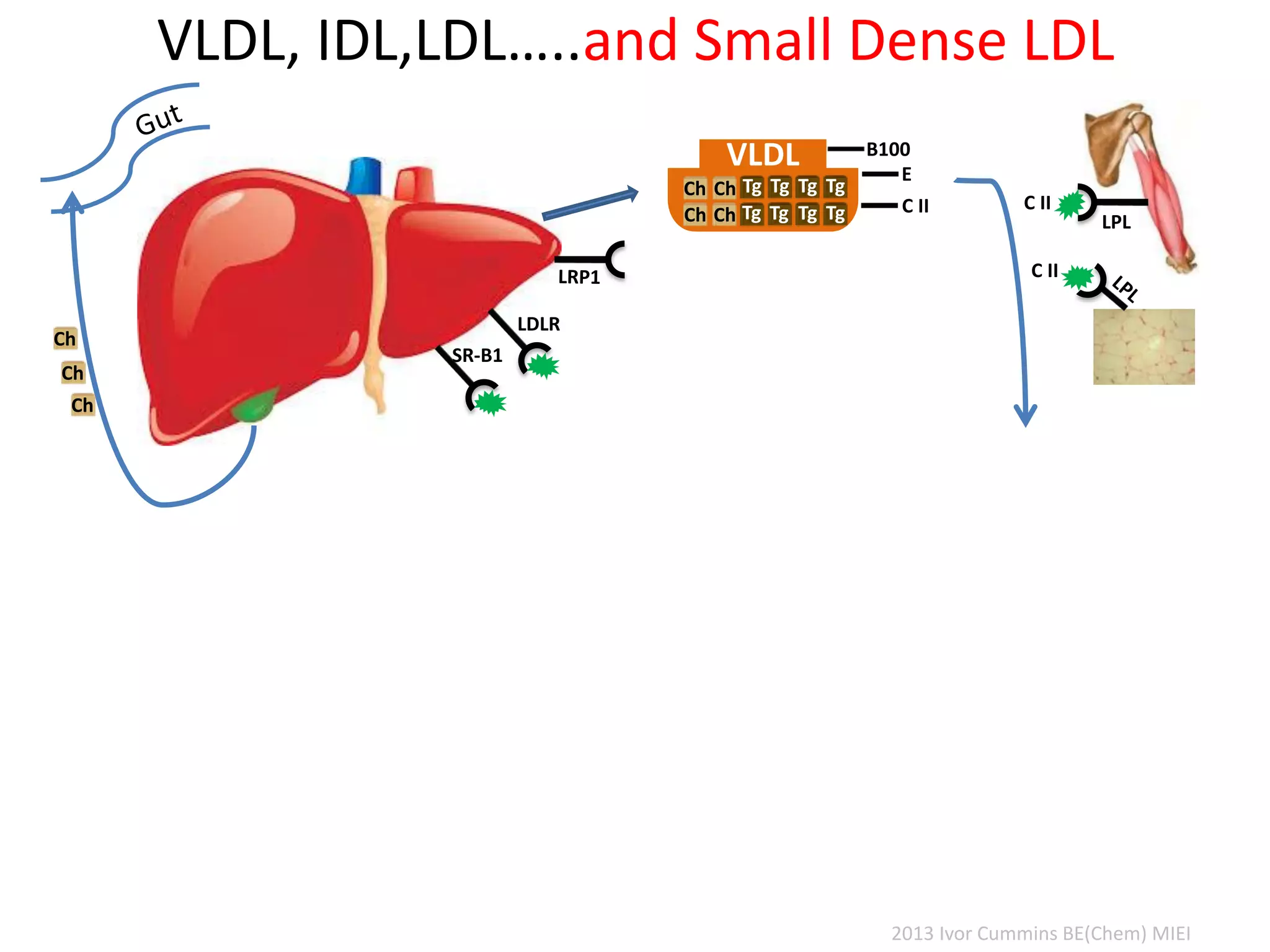
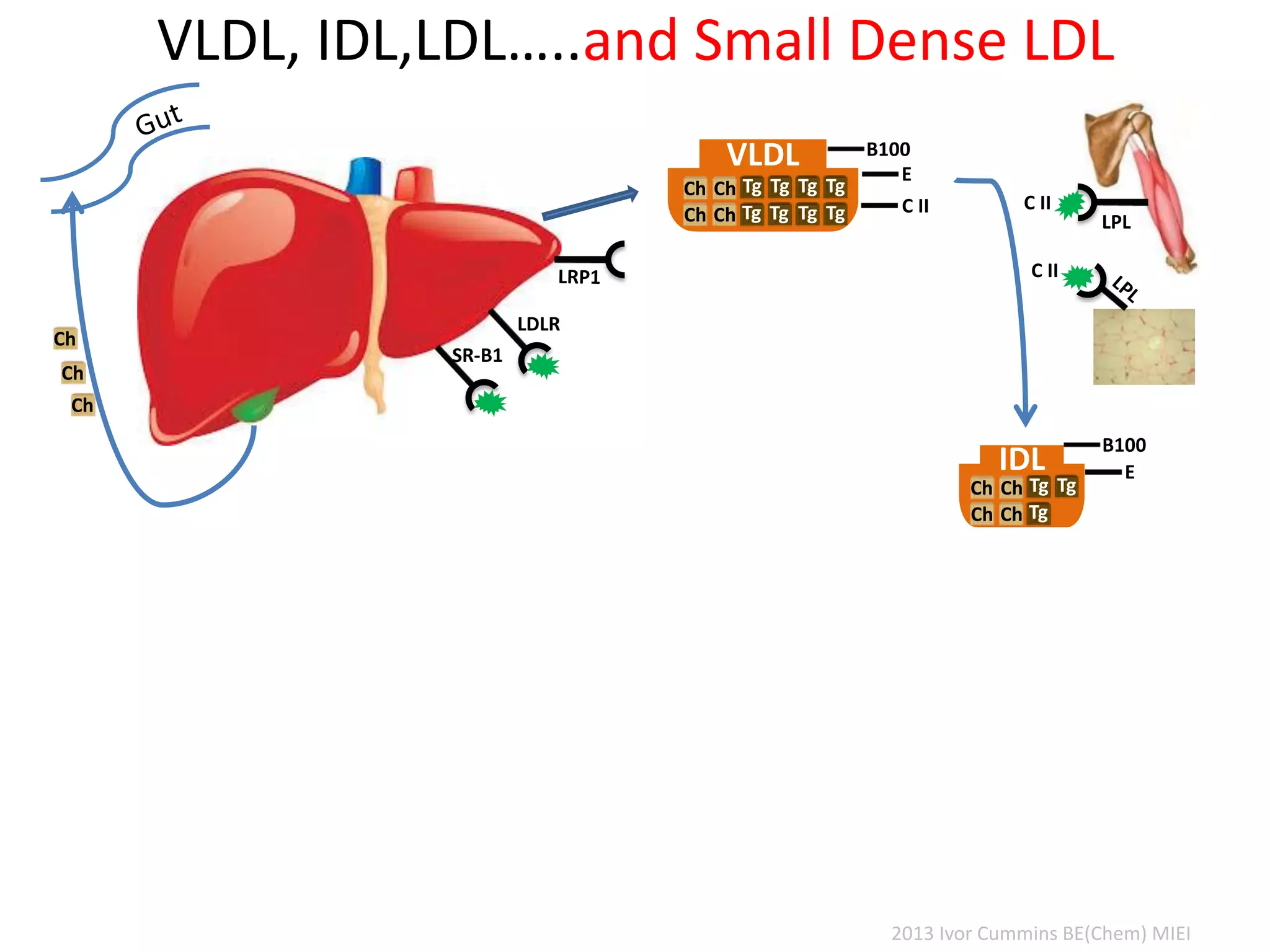
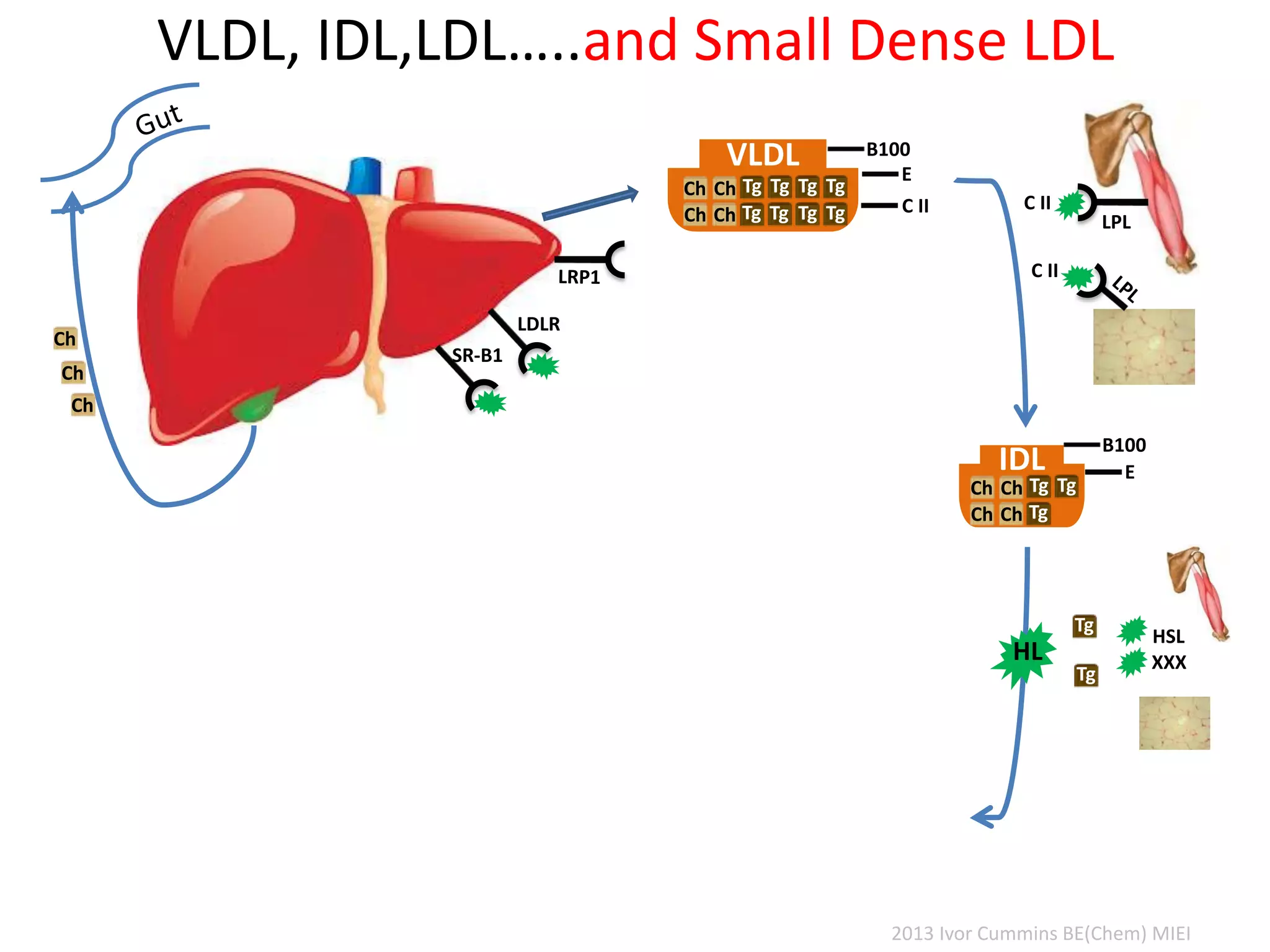
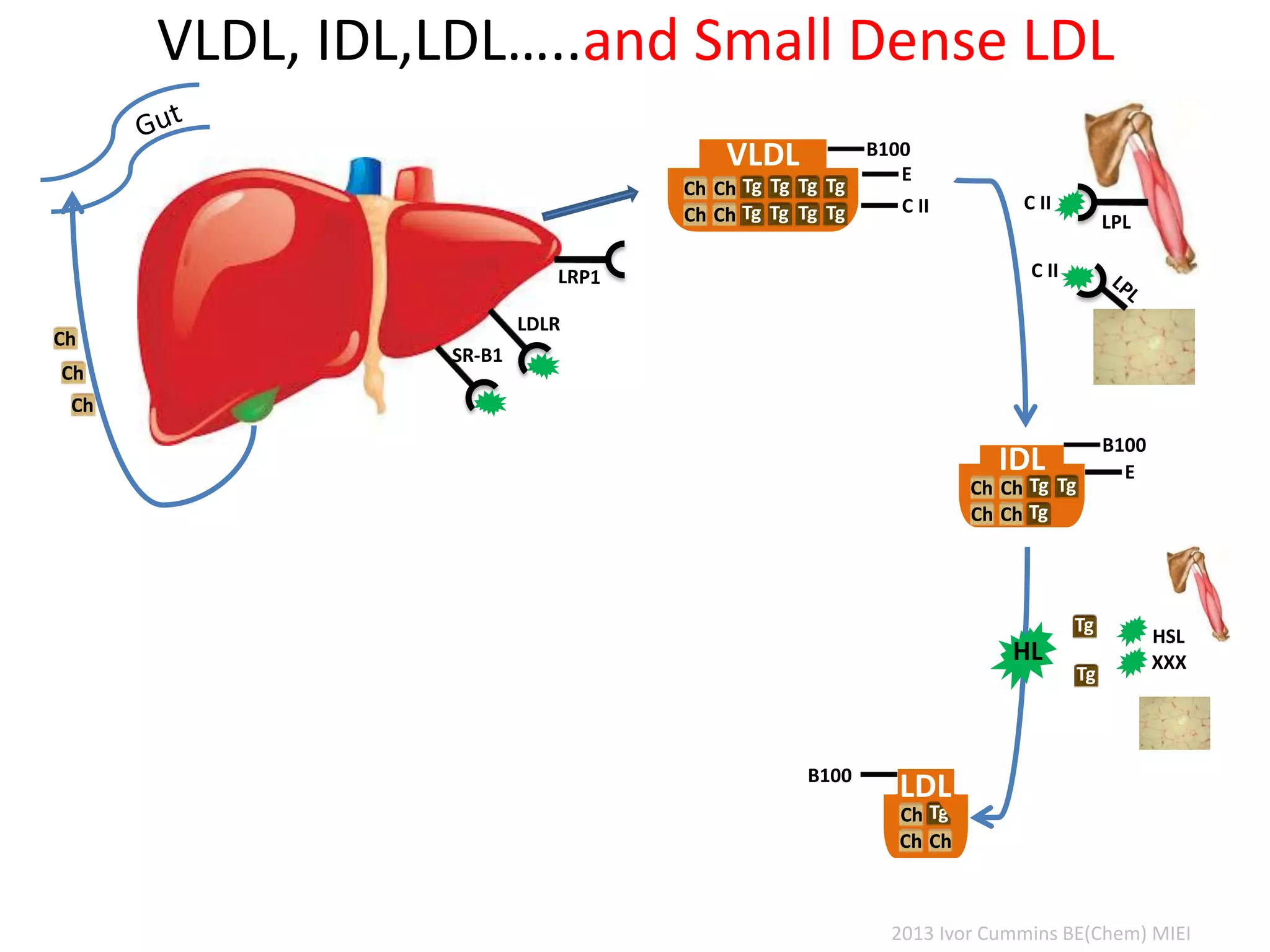
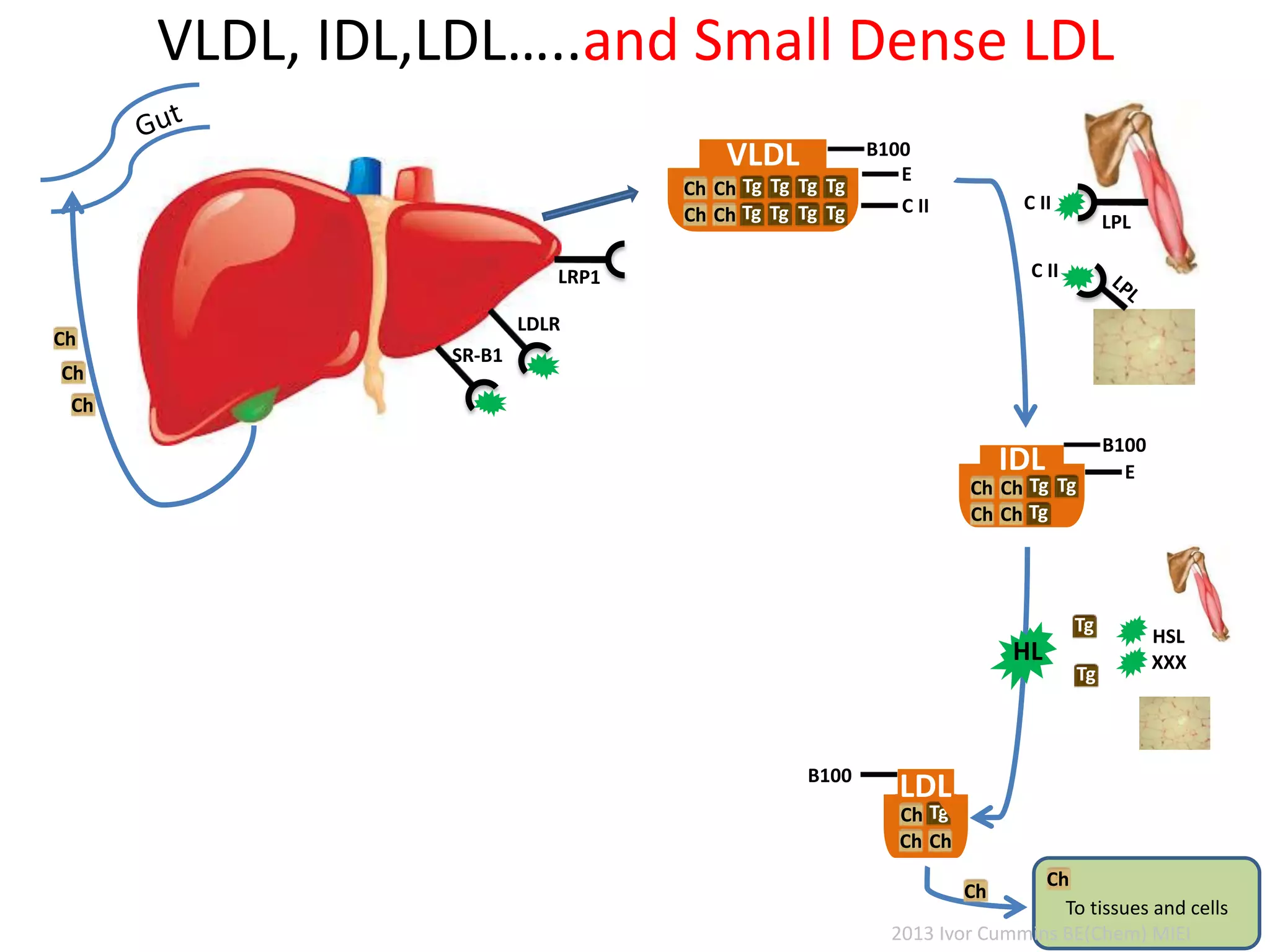
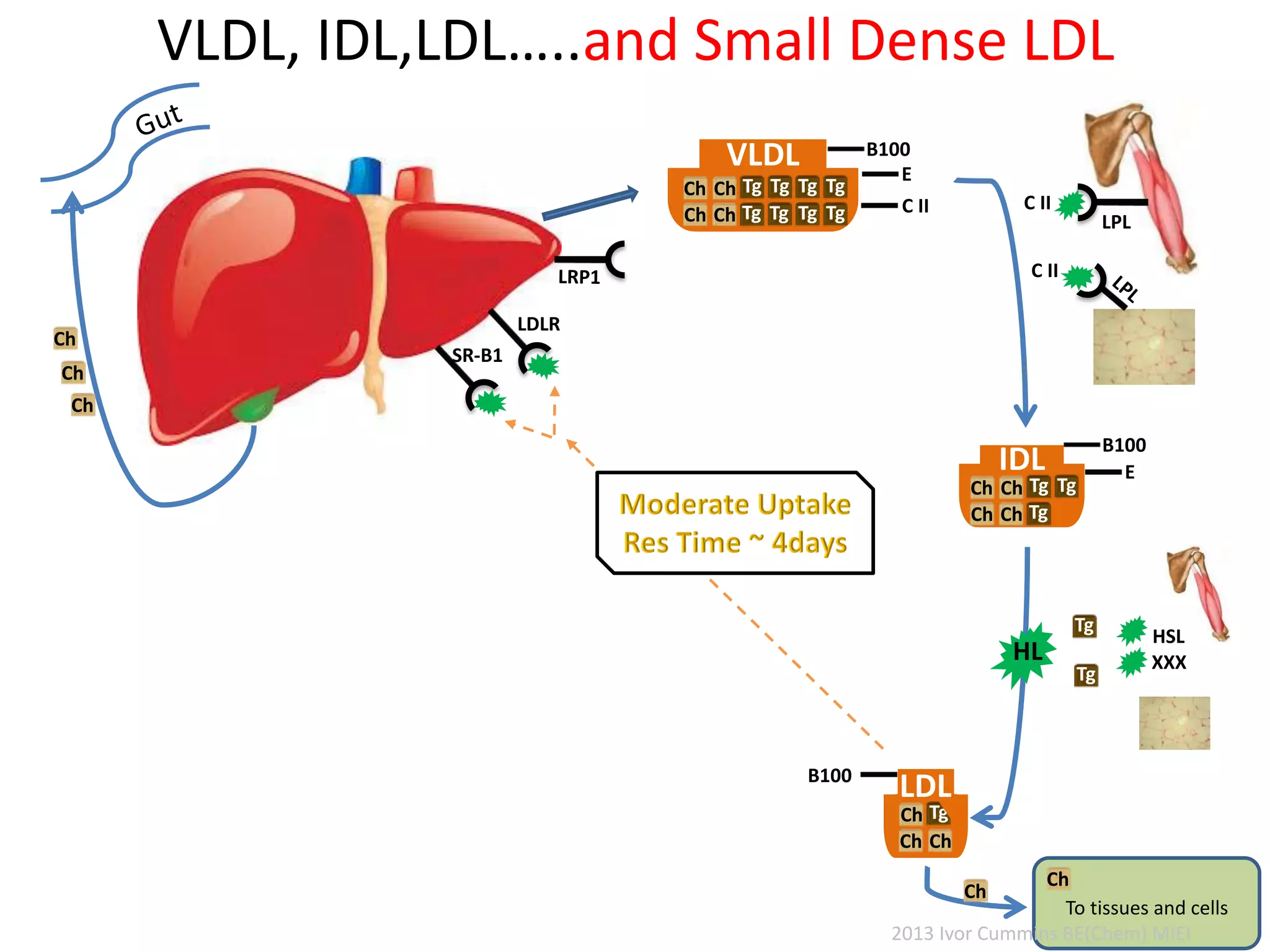
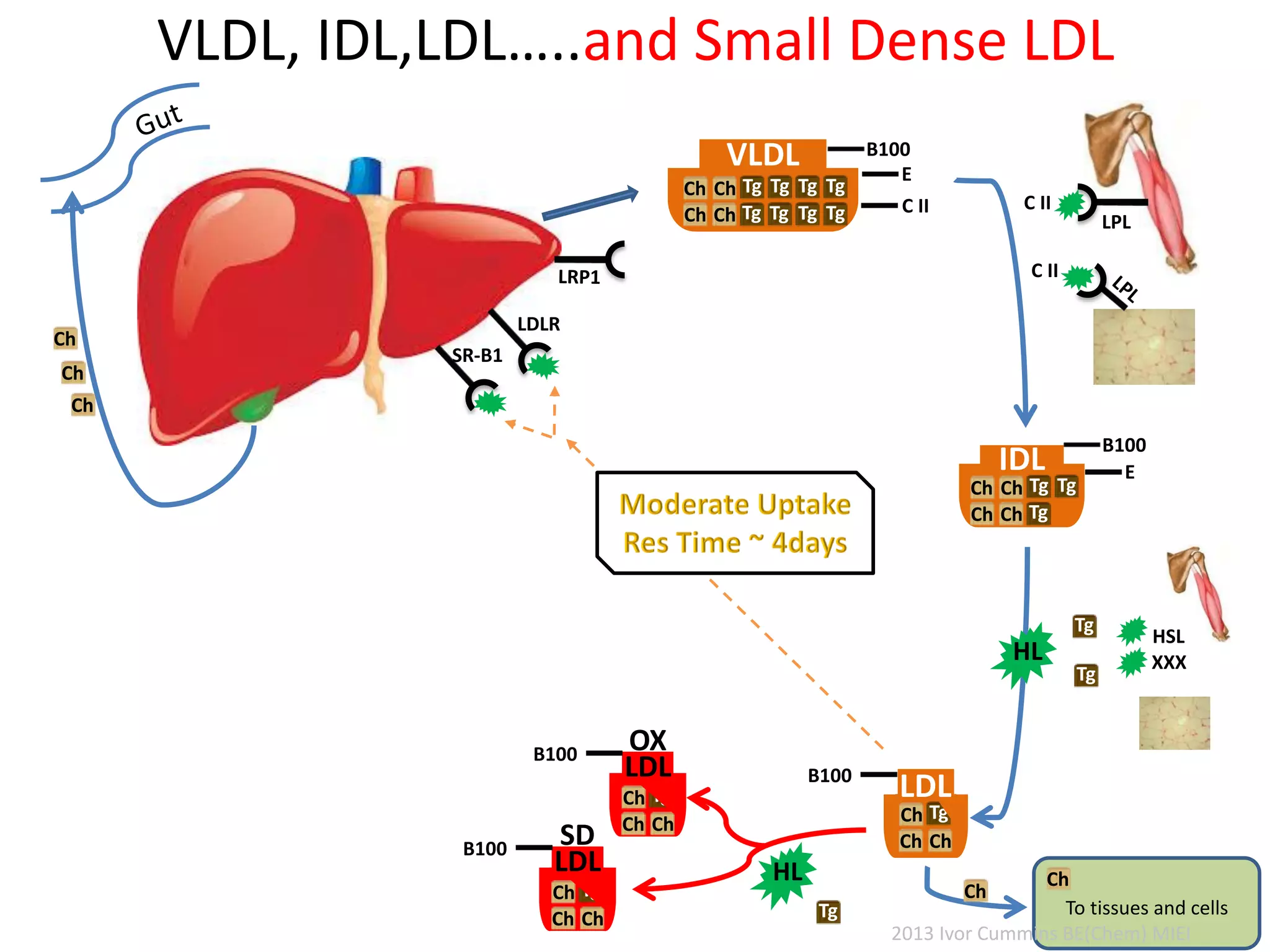
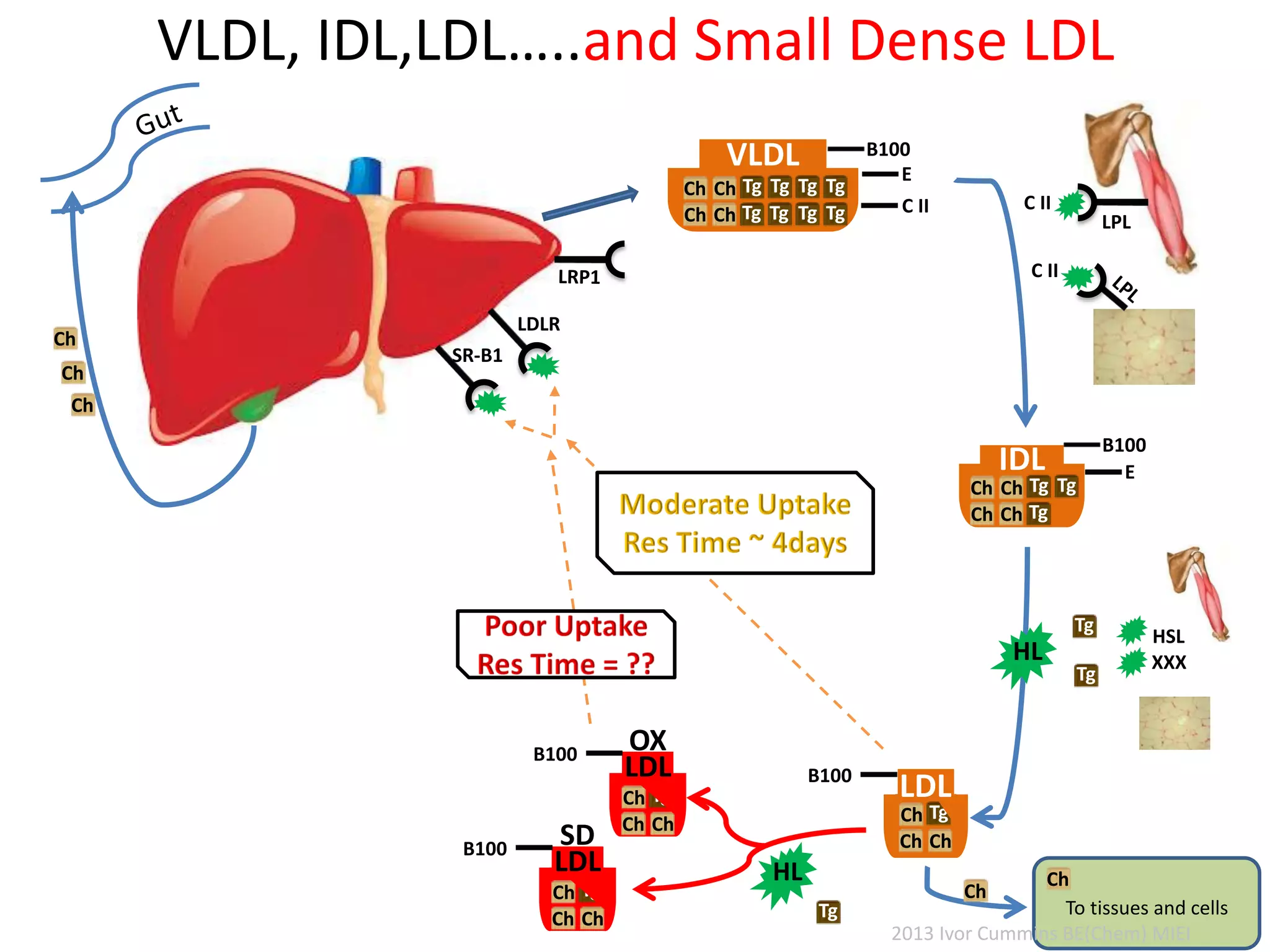
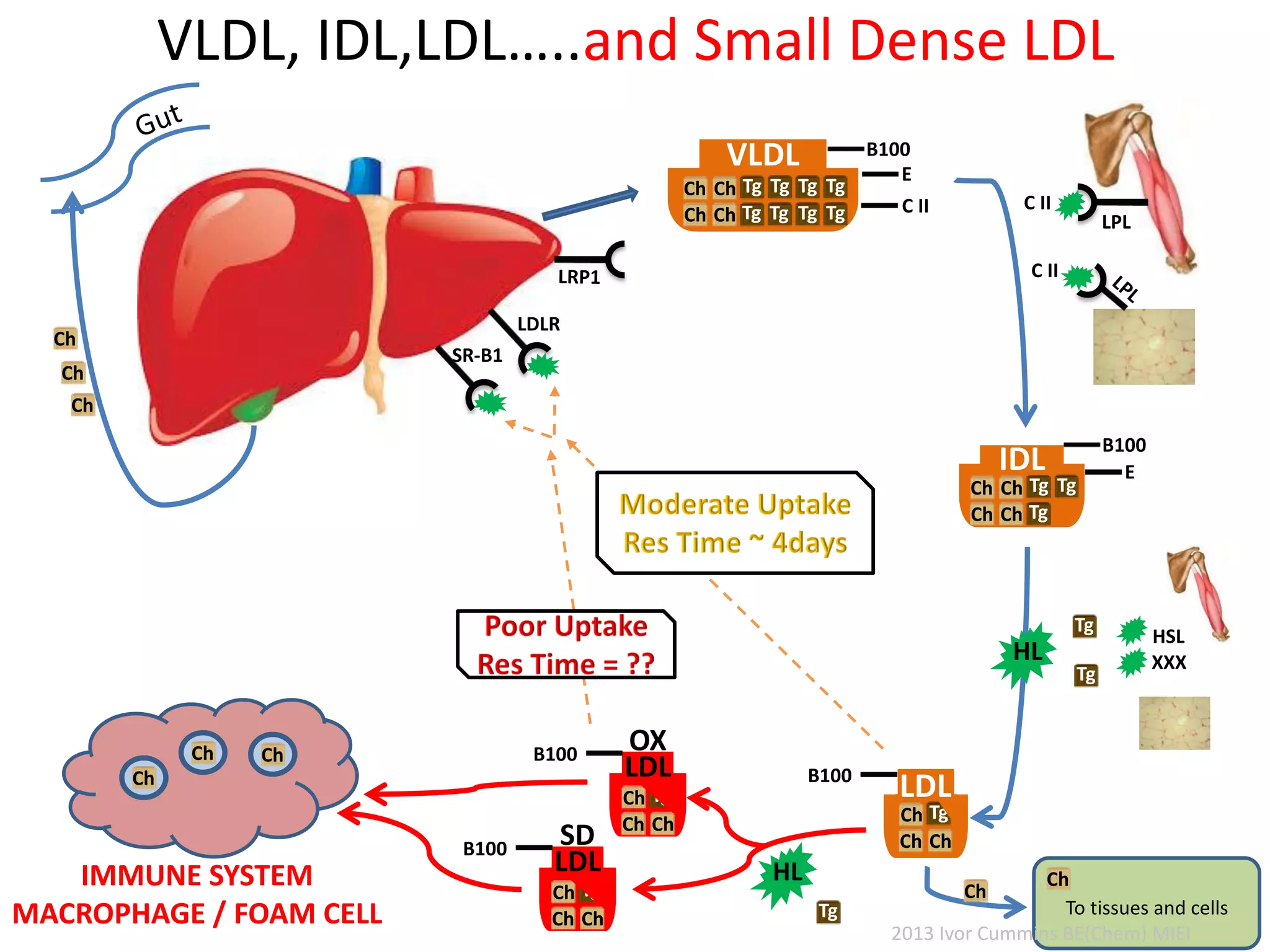
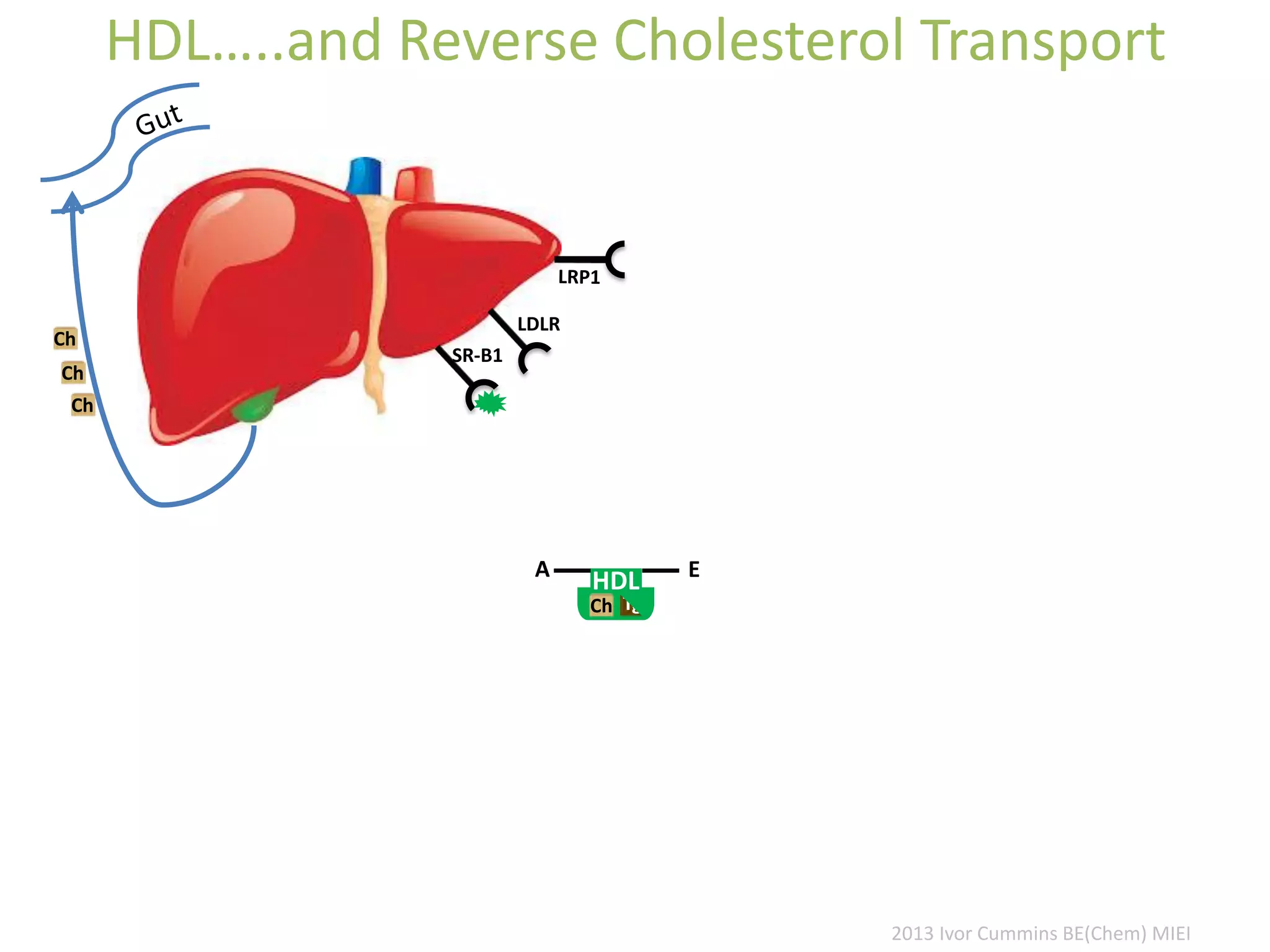
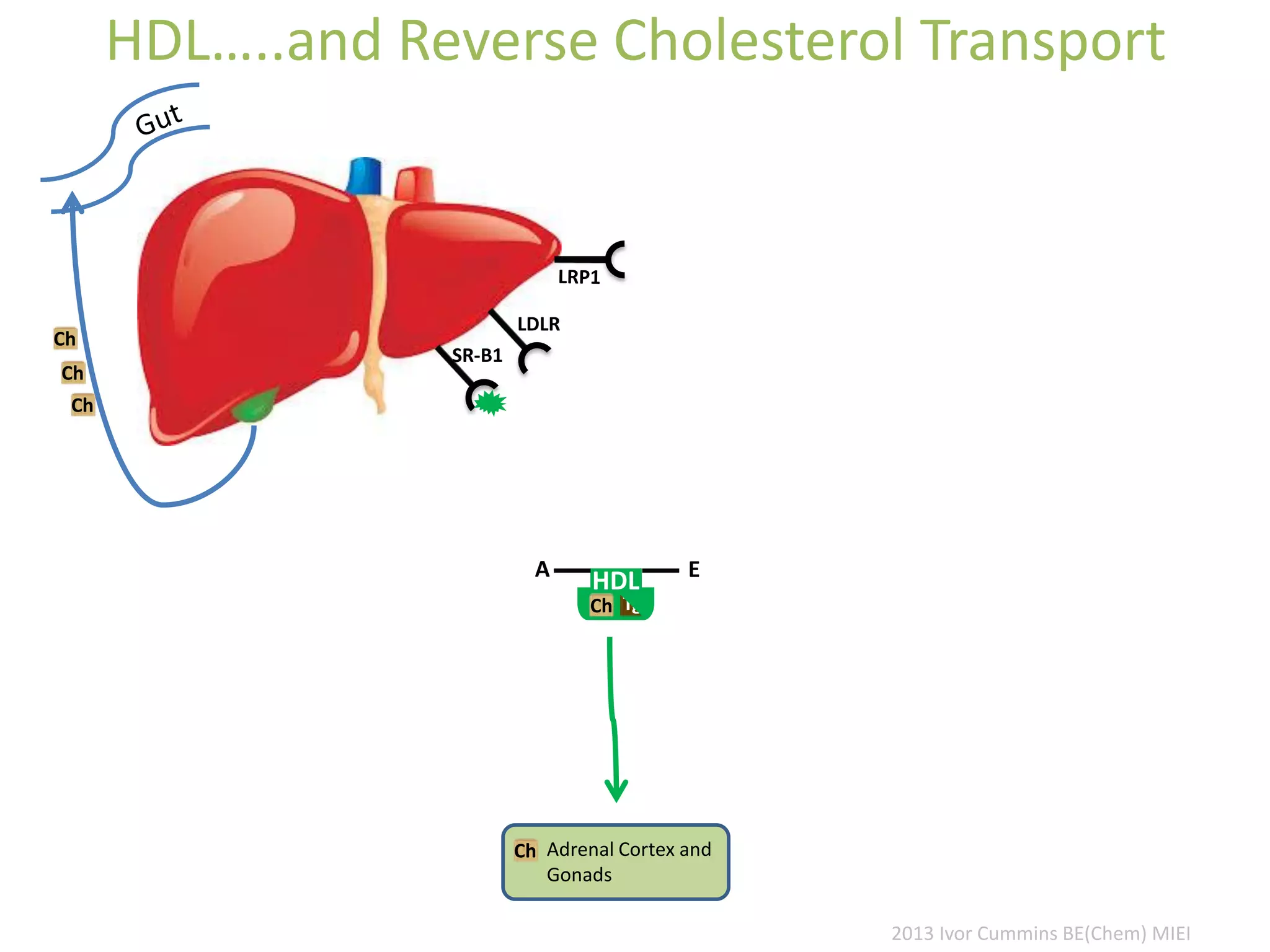
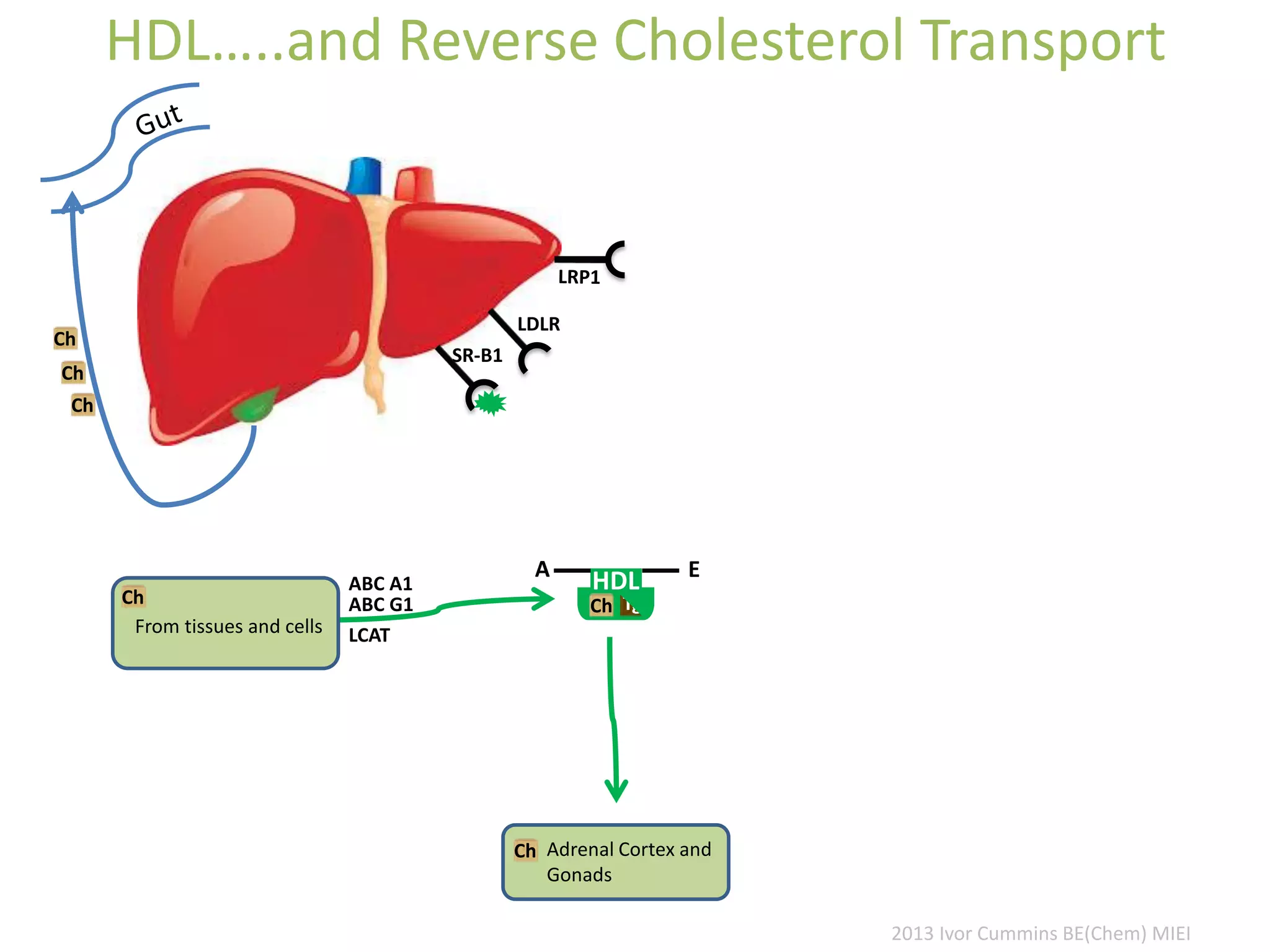
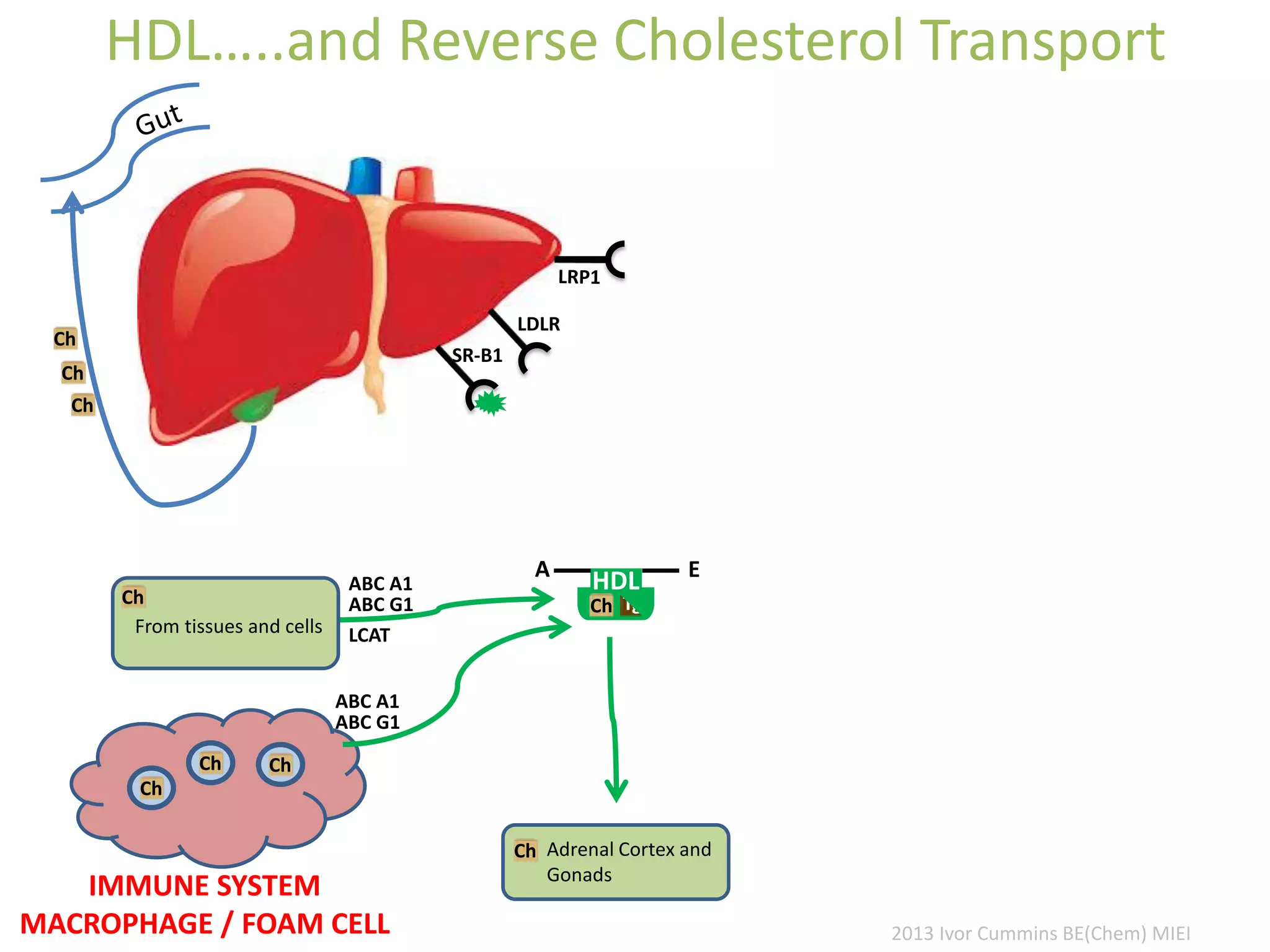
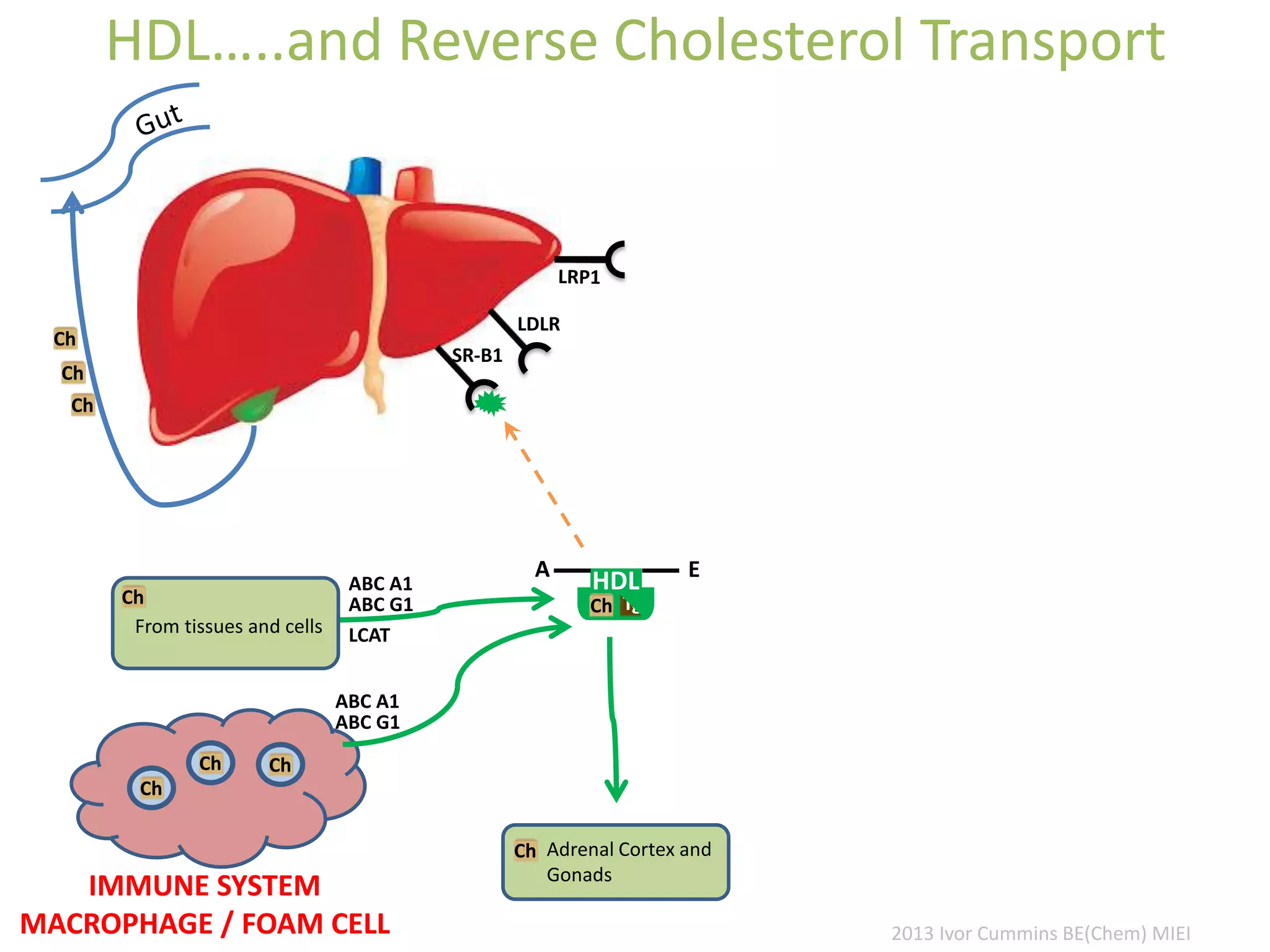
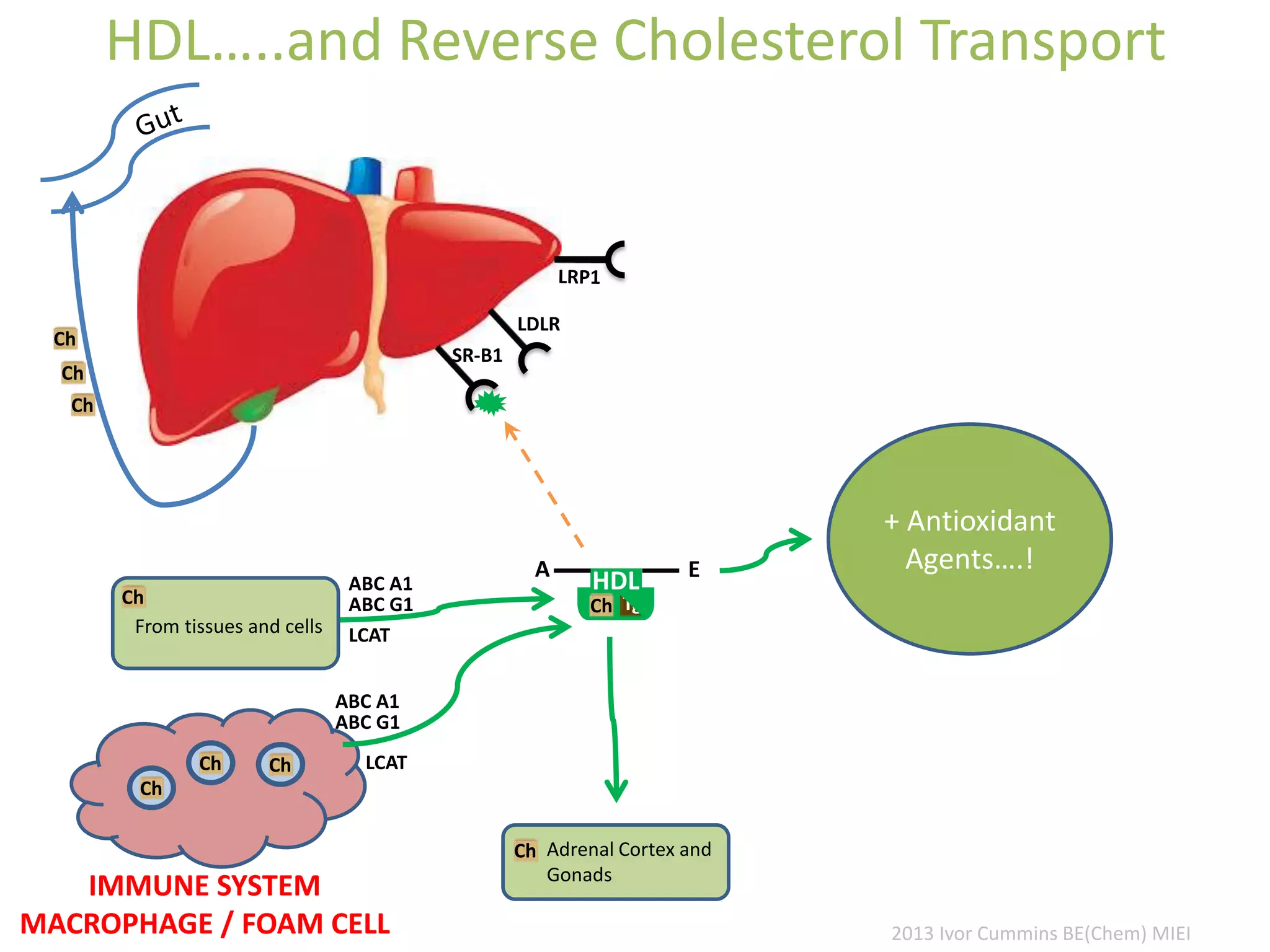
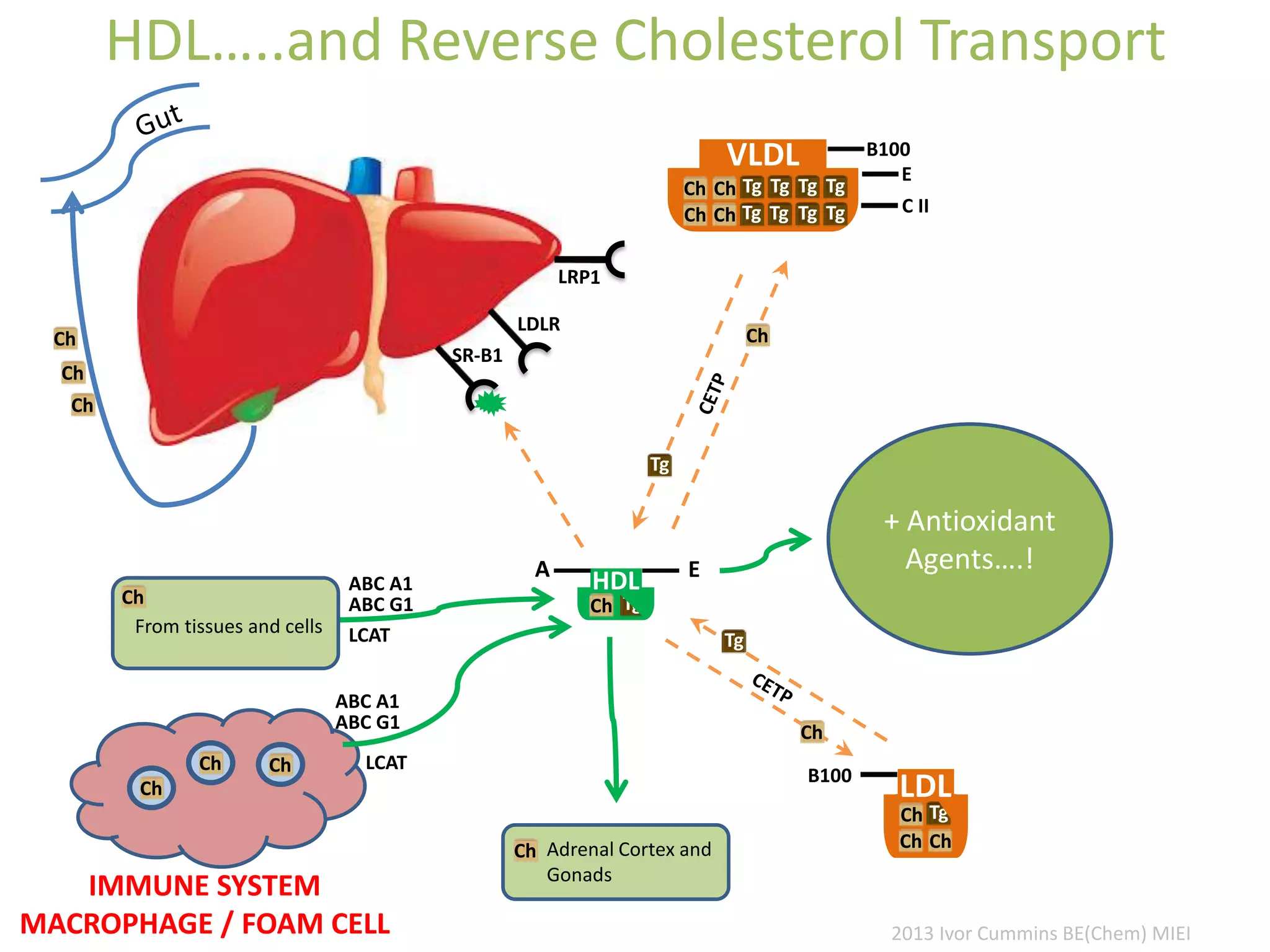
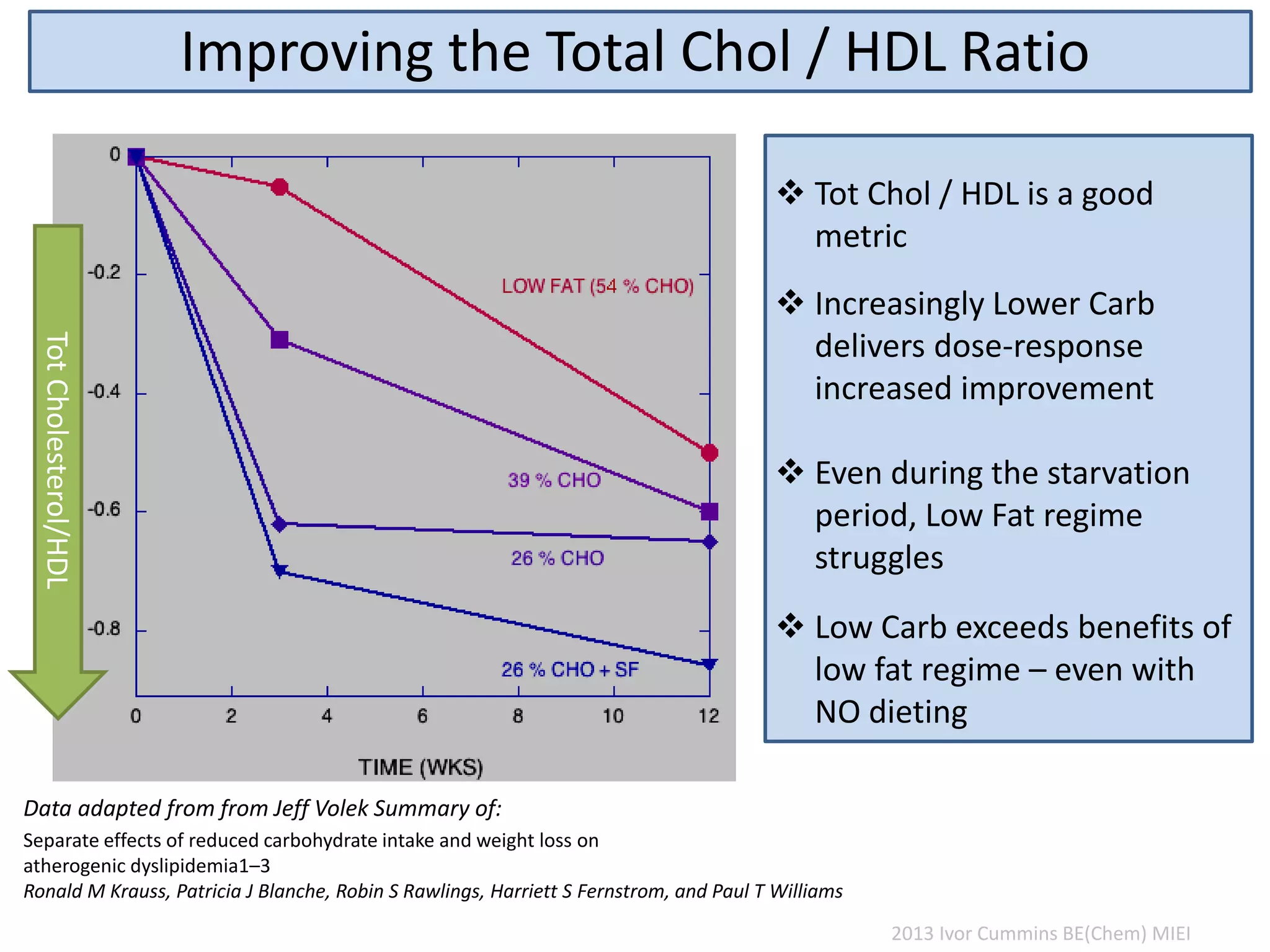
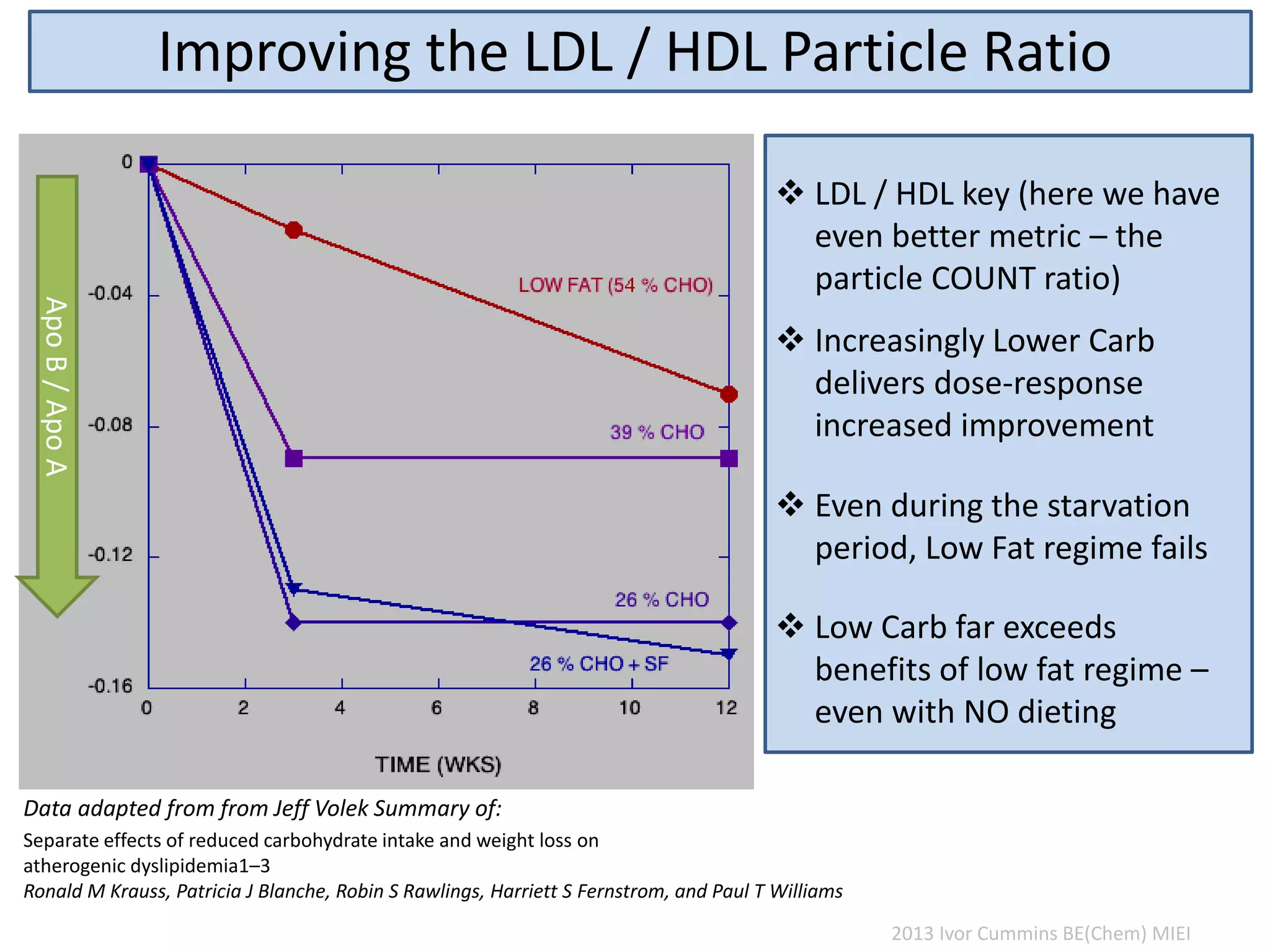
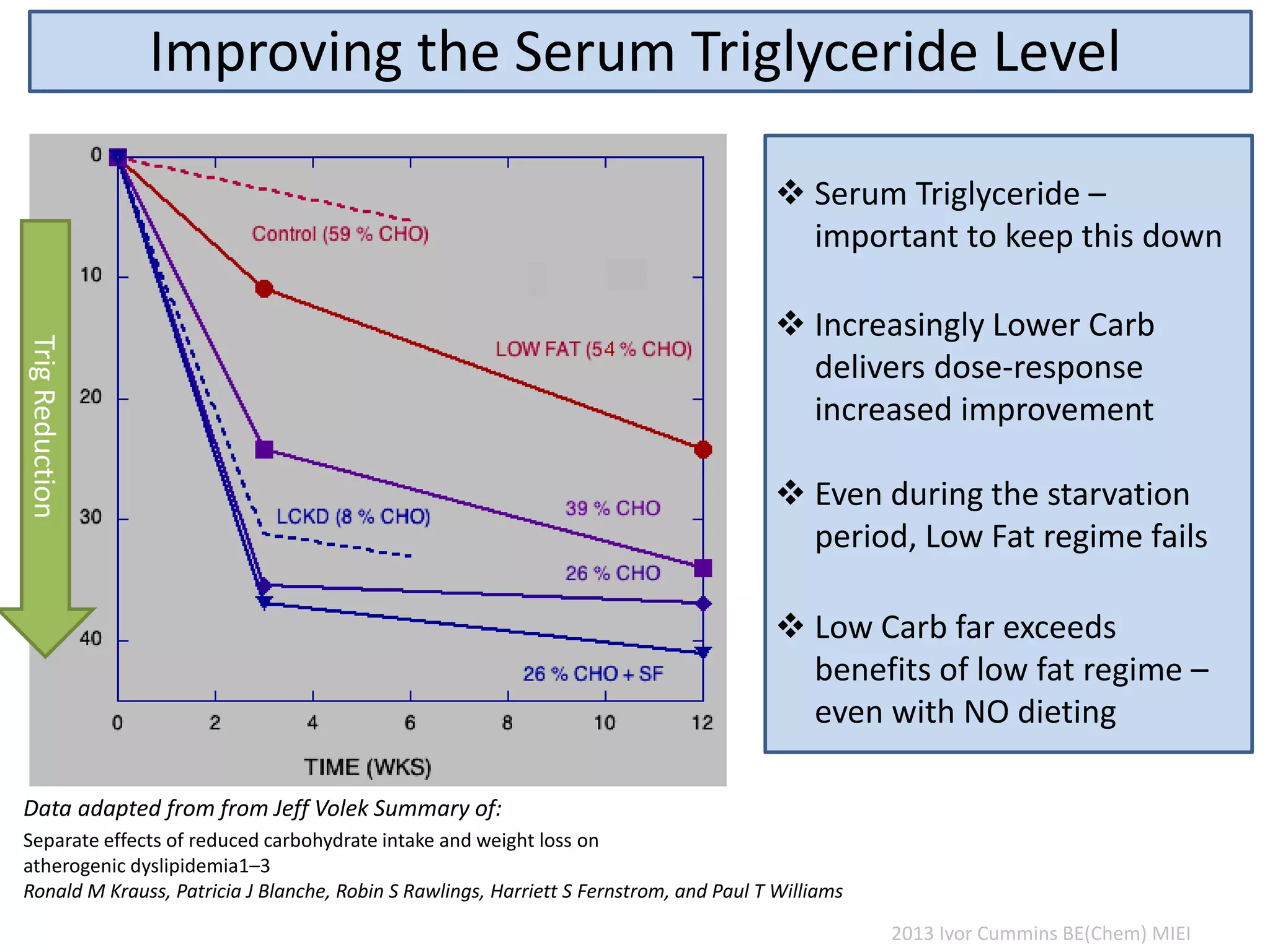
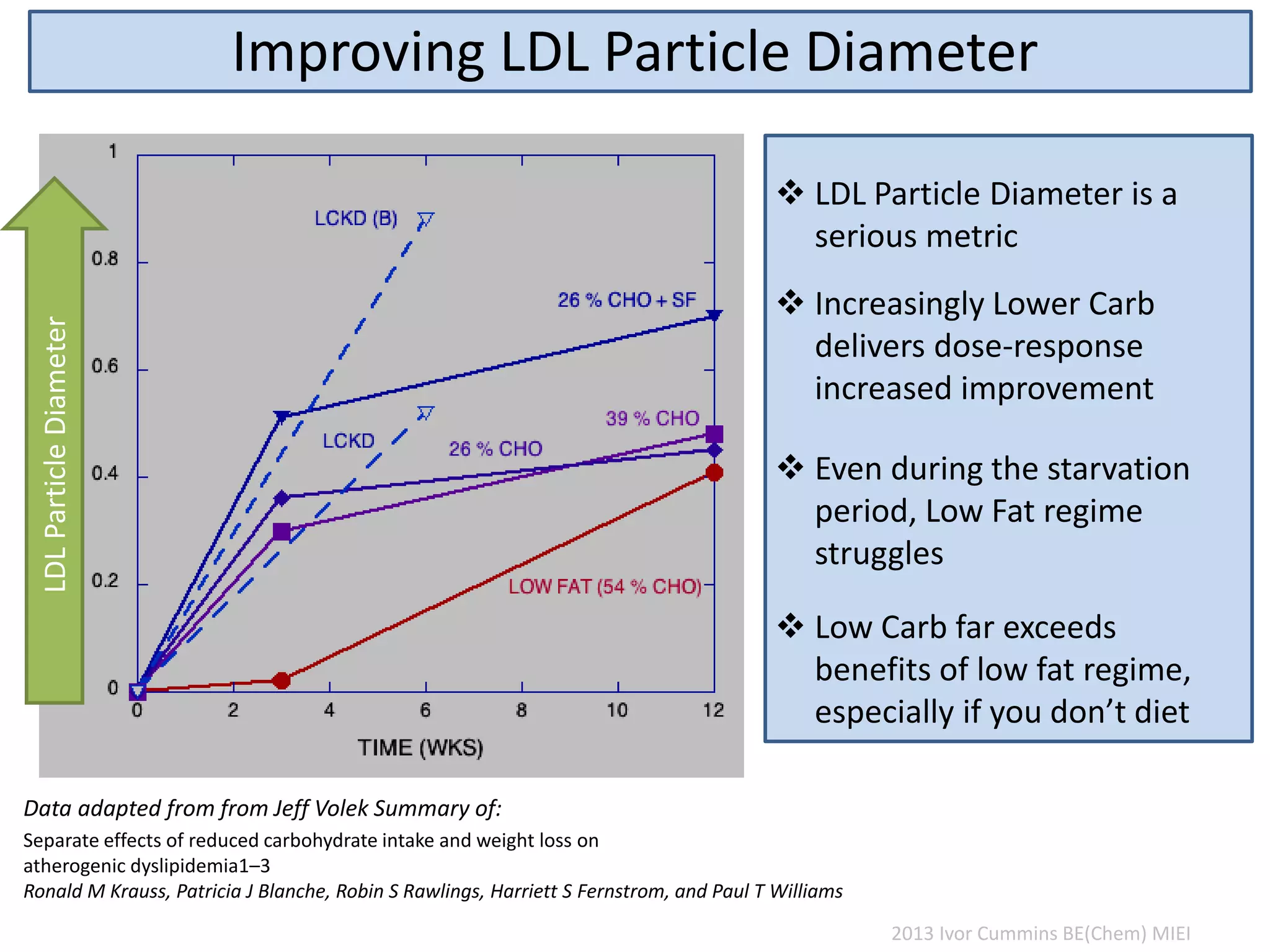
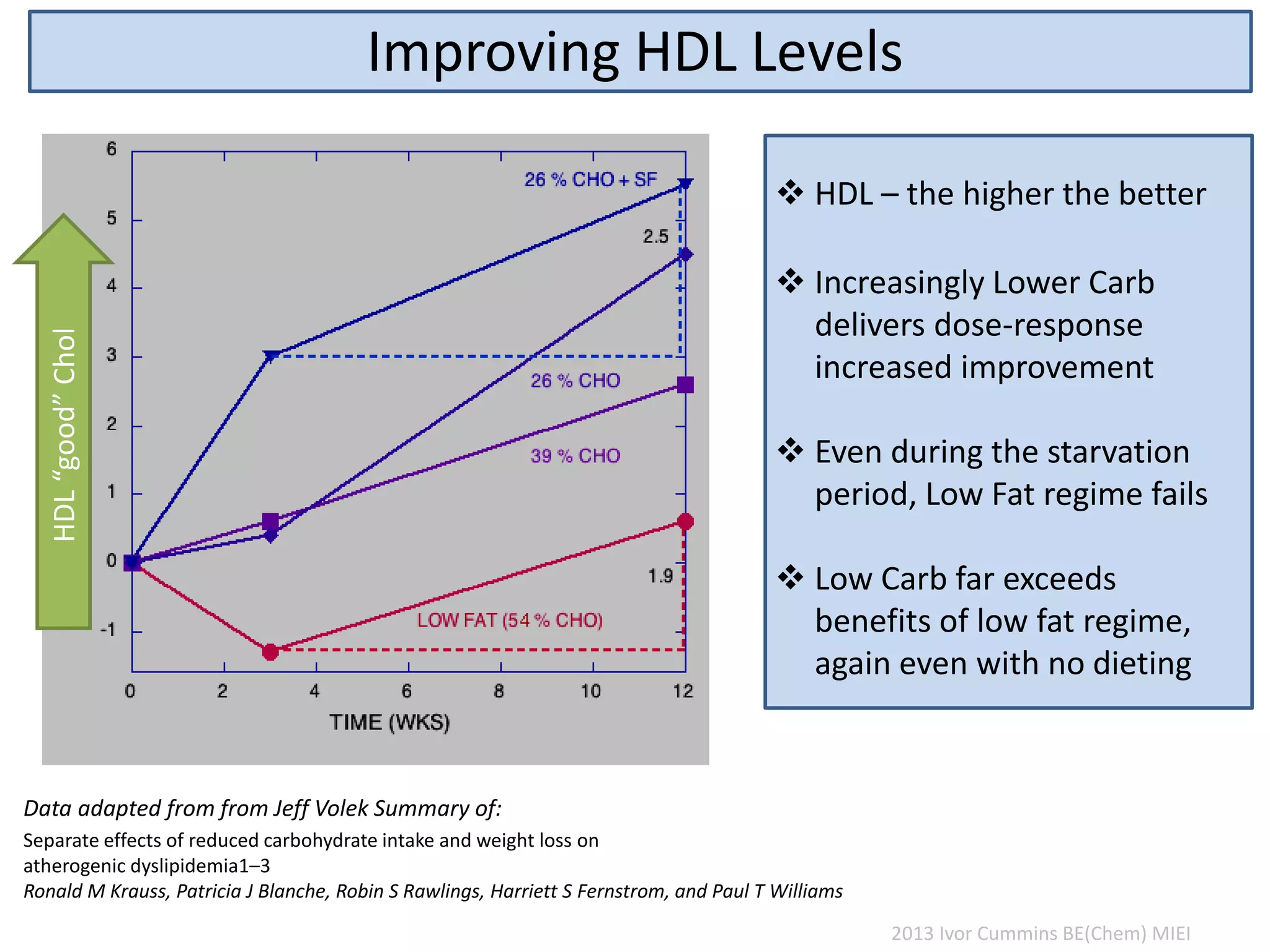
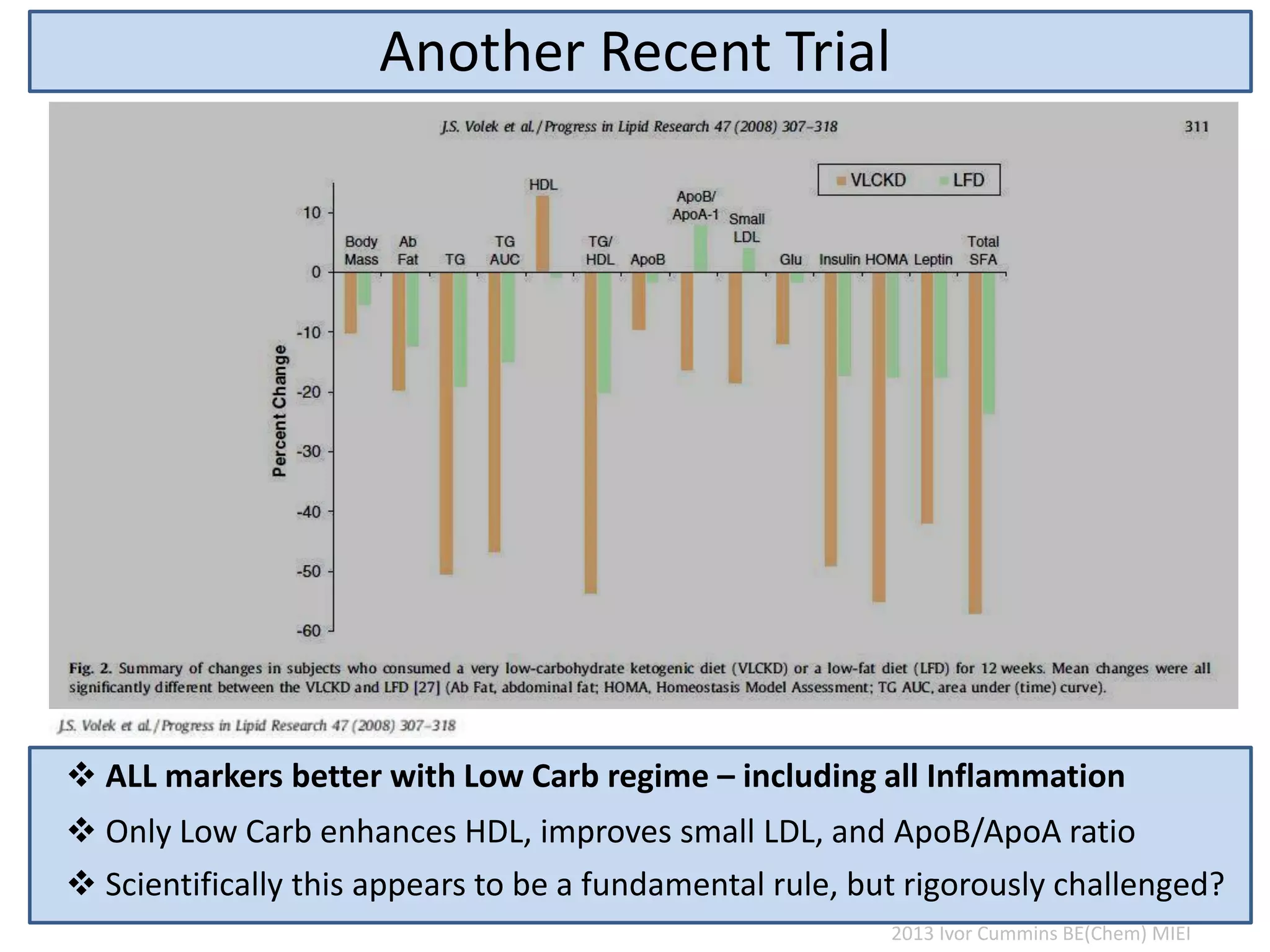
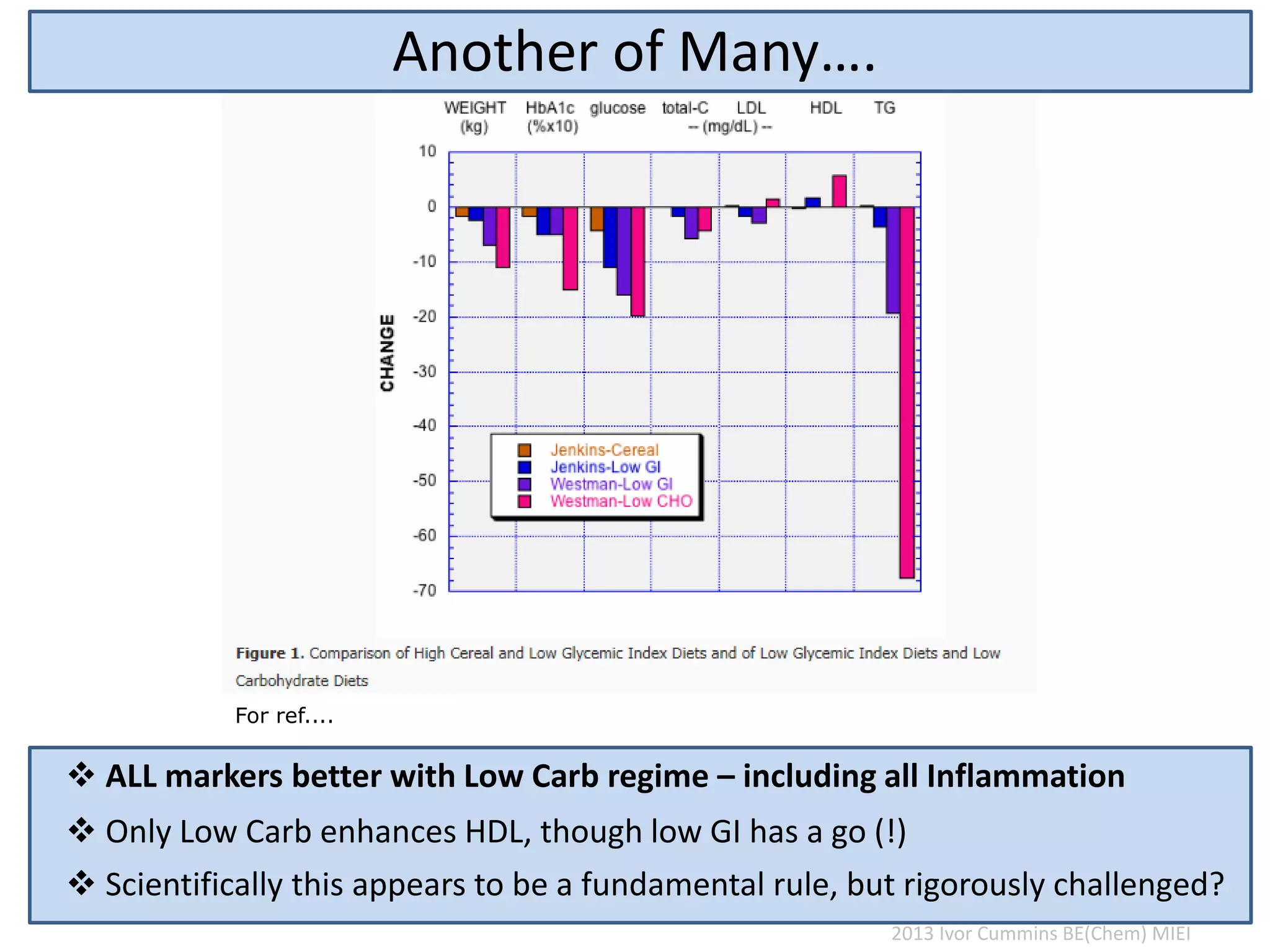
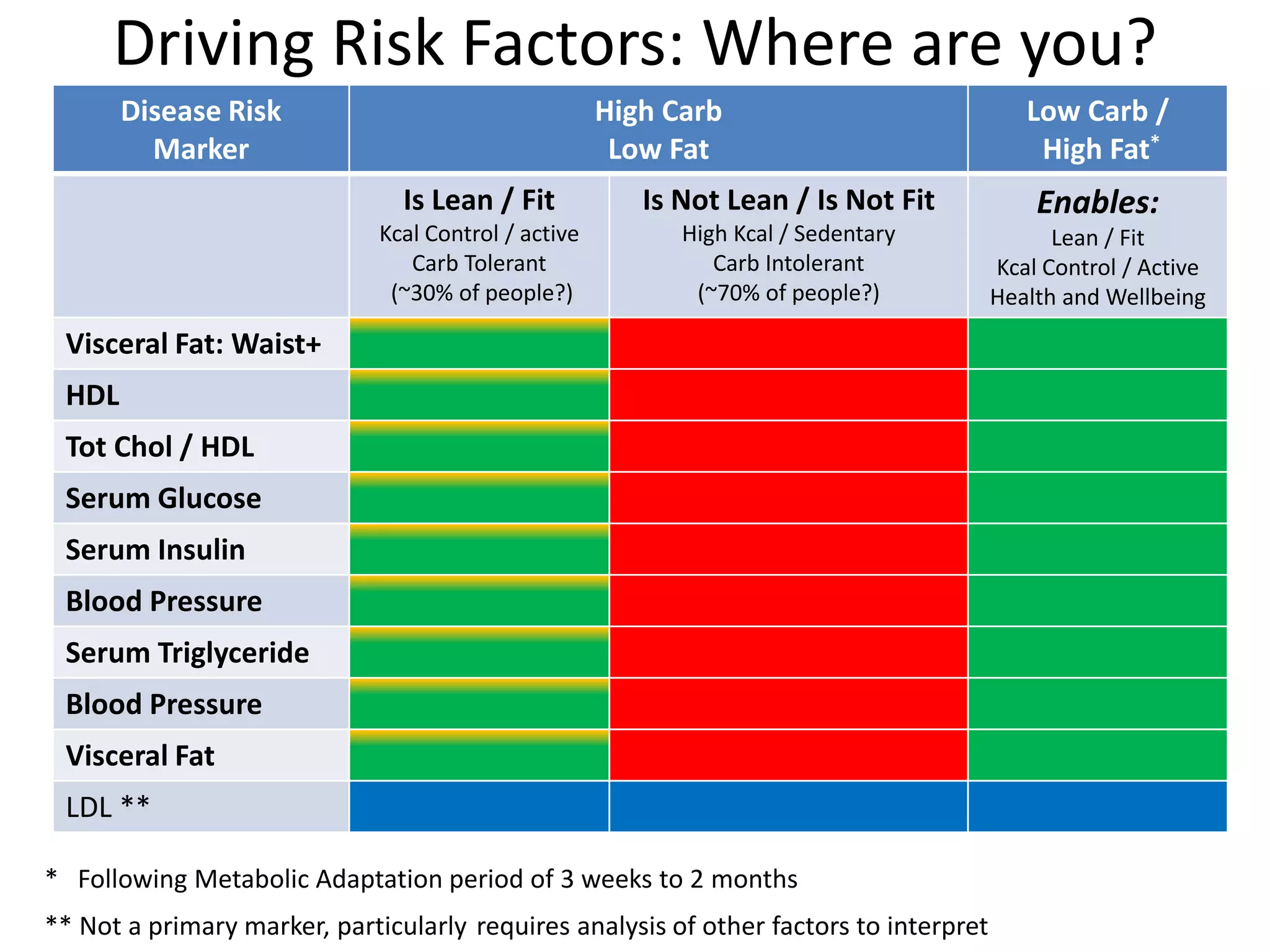
The document discusses the complexities of cholesterol, triglycerides, and their roles in health, emphasizing the importance of lipoproteins in transporting these molecules. It challenges traditional views on cholesterol as a primary risk factor for cardiovascular disease, arguing that factors like insulin resistance and specific lipoprotein types are more critical. A significant finding is the diminishing relevance of total cholesterol in predicting mortality risk, as supported by extensive research data.