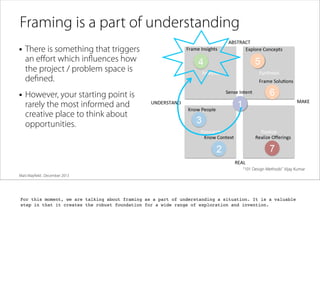
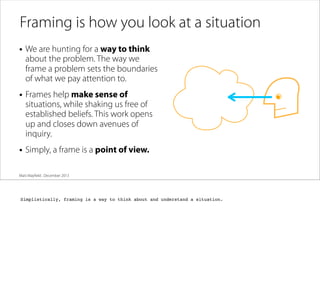
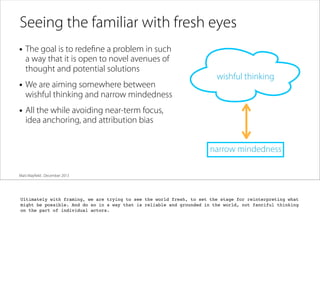
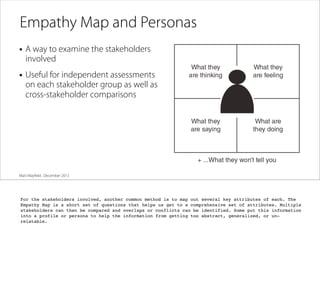
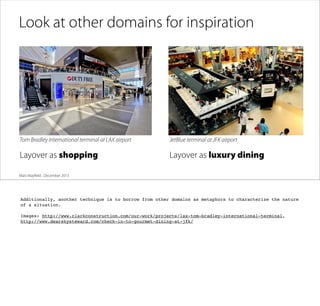
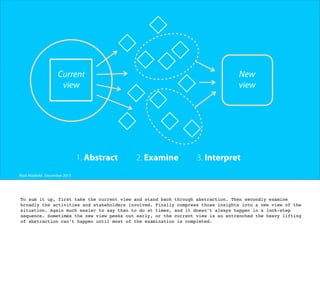
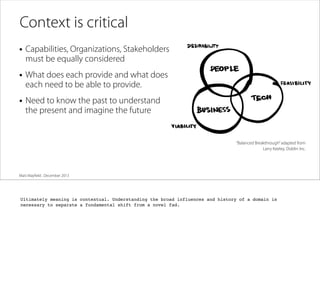
The document discusses the process of framing problems to find innovative opportunities. It defines framing as looking beyond surface-level symptoms to understand the core issues, and examines stakeholders and activities to challenge assumptions. The framing process involves three steps - abstracting the problem to remove constraints, examining activities and stakeholders with fresh perspectives, and interpreting insights to develop a new understanding. Framing requires embracing ambiguity and paradoxes, avoiding premature solutions, and being open to changing frames as new information emerges. The goal is to generate a holistic frame that examines core assumptions and inspires multiple potential solutions.