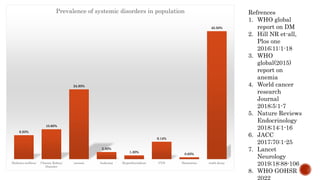
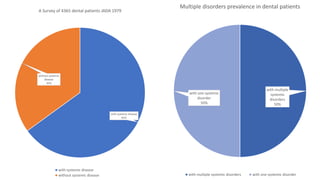
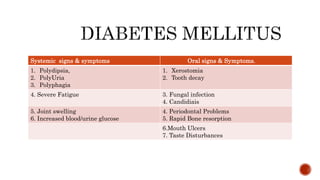
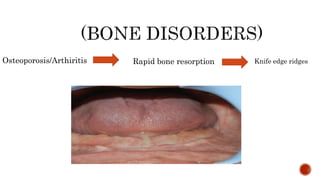
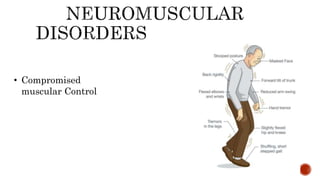
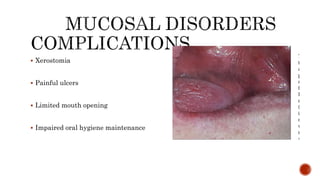
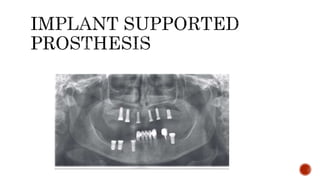
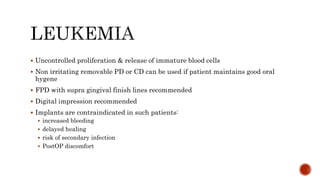
The document discusses the relationship between oral health and systemic health, noting that evaluation of a patient's overall health status is important prior to dental treatment. It then focuses on the effects of various systemic diseases on prosthodontic patients, including direct and indirect effects on oral tissues, drug interactions, immune system compromise, and sensory/motor disturbances. Specific systemic diseases that are discussed include diabetes, chronic kidney disease, anemia, leukemia, hyperthyroidism, cardiovascular disease, and dementias. Management strategies for prosthodontic treatment of patients with these conditions are provided.