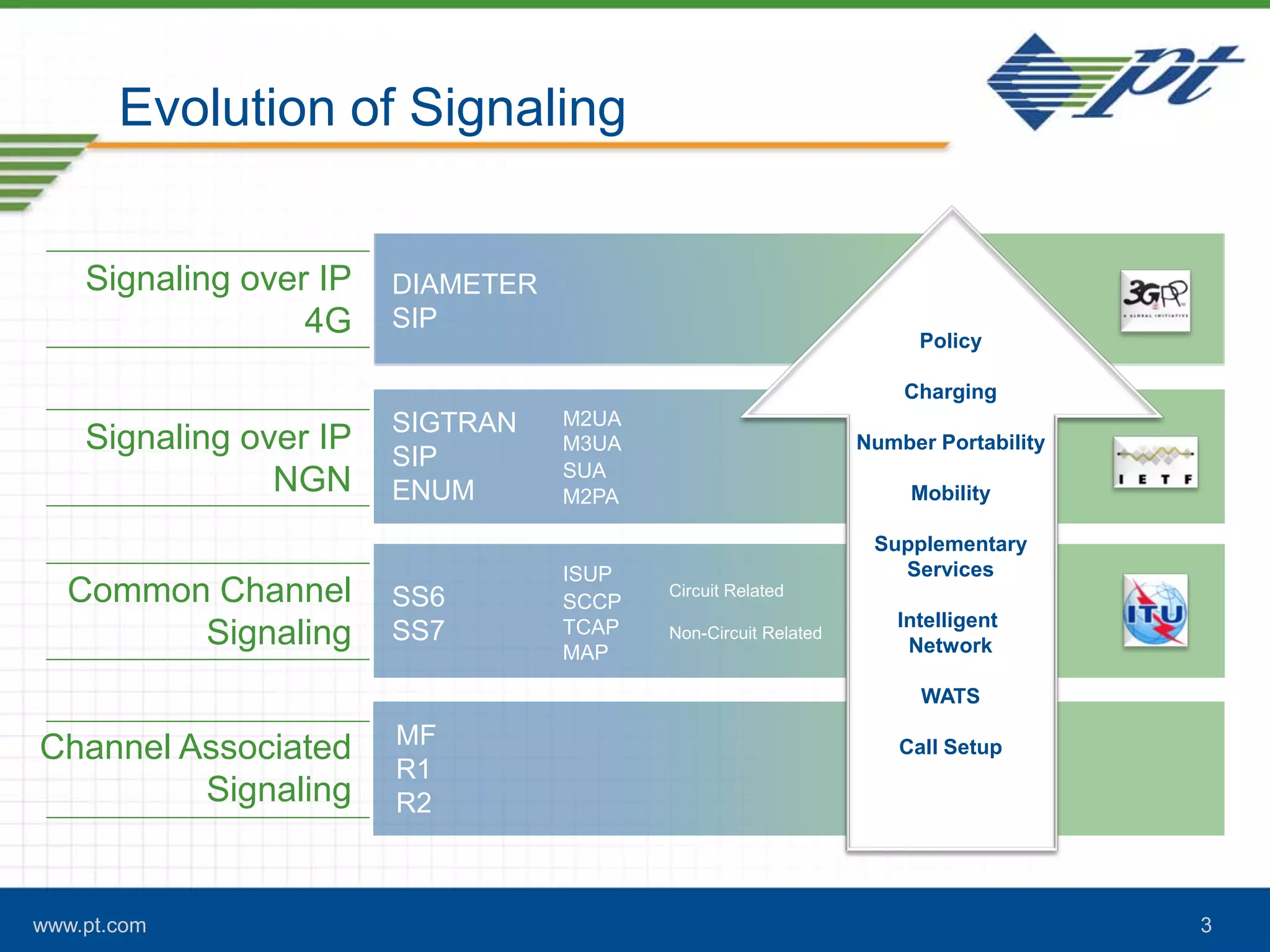
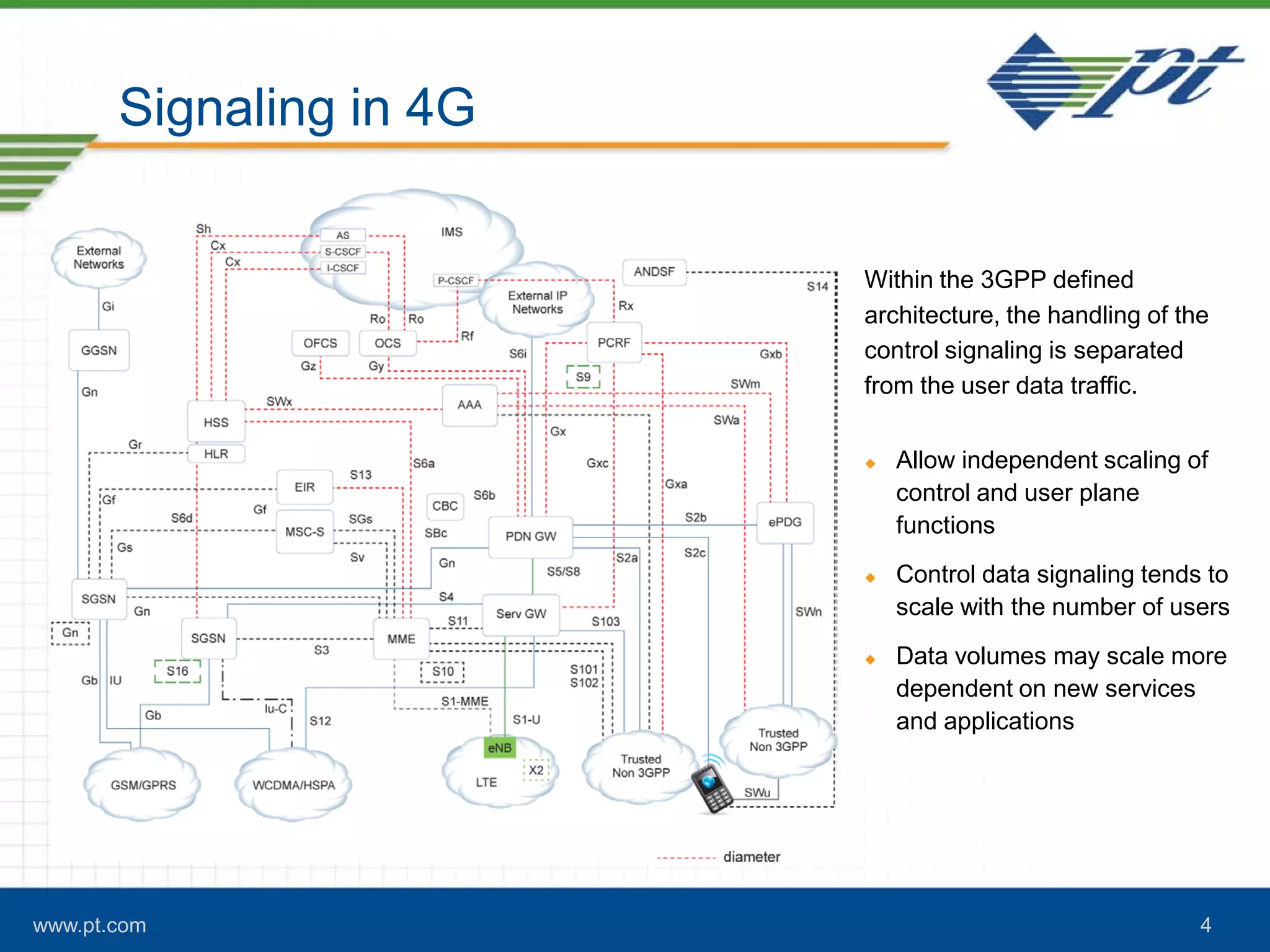
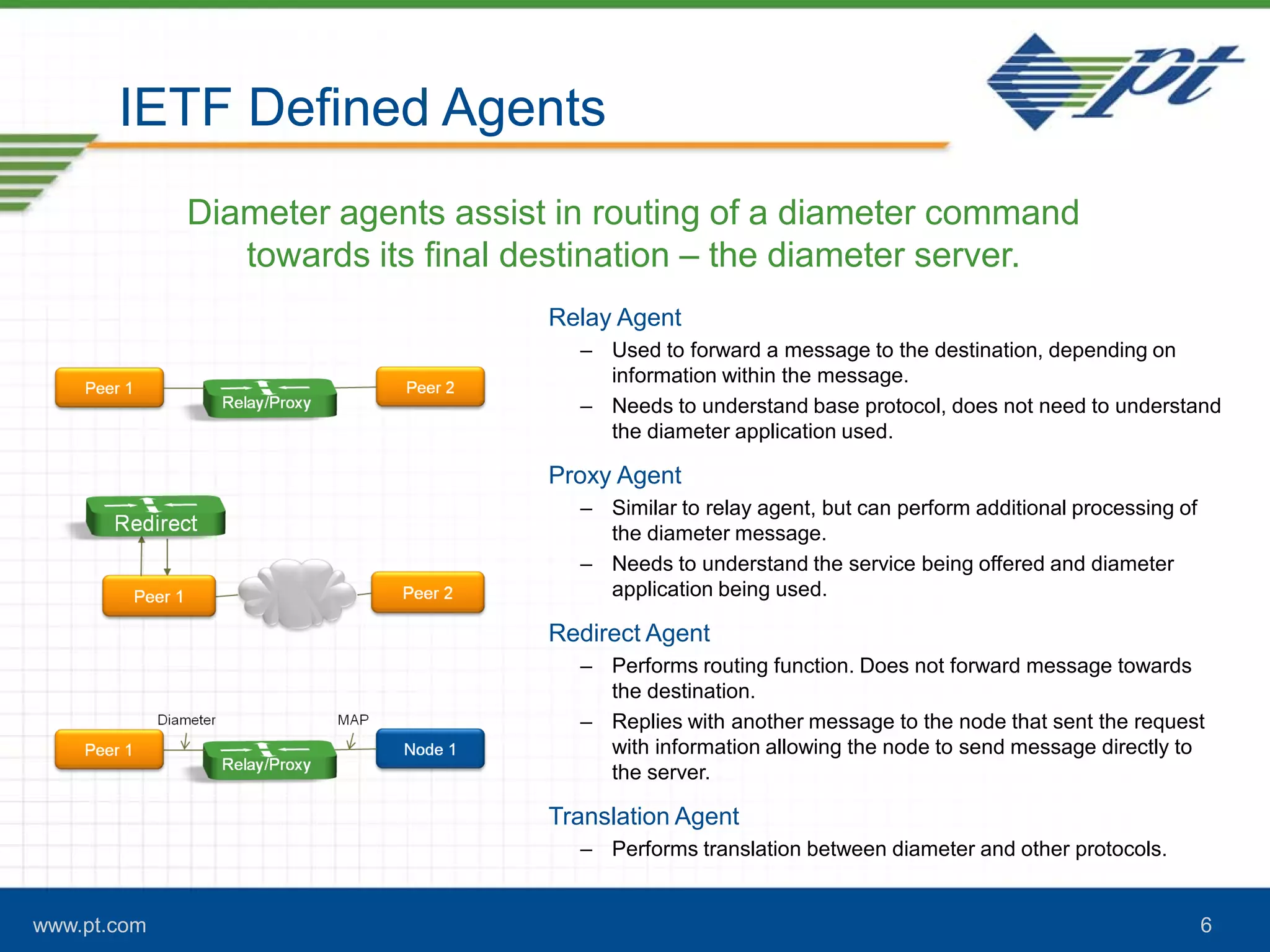
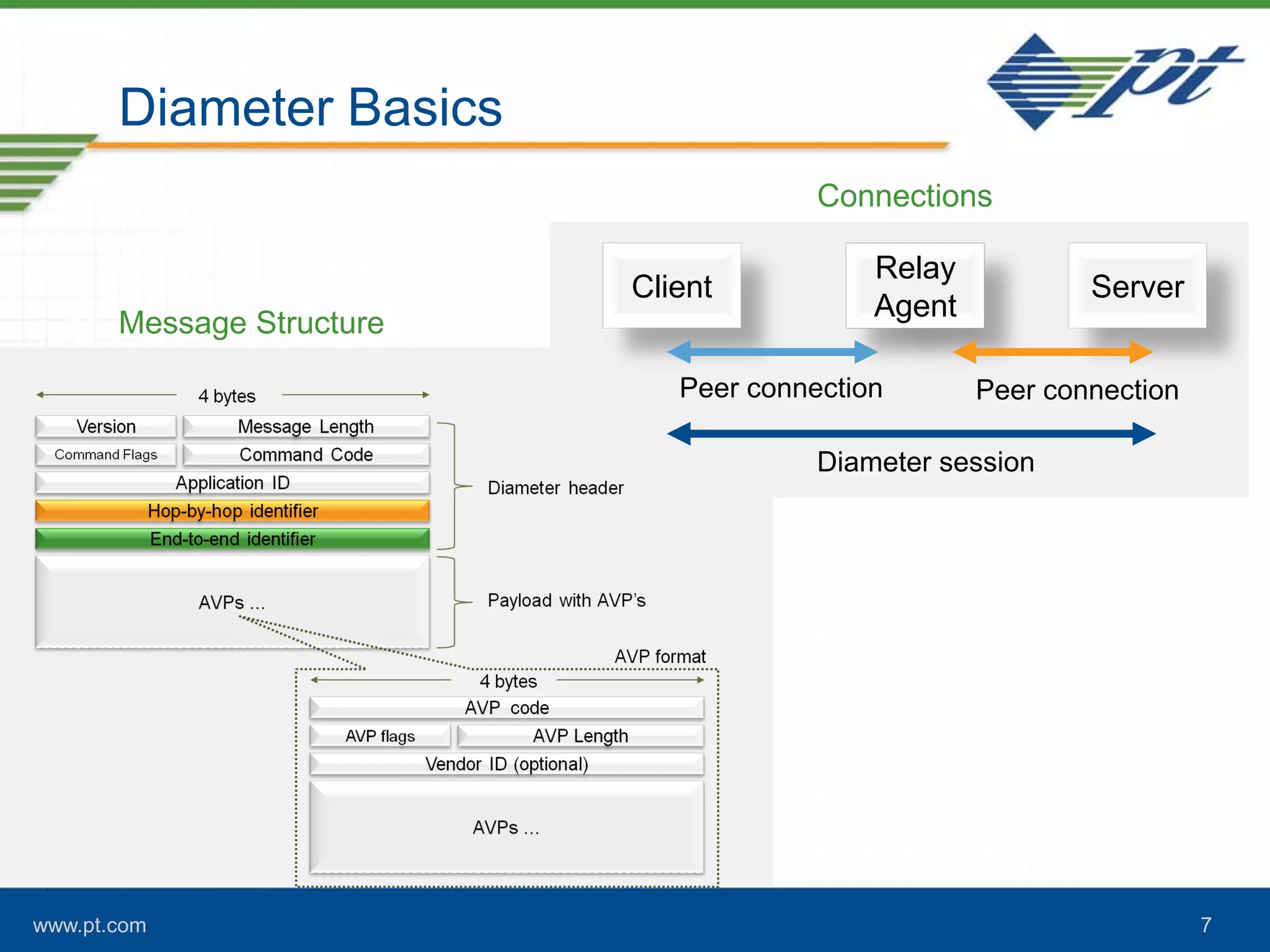
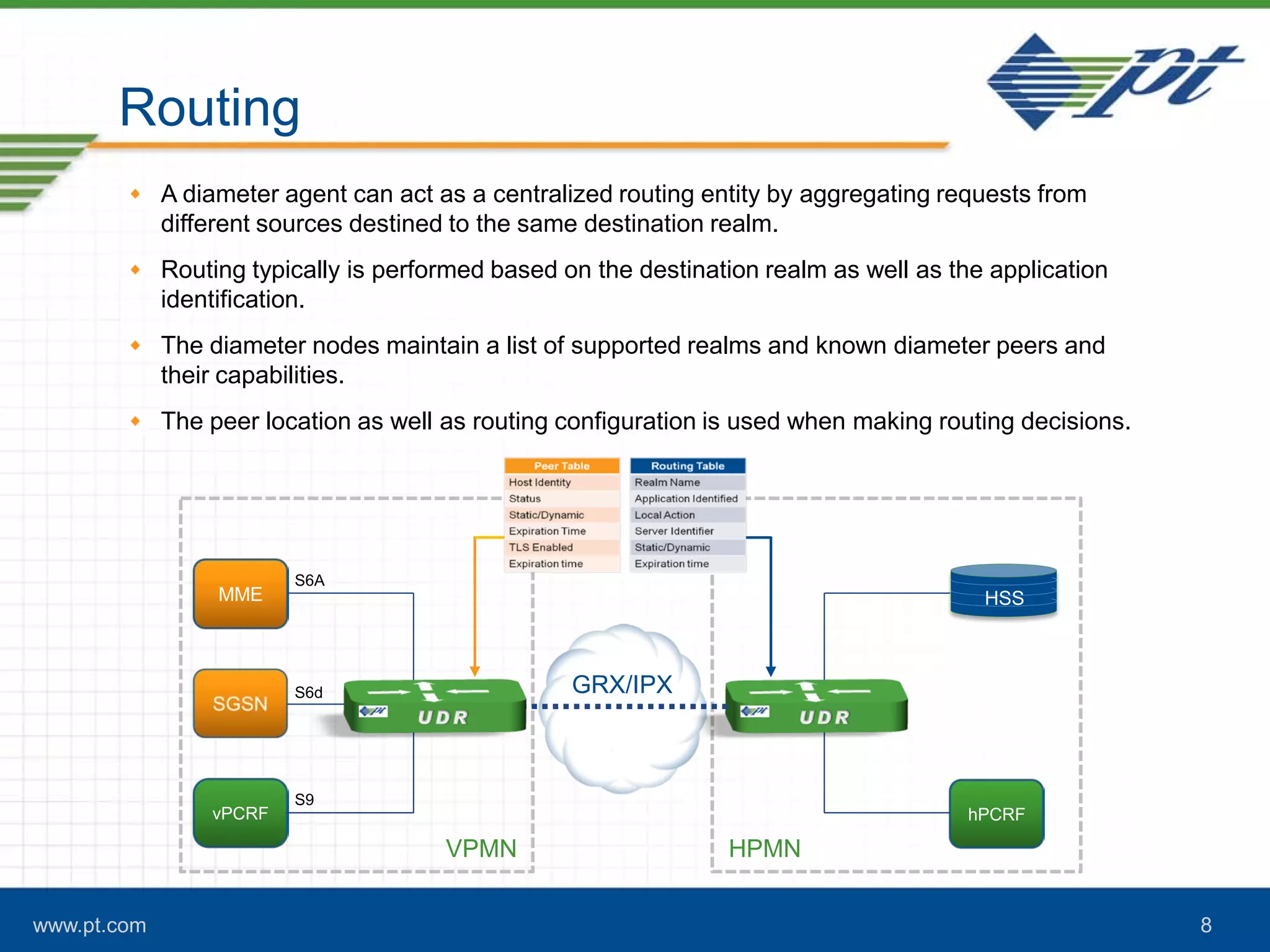
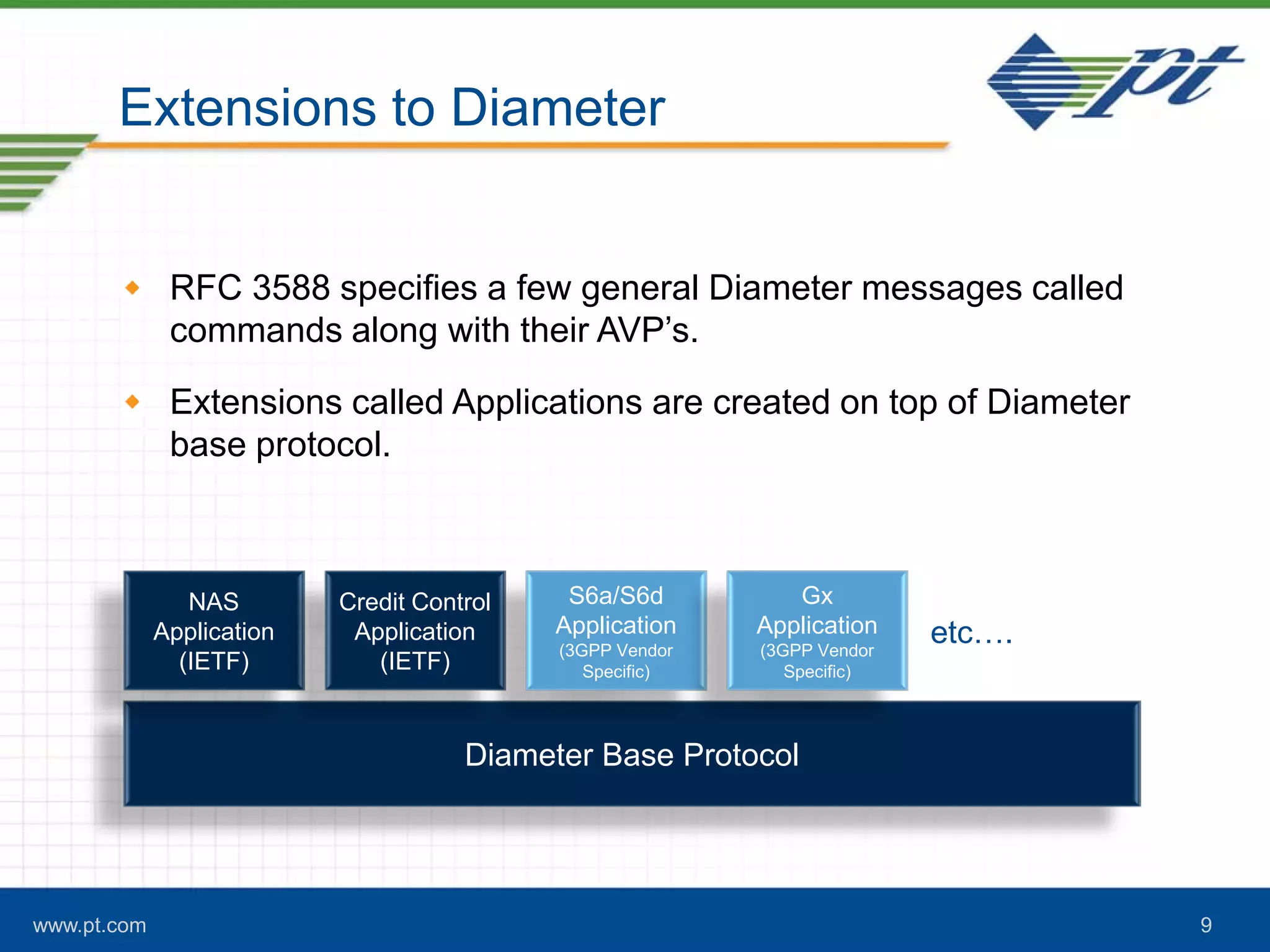
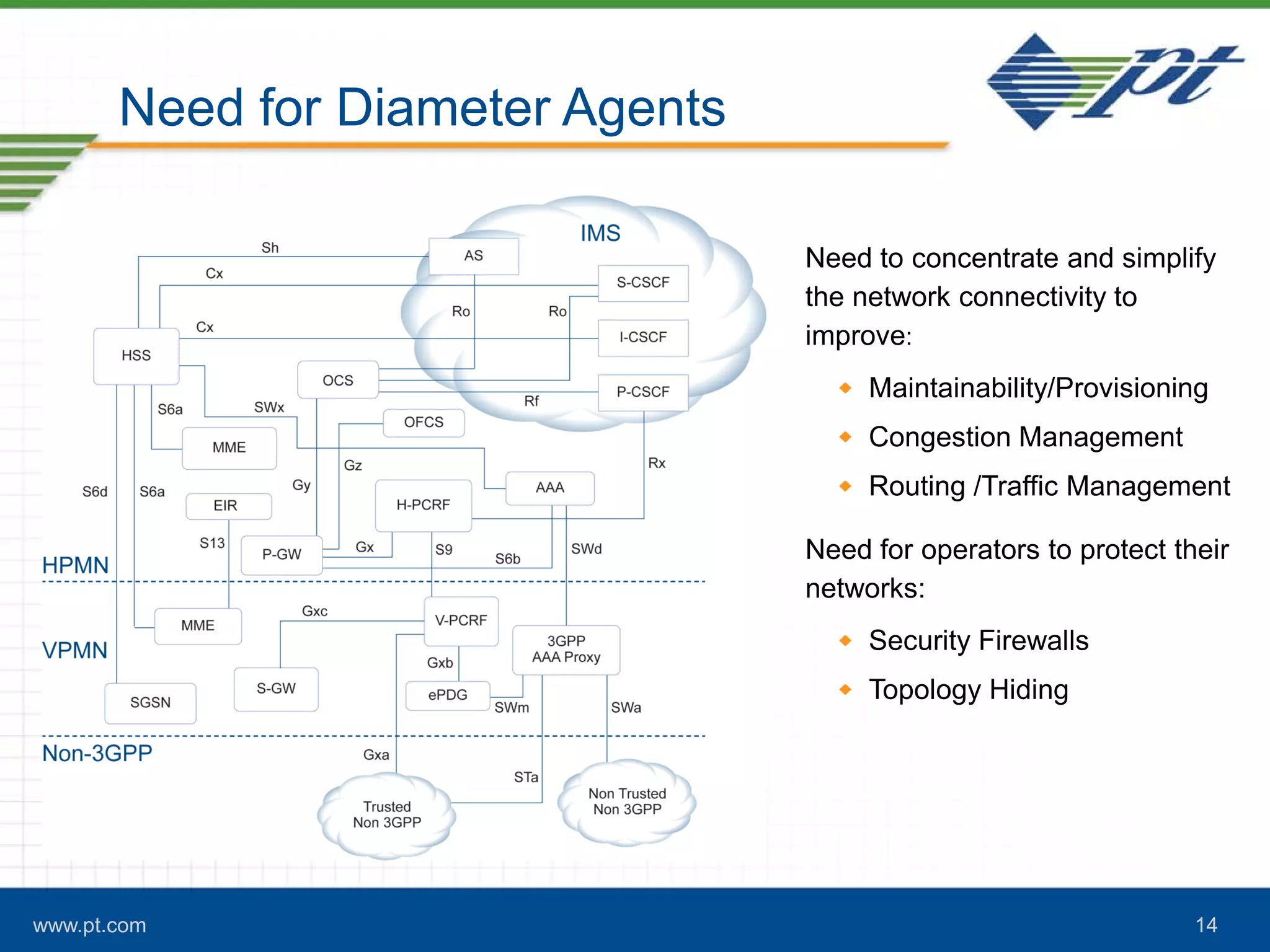
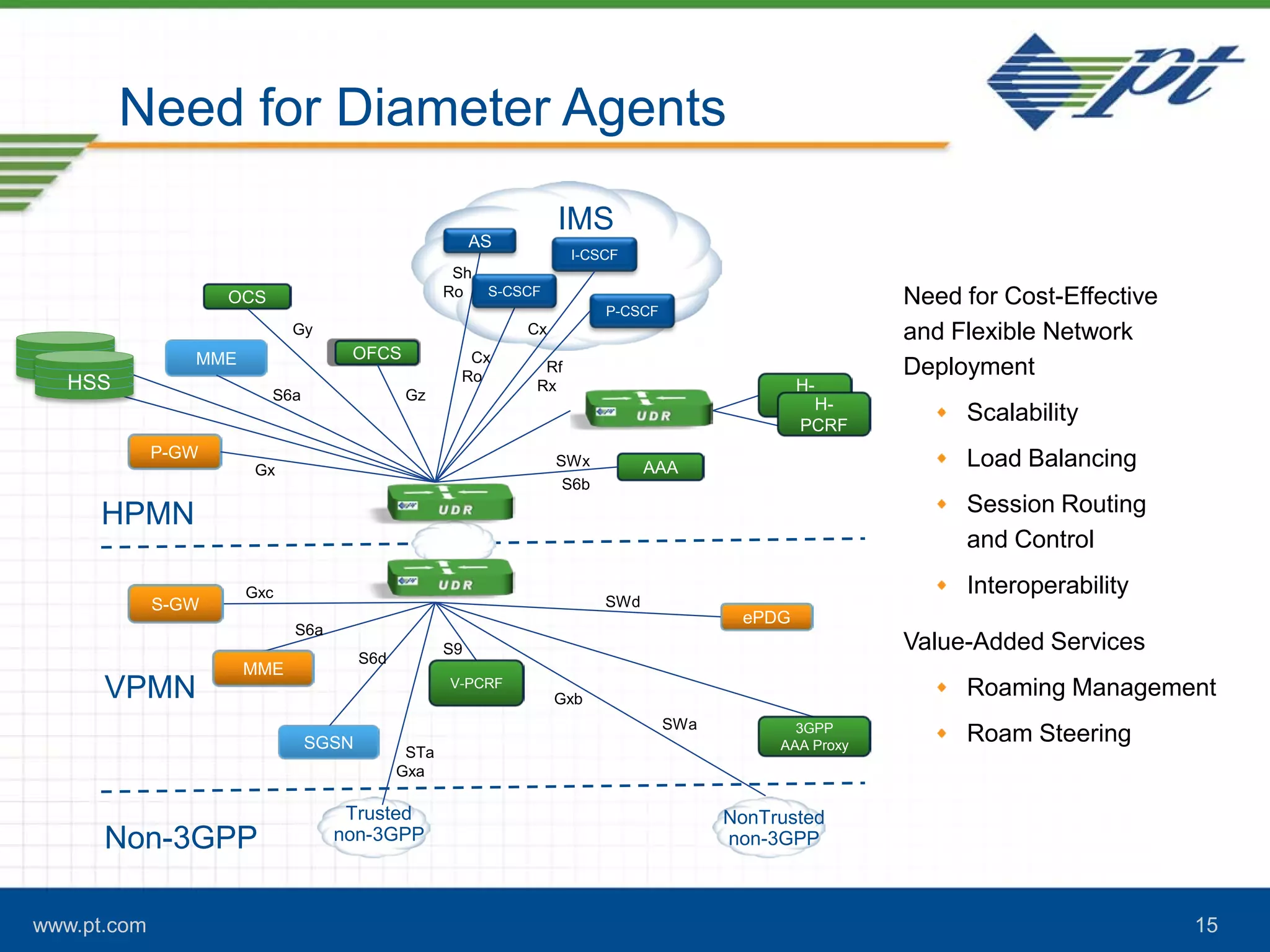
The document discusses the evolution of signaling in telecommunications, highlighting the role of Diameter in managing control signaling and transactional events in 4G networks. It details the functionality of Diameter agents in routing commands and the impact of increasing signaling traffic due to the prevalence of smartphones and always-on applications. Additionally, it emphasizes the need for effective congestion management and security measures in network connectivity.