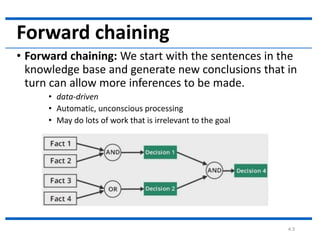
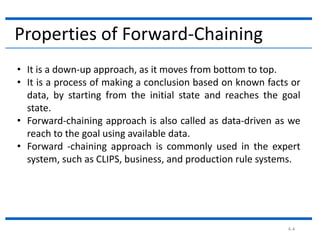
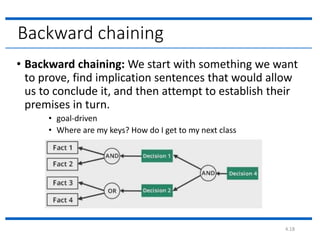
This document provides examples of forward chaining and backward chaining for a knowledge base about animals. The forward chaining example starts with the fact that Fritz croaks and eats flies, and uses rules in the knowledge base to infer that Fritz is a frog and is colored green. The backward chaining example starts with the goal of determining Fritz's color, and works backwards from rules in the knowledge base to reach the same conclusion.


![4.5
Forward Chaining Example
• Knowledge Base:
• If [X croaks and eats flies] Then [X is a frog]
• If [X chirps and sings] Then [X is a canary]
• If [X is a frog] Then [X is colored green]
• If [X is a canary] Then [X is colored yellow]
• [Fritz croaks and eats flies]
• Goal:
• [Fritz is colored Y]?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-210712073340/85/2-forward-chaning-5-320.jpg)
![4.6
Forward Chaining Example
Knowledge Base
If [X croaks and eats flies]
Then [X is a frog]
If [X chirps and sings]
Then [X is a canary]
If [X is a frog]
Then [X is colored green]
If [X is a canary]
Then [X is colored yellow]
[Fritz croaks and eats flies]
Goal
[Fritz is colored Y]?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-210712073340/85/2-forward-chaning-6-320.jpg)
![4.7
Forward Chaining Example
Knowledge Base
If [X croaks and eats flies]
Then [X is a frog]
If [X chirps and sings]
Then [X is a canary]
If [X is a frog]
Then [X is colored green]
If [X is a canary]
Then [X is colored yellow]
[Fritz croaks and eats flies]
Goal
[Fritz is colored Y]?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-210712073340/85/2-forward-chaning-7-320.jpg)
![4.8
Forward Chaining Example
Knowledge Base
If [X croaks and eats flies]
Then [X is a frog]
If [X chirps and sings]
Then [X is a canary]
If [X is a frog]
Then [X is colored green]
If [X is a canary]
Then [X is colored yellow]
[Fritz croaks and eats flies]
Goal
[Fritz is colored Y]?
If [X croaks and eats flies]
Then [X is a frog]
[Fritz croaks and eats flies]
[Fritz is a frog]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-210712073340/85/2-forward-chaning-8-320.jpg)
![4.9
Forward Chaining Example
If [X croaks and eats flies]
Then [X is a frog]
[Fritz croaks and eats flies]
[Fritz is a frog]
Knowledge Base
If [X croaks and eats flies]
Then [X is a frog]
If [X chirps and sings]
Then [X is a canary]
If [X is a frog]
Then [X is colored green]
If [X is a canary]
Then [X is colored yellow]
[Fritz croaks and eats flies]
[Fritz is a frog]
Goal
[Fritz is colored Y]?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-210712073340/85/2-forward-chaning-9-320.jpg)
![4.10
Forward Chaining Example
If [X croaks and eats flies]
Then [X is a frog]
[Fritz croaks and eats flies]
[Fritz is a frog]
Knowledge Base
If [X croaks and eats flies]
Then [X is a frog]
If [X chirps and sings]
Then [X is a canary]
If [X is a frog]
Then [X is colored green]
If [X is a canary]
Then [X is colored yellow]
[Fritz croaks and eats flies]
[Fritz is a frog]
Goal
[Fritz is colored Y]?
?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-210712073340/85/2-forward-chaning-10-320.jpg)
![4.11
Forward Chaining Example
If [X croaks and eats flies]
Then [X is a frog]
[Fritz croaks and eats flies]
[Fritz is a frog]
Knowledge Base
If [X croaks and eats flies]
Then [X is a frog]
If [X chirps and sings]
Then [X is a canary]
If [X is a frog]
Then [X is colored green]
If [X is a canary]
Then [X is colored yellow]
[Fritz croaks and eats flies]
[Fritz is a frog]
Goal
[Fritz is colored Y]?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-210712073340/85/2-forward-chaning-11-320.jpg)
![4.12
Forward Chaining Example
If [X croaks and eats flies]
Then [X is a frog]
[Fritz croaks and eats flies]
[Fritz is a frog]
Knowledge Base
If [X croaks and eats flies]
Then [X is a frog]
If [X chirps and sings]
Then [X is a canary]
If [X is a frog]
Then [X is colored green]
If [X is a canary]
Then [X is colored yellow]
[Fritz croaks and eats flies]
[Fritz is a frog]
Goal
[Fritz is colored Y]?
If [X is a frog]
Then [X is colored green]
[Fritz is colored green]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-210712073340/85/2-forward-chaning-12-320.jpg)
![4.13
Forward Chaining Example
If [X croaks and eats flies]
Then [X is a frog]
[Fritz croaks and eats flies]
[Fritz is a frog]
If [X is a frog]
Then [X is colored green]
[Fritz is colored green]
Knowledge Base
If [X croaks and eats flies]
Then [X is a frog]
If [X chirps and sings]
Then [X is a canary]
If [X is a frog]
Then [X is colored green]
If [X is a canary]
Then [X is colored yellow]
[Fritz croaks and eats flies]
[Fritz is a frog]
[Fritz is colored green]
Goal
[Fritz is colored Y]?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-210712073340/85/2-forward-chaning-13-320.jpg)
![4.14
Forward Chaining Example
If [X croaks and eats flies]
Then [X is a frog]
[Fritz croaks and eats flies]
[Fritz is a frog]
If [X is a frog]
Then [X is colored green]
[Fritz is colored green]
Knowledge Base
If [X croaks and eats flies]
Then [X is a frog]
If [X chirps and sings]
Then [X is a canary]
If [X is a frog]
Then [X is colored green]
If [X is a canary]
Then [X is colored yellow]
[Fritz croaks and eats flies]
[Fritz is a frog]
[Fritz is colored green]
Goal
[Fritz is colored Y]?
?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-210712073340/85/2-forward-chaning-14-320.jpg)
![4.15
Forward Chaining Example
If [X croaks and eats flies]
Then [X is a frog]
[Fritz croaks and eats flies]
[Fritz is a frog]
If [X is a frog]
Then [X is colored green]
[Fritz is colored green]
Knowledge Base
If [X croaks and eats flies]
Then [X is a frog]
If [X chirps and sings]
Then [X is a canary]
If [X is a frog]
Then [X is colored green]
If [X is a canary]
Then [X is colored yellow]
[Fritz croaks and eats flies]
[Fritz is a frog]
[Fritz is colored green]
Goal
[Fritz is colored Y]?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-210712073340/85/2-forward-chaning-15-320.jpg)
![4.16
Forward Chaining Example
If [X croaks and eats flies]
Then [X is a frog]
[Fritz croaks and eats flies]
[Fritz is a frog]
If [X is a frog]
Then [X is colored green]
[Fritz is colored green]
Knowledge Base
If [X croaks and eats flies]
Then [X is a frog]
If [X chirps and sings]
Then [X is a canary]
If [X is a frog]
Then [X is colored green]
If [X is a canary]
Then [X is colored yellow]
[Fritz croaks and eats flies]
[Fritz is a frog]
[Fritz is colored green]
Goal
[Fritz is colored Y]?
[Fritz is colored Y] ?
Y = green](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-210712073340/85/2-forward-chaning-16-320.jpg)


![4.20
Backward Chaining Example
Knowledge Base
If [X croaks and eats flies]
Then [X is a frog]
If [X chirps and sings]
Then [X is a canary]
If [X is a frog]
Then [X is colored green]
If [X is a canary]
Then [X is colored yellow]
[Fritz croaks and eats flies]
Goals
[Fritz is colored Y]?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-210712073340/85/2-forward-chaning-20-320.jpg)
![4.21
Backward Chaining Example
Knowledge Base
If [X croaks and eats flies]
Then [X is a frog]
If [X chirps and sings]
Then [X is a canary]
If [X is a frog]
Then [X is colored green]
If [X is a canary]
Then [X is colored yellow]
[Fritz croaks and eats flies]
Goals
[Fritz is colored Y]?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-210712073340/85/2-forward-chaning-21-320.jpg)
![4.22
Backward Chaining Example
Knowledge Base
If [X croaks and eats flies]
Then [X is a frog]
If [X chirps and sings]
Then [X is a canary]
If [X is a frog]
Then [X is colored green]
If [X is a canary]
Then [X is colored yellow]
[Fritz croaks and eats flies]
Goals
[Fritz is colored Y]?
[Fritz is colored Y]
If [X is a frog]
Then [X is colored green]
[X is a frog]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-210712073340/85/2-forward-chaning-22-320.jpg)
![4.23
Backward Chaining Example
[Fritz is colored Y]
If [X is a frog]
Then [X is colored green]
[X is a frog]
Knowledge Base
If [X croaks and eats flies]
Then [X is a frog]
If [X chirps and sings]
Then [X is a canary]
If [X is a frog]
Then [X is colored green]
If [X is a canary]
Then [X is colored yellow]
[Fritz croaks and eats flies]
Goals
[Fritz is colored Y]?
[X is a frog]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-210712073340/85/2-forward-chaning-23-320.jpg)
![4.24
Backward Chaining Example
[Fritz is colored Y]
If [X is a frog]
Then [X is colored green]
[X is a frog]
Knowledge Base
If [X croaks and eats flies]
Then [X is a frog]
If [X chirps and sings]
Then [X is a canary]
If [X is a frog]
Then [X is colored green]
If [X is a canary]
Then [X is colored yellow]
[Fritz croaks and eats flies]
Goals
[Fritz is colored Y]?
[X is a frog]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-210712073340/85/2-forward-chaning-24-320.jpg)
![4.25
Backward Chaining Example
[Fritz is colored Y]
If [X is a frog]
Then [X is colored green]
[X is a frog]
Knowledge Base
If [X croaks and eats flies]
Then [X is a frog]
If [X chirps and sings]
Then [X is a canary]
If [X is a frog]
Then [X is colored green]
If [X is a canary]
Then [X is colored yellow]
[Fritz croaks and eats flies]
Goals
[Fritz is colored Y]?
[X is a frog]
If [X is a canary]
Then [X is colored yellow]
[X is a canary]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-210712073340/85/2-forward-chaning-25-320.jpg)
![4.26
Backward Chaining Example
[Fritz is colored Y]
If [X is a frog]
Then [X is colored green]
[X is a frog]
If [X is a canary]
Then [X is colored yellow]
[X is a canary]
Knowledge Base
If [X croaks and eats flies]
Then [X is a frog]
If [X chirps and sings]
Then [X is a canary]
If [X is a frog]
Then [X is colored green]
If [X is a canary]
Then [X is colored yellow]
[Fritz croaks and eats flies]
Goals
[Fritz is colored Y]?
[X is a frog]
[X is a canary]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-210712073340/85/2-forward-chaning-26-320.jpg)
![4.27
Backward Chaining Example
[Fritz is colored Y]
If [X is a frog]
Then [X is colored green]
[X is a frog]
If [X is a canary]
Then [X is colored yellow]
[X is a canary]
Knowledge Base
If [X croaks and eats flies]
Then [X is a frog]
If [X chirps and sings]
Then [X is a canary]
If [X is a frog]
Then [X is colored green]
If [X is a canary]
Then [X is colored yellow]
[Fritz croaks and eats flies]
Goals
[Fritz is colored Y]?
[X is a frog]
[X is a canary]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-210712073340/85/2-forward-chaning-27-320.jpg)
![4.28
Backward Chaining Example
[Fritz is colored Y]
If [X is a frog]
Then [X is colored green]
[X is a frog]
If [X is a canary]
Then [X is colored yellow]
[X is a canary]
Knowledge Base
If [X croaks and eats flies]
Then [X is a frog]
If [X chirps and sings]
Then [X is a canary]
If [X is a frog]
Then [X is colored green]
If [X is a canary]
Then [X is colored yellow]
[Fritz croaks and eats flies]
Goals
[Fritz is colored Y]?
[X is a frog]
[X is a canary]
If [X croaks and eats flies]
Then [X is a frog]
[X croaks and eats flies]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-210712073340/85/2-forward-chaning-28-320.jpg)
![4.29
Backward Chaining Example
[Fritz is colored Y]
If [X is a frog]
Then [X is colored green]
[X is a frog]
If [X is a canary]
Then [X is colored yellow]
[X is a canary]
If [X croaks and eats flies]
Then [X is a frog]
[X croaks and eats flies]
Knowledge Base
If [X croaks and eats flies]
Then [X is a frog]
If [X chirps and sings]
Then [X is a canary]
If [X is a frog]
Then [X is colored green]
If [X is a canary]
Then [X is colored yellow]
[Fritz croaks and eats flies]
Goals
[Fritz is colored Y]?
[X is a frog]
[X is a canary]
[X croaks and eats flies]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-210712073340/85/2-forward-chaning-29-320.jpg)
![4.30
Backward Chaining Example
[Fritz is colored Y]
If [X is a frog]
Then [X is colored green]
[X is a frog]
If [X is a canary]
Then [X is colored yellow]
[X is a canary]
If [X croaks and eats flies]
Then [X is a frog]
[X croaks and eats flies]
Knowledge Base
If [X croaks and eats flies]
Then [X is a frog]
If [X chirps and sings]
Then [X is a canary]
If [X is a frog]
Then [X is colored green]
If [X is a canary]
Then [X is colored yellow]
[Fritz croaks and eats flies]
Goals
[Fritz is colored Y]?
[X is a frog]
[X is a canary]
[X croaks and eats flies]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-210712073340/85/2-forward-chaning-30-320.jpg)
![4.31
Backward Chaining Example
[Fritz is colored Y]
If [X is a frog]
Then [X is colored green]
[X is a frog]
If [X is a canary]
Then [X is colored yellow]
[X is a canary]
If [X croaks and eats flies]
Then [X is a frog]
[X croaks and eats flies]
Knowledge Base
If [X croaks and eats flies]
Then [X is a frog]
If [X chirps and sings]
Then [X is a canary]
If [X is a frog]
Then [X is colored green]
If [X is a canary]
Then [X is colored yellow]
[Fritz croaks and eats flies]
Goals
[Fritz is colored Y]?
[X is a frog]
[X is a canary]
[X croaks and eats flies]
[Fritz croaks and eats flies]
X = Fritz, Y = green](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-210712073340/85/2-forward-chaning-31-320.jpg)
