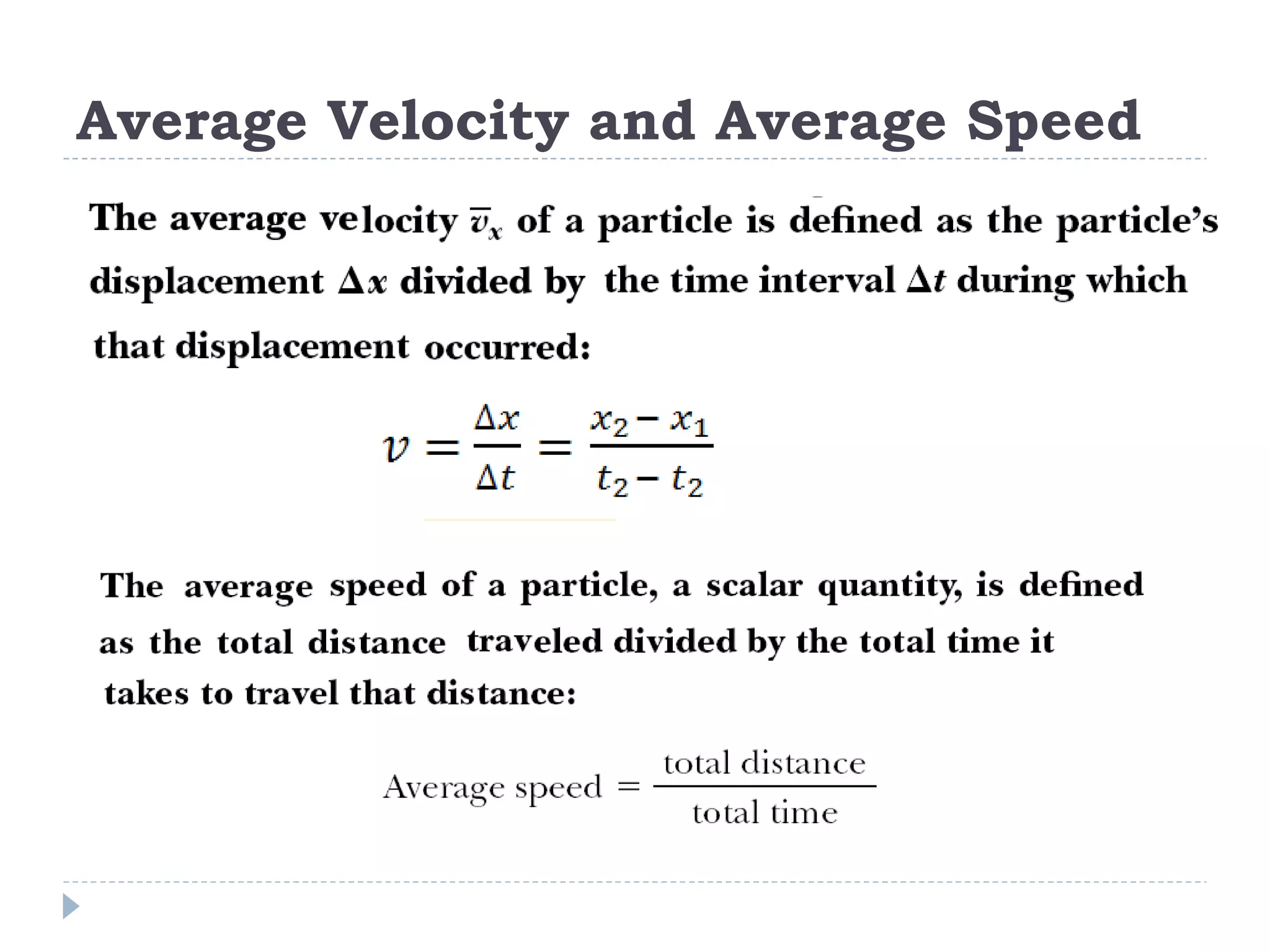
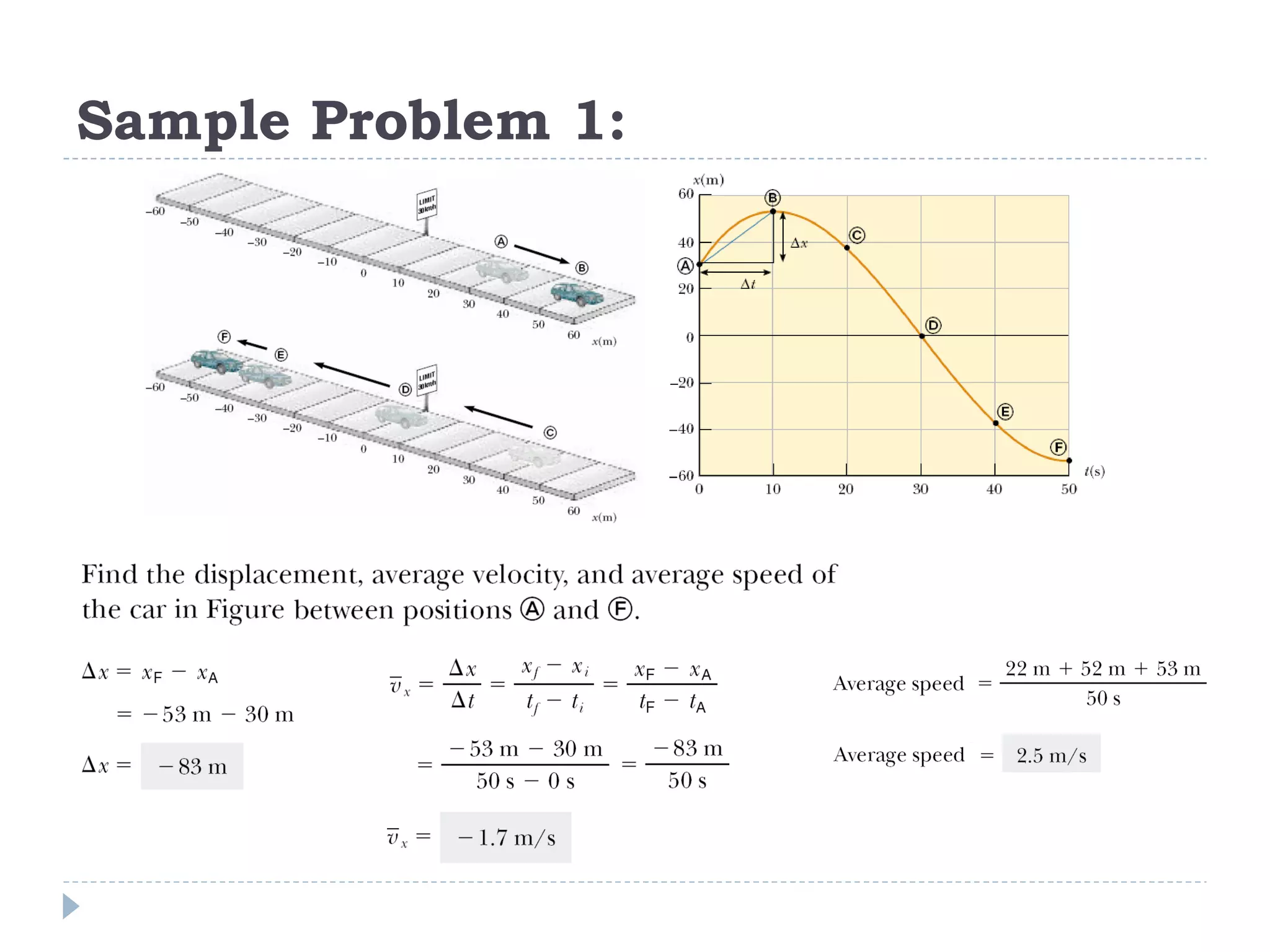
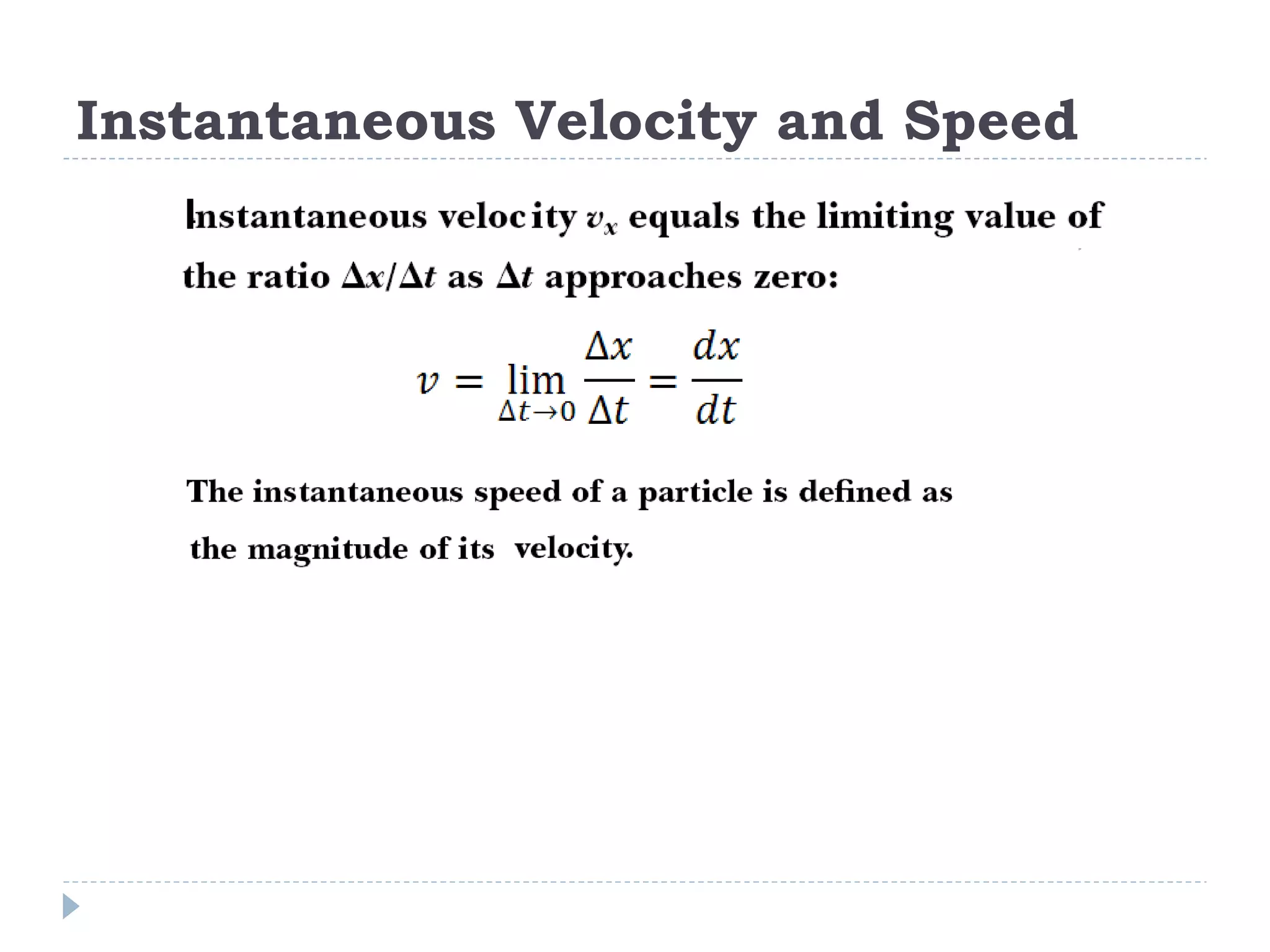
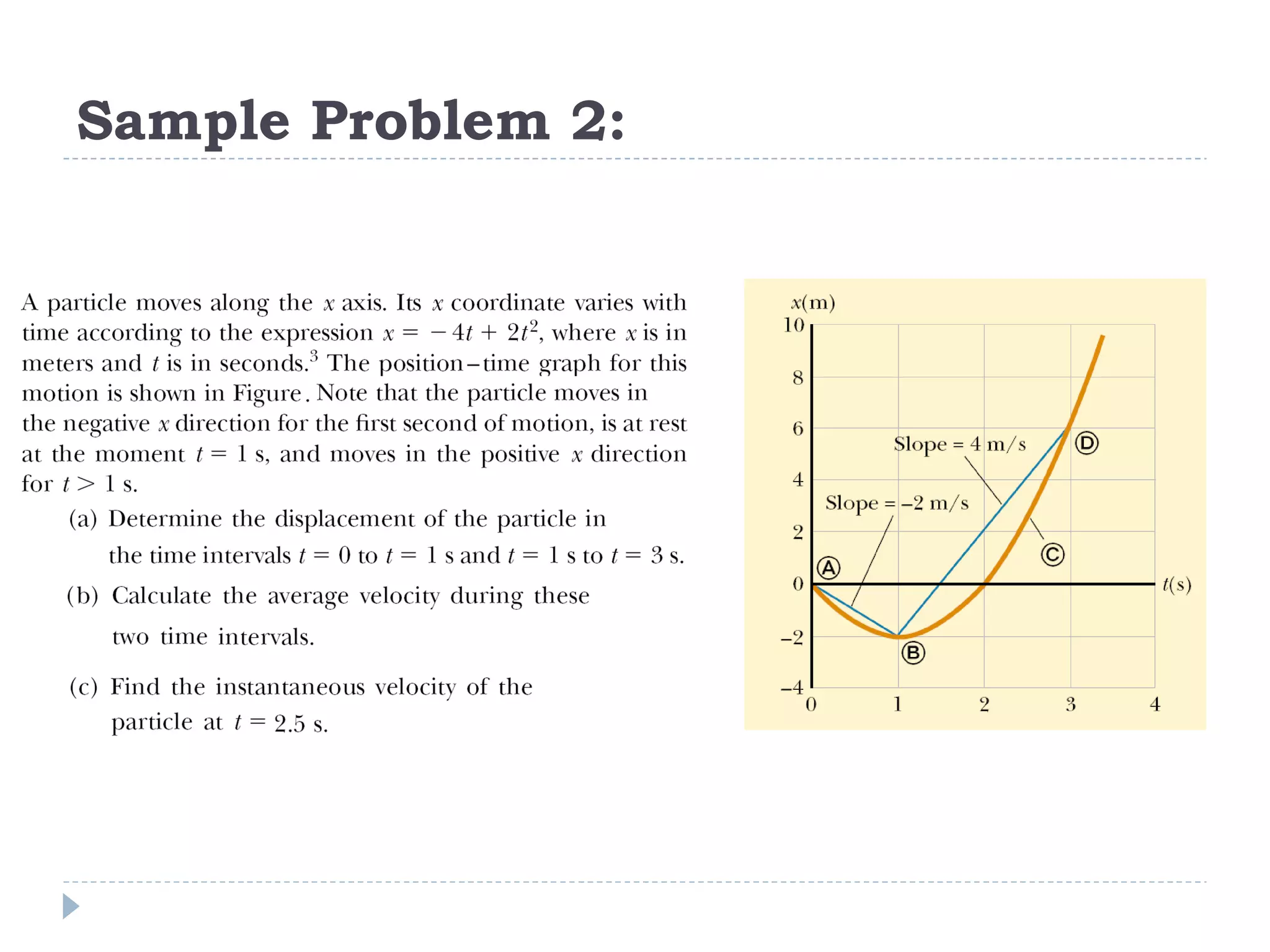
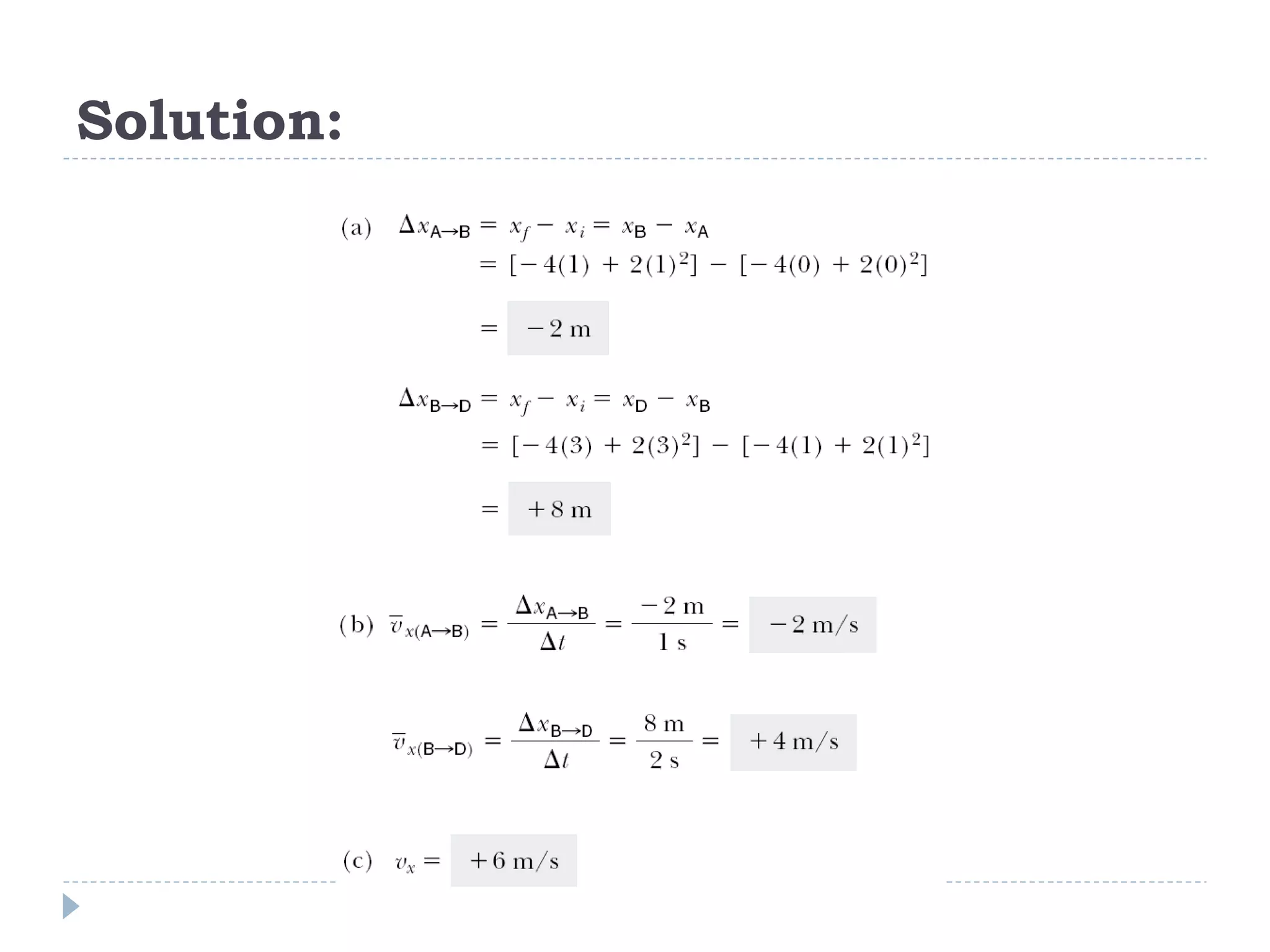
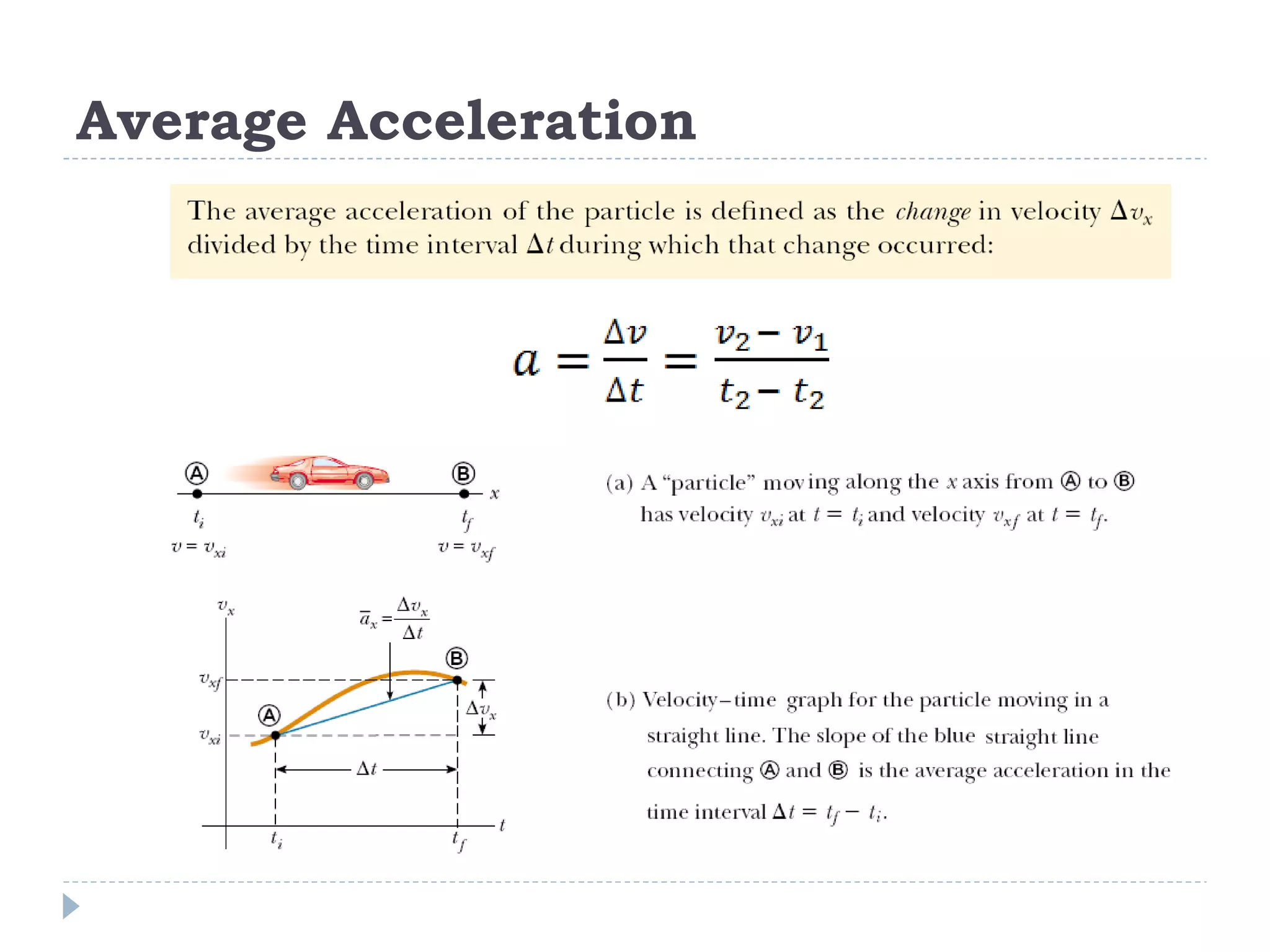
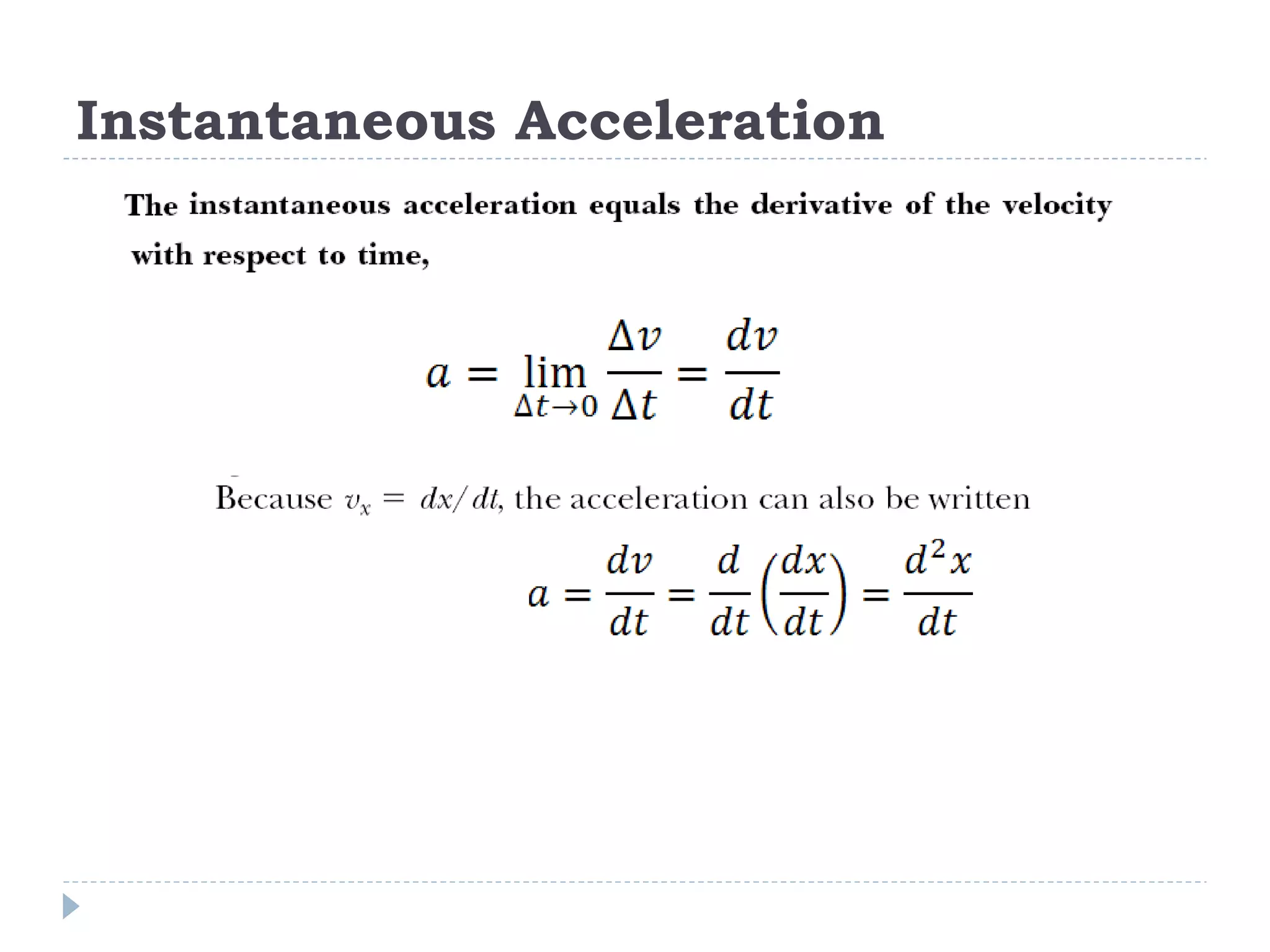
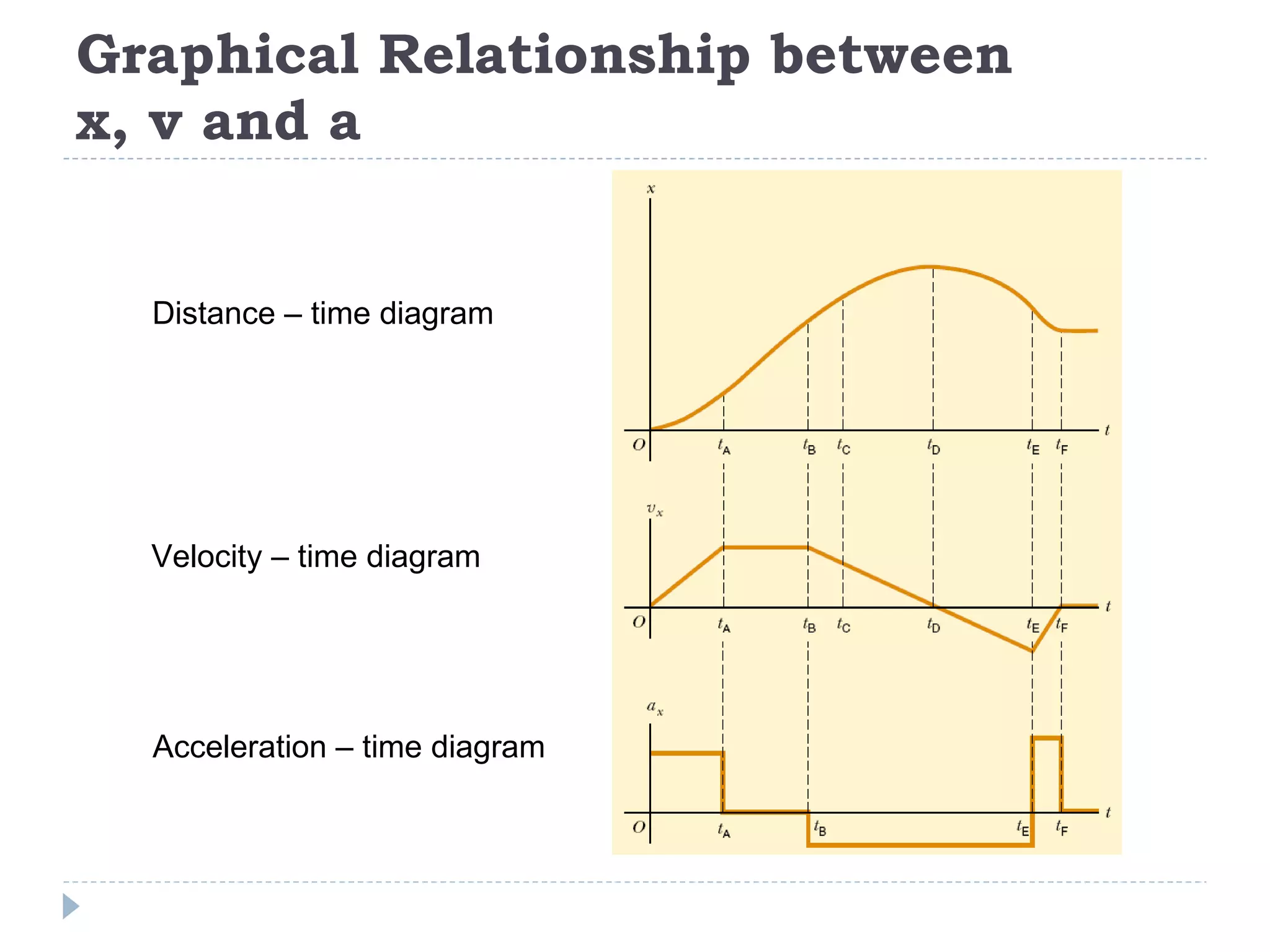
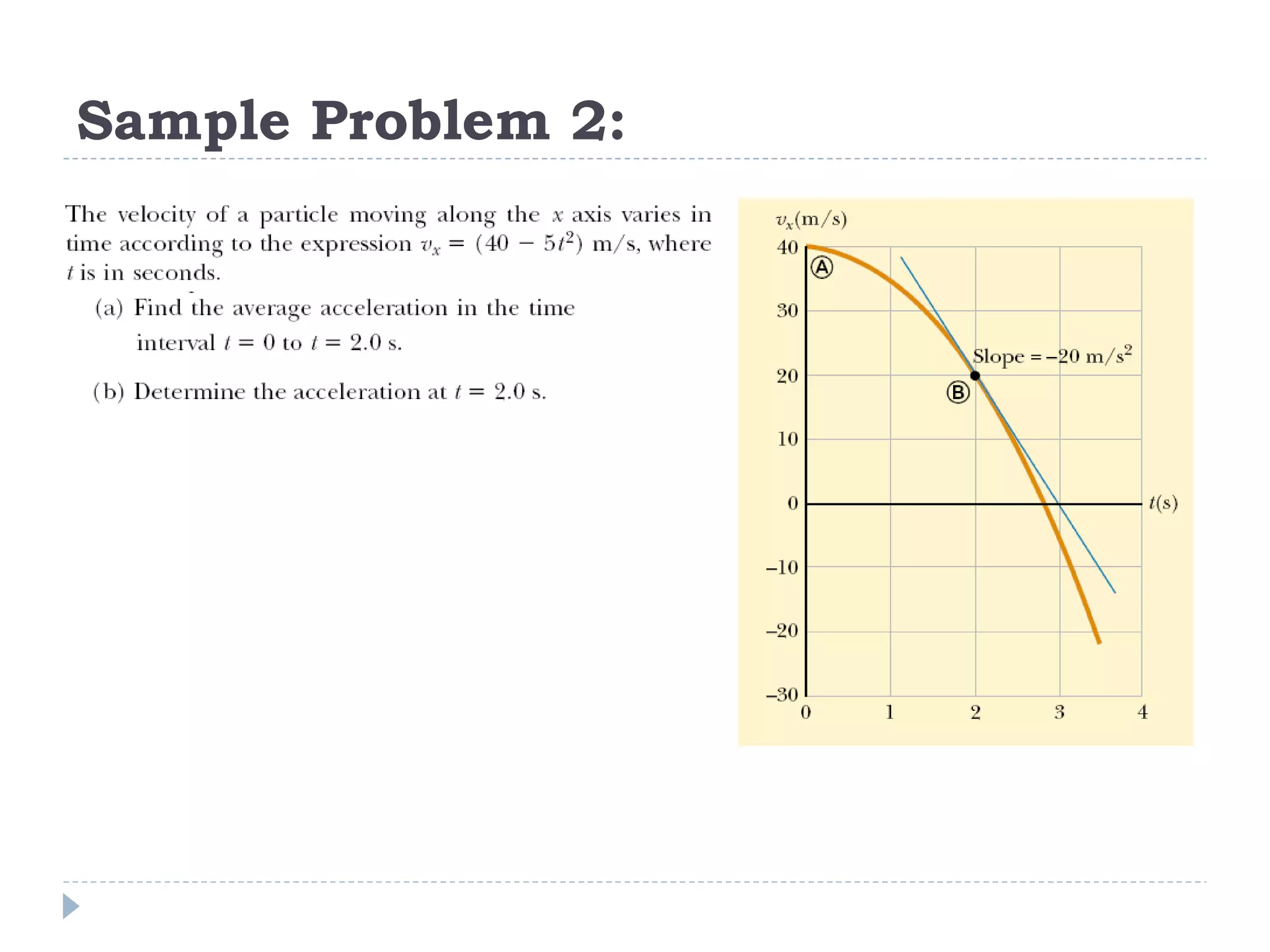
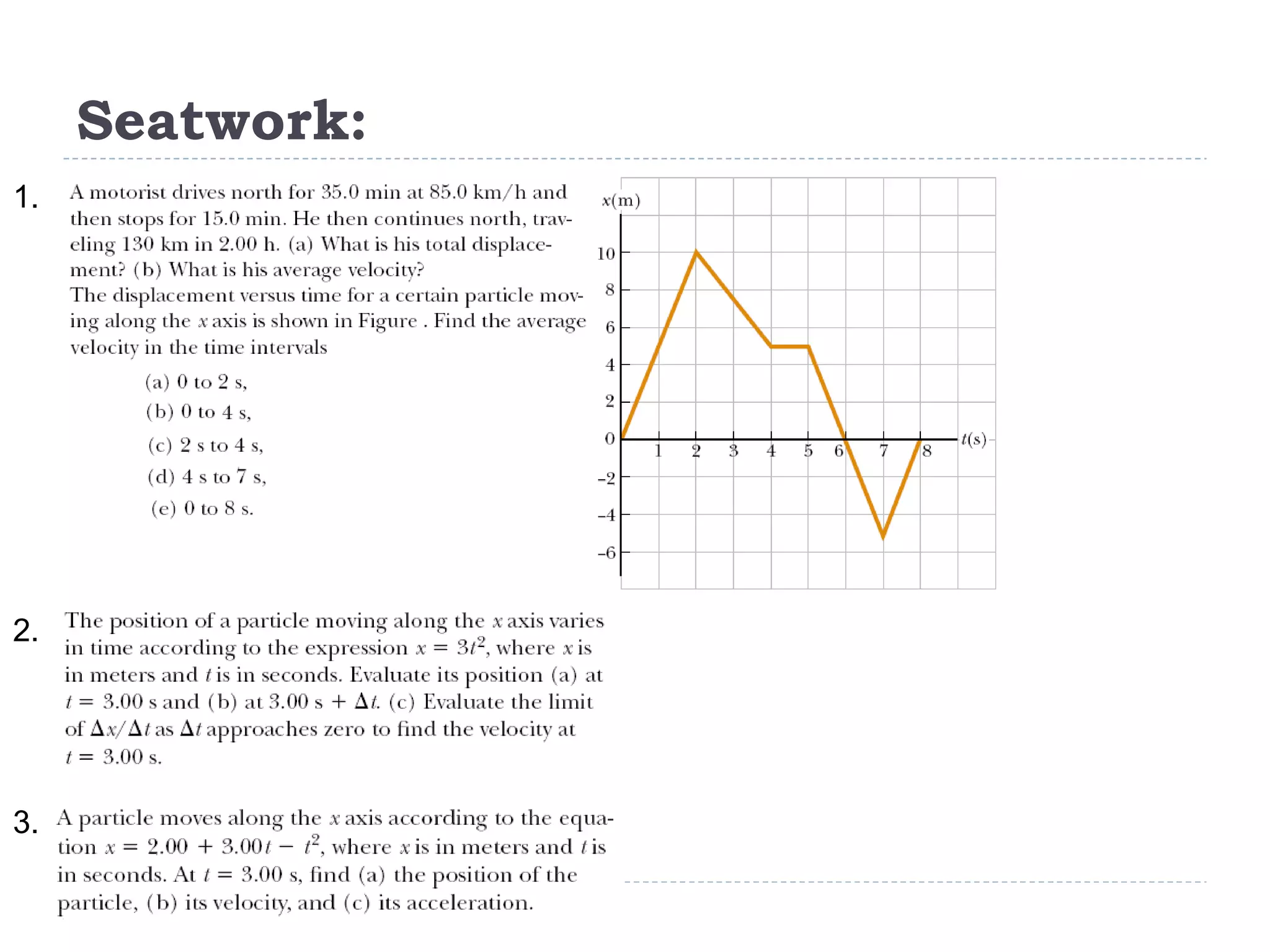
Linear motion is a topic in physics that studies the precise description of motion without regard to causes. It examines concepts like distance, displacement, speed, velocity, and acceleration. Solving linear motion problems involves defining variables, converting units, and using the appropriate kinematic equations and algebraic and trigonometric skills to calculate unknown values and check answers. Graphs of distance-time, velocity-time, and acceleration-time relationships can also help analyze linear motion.