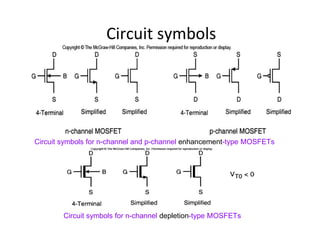
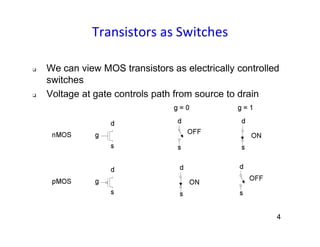
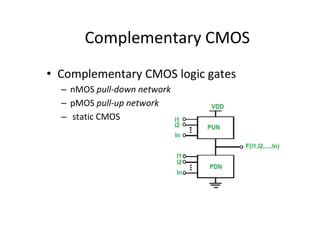
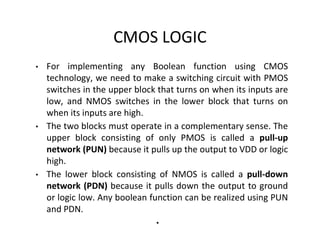
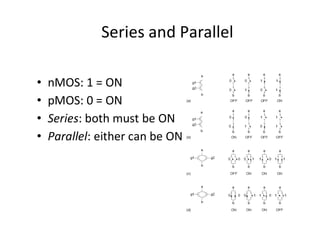
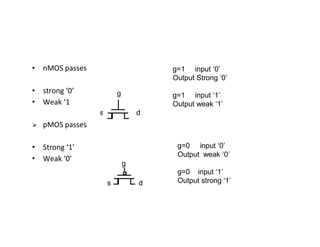
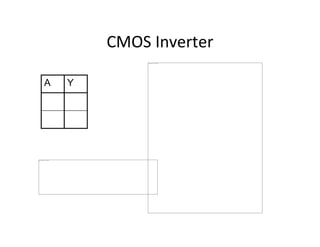
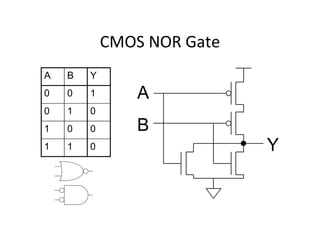
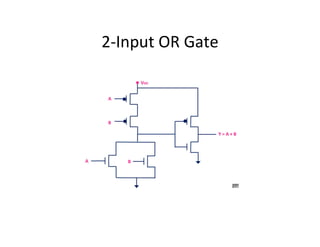
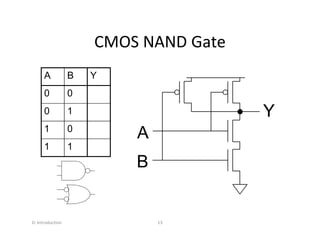
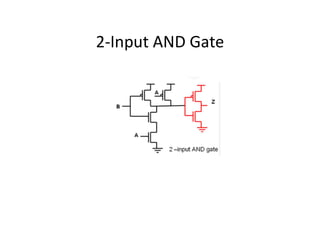
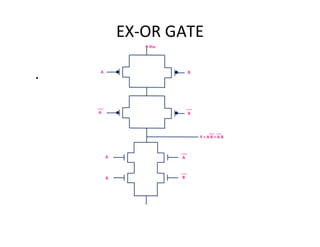
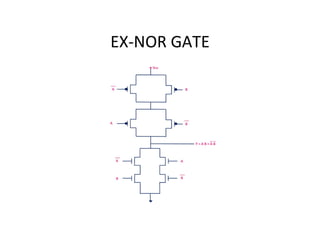
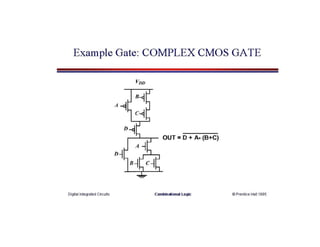
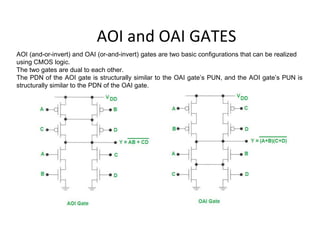
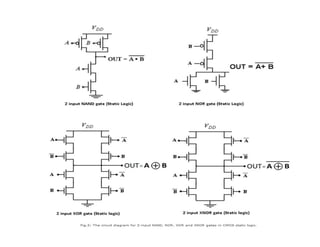
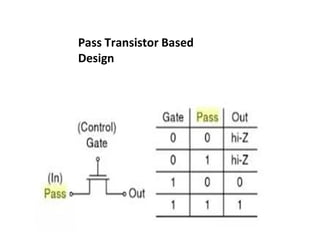
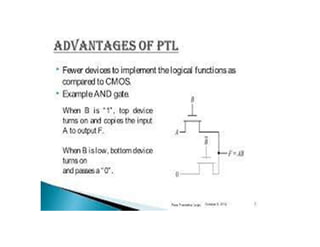
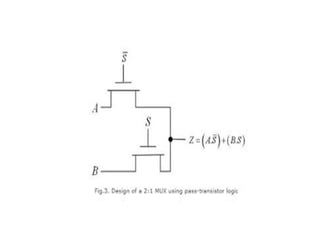
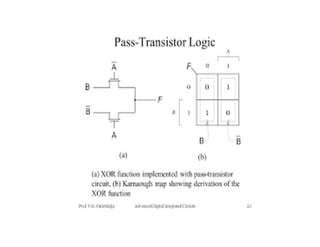
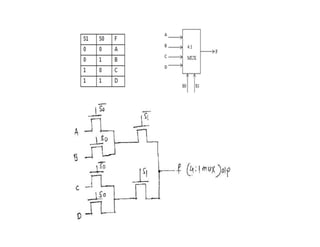
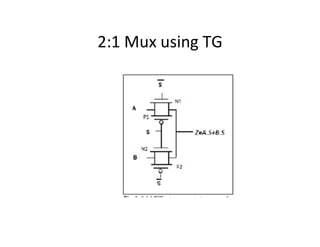
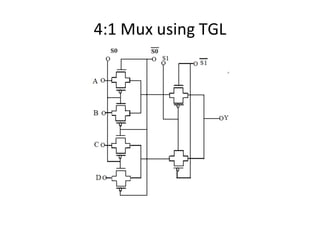
This document discusses VLSI design and CMOS logic. It covers circuit symbols for MOSFETs, using transistors as switches, power supply voltages, complementary CMOS logic gates, CMOS inverters, NAND gates, NOR gates, AND gates, multiplexers, and other design styles like pass transistor logic and transmission gate logic. CMOS logic uses both n-type and p-type MOSFETs arranged in a complementary fashion to implement Boolean logic functions with low power consumption and high performance.