1) The document summarizes the status and targets of European standardization in facility management through CEN TC 348.
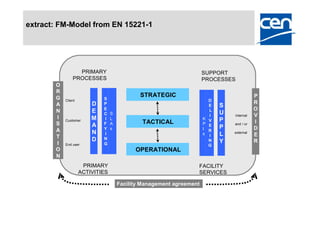
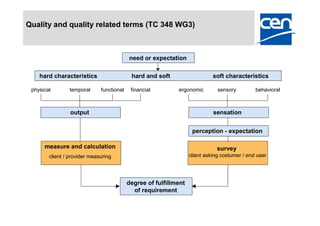
2) It provides an overview of existing standards like EN 15221-1 and -2 and current projects to develop additional standards around quality management (EN 15221-3), facility management taxonomy (EN 15221-4), process development (EN 15221-5), and space measurement (EN 15221-6).
3) It then focuses on a draft