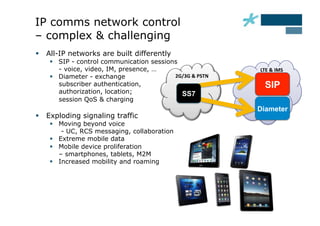
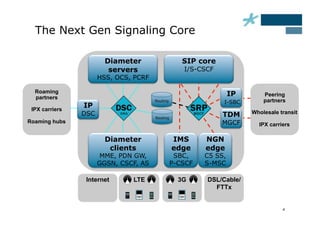
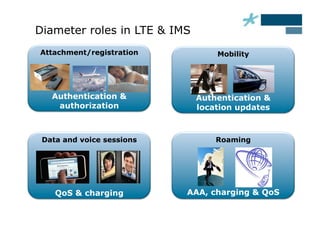
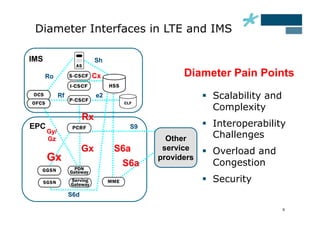
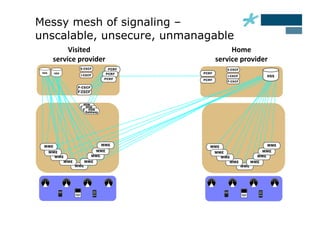
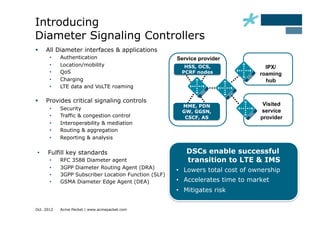
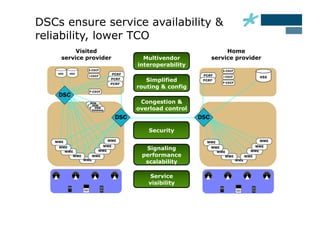
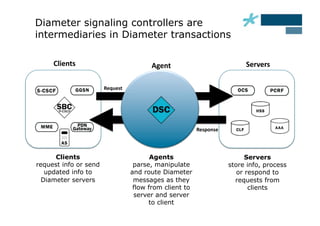
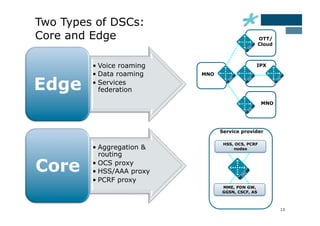
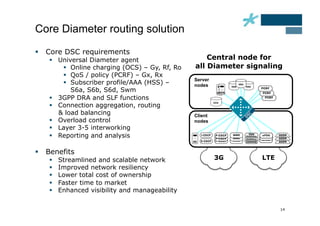
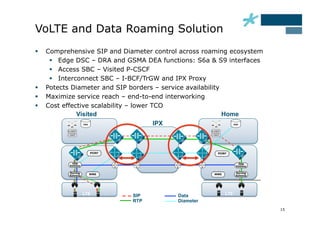
This document discusses the role of Diameter signaling controllers in mobile networks. Diameter controllers help address challenges around scalability, interoperability, overload, and security for Diameter signaling, which is used for subscriber authentication, authorization, location updates, and session quality of service and charging in LTE and IMS networks. Diameter signaling controllers provide routing, traffic control, security, and interworking functions to help service providers manage Diameter interfaces across vendors and networks.